Bitwise Operators in C
What are Bitwise Operators in C?
Bitwise operators are the operators that execute operations on data at the bit level. Bit-level programming refers to the process of performing bitwise operations. It consists of two numerals, which might be either 0 or 1. Its main use is to speed up numerical computations.
Types of Bitwise Operators in C
There are numerous types of bitwise operators in C, which include:
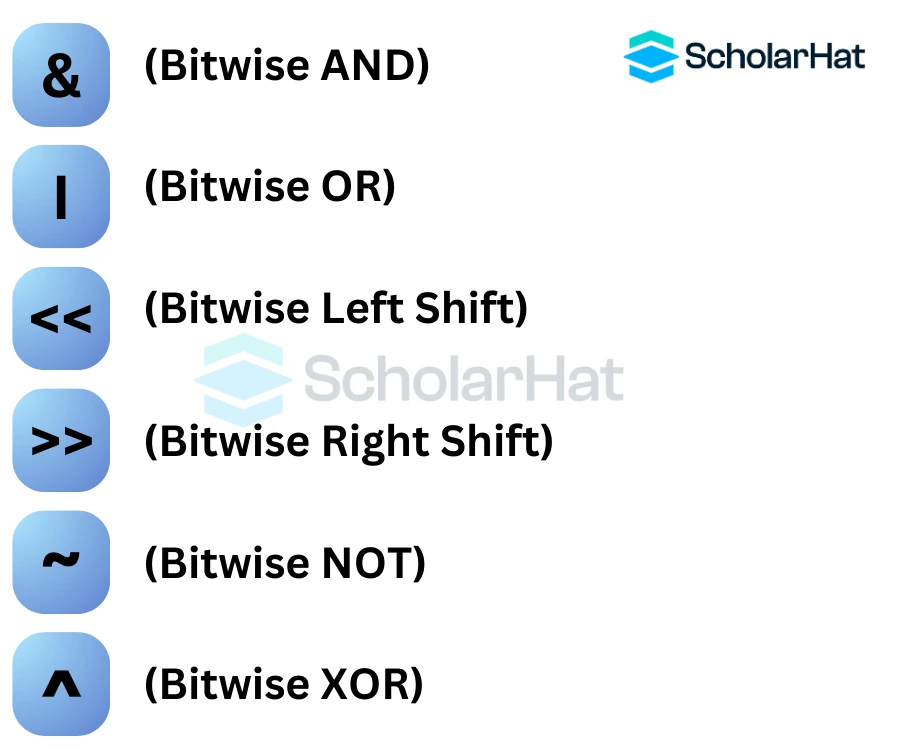
- Bitwise AND Operator
- Bitwise OR Operator
- Bitwise Exclusive OR Operator
- Bitwise Left Shift Operator
- Bitwise Right Shift Operator
- Bitwise NOT Operator
Bitwise AND
This operator applies the & operation to each bit of the two operands. The result is 1 if both operand bits are 1, and 0 otherwise.
Bitwise OR
This operator applies the | operation to each bit of the two operands. The result is 1 if one of the operands' bits is 1, and 0 otherwise.
Bitwise Exclusive OR
The bitwise exclusive OR (XOR) operator "^" compares two operands bit by bit and returns 1 if the corresponding bits of the two operands are opposite.
Bitwise Left Shift Operator (<<)
The Bitwise Left Shift Operator (<<) shifts the bits of the first operand to the left by the number of places given in the second operand. It fills empty spaces with zeros.
Bitwise Right Shift Operator (>>)
The Bitwise Right Shift Operator (>>) shifts the bits of the first operand to the right by the number of places provided in the second operand. For signed data types, the leftmost bits are filled with the sign bit, while for unsigned types they are filled with zeros.
Bitwise Complement Operator
The bitwise complement operator is also called the one's complement operator. It is denoted by the symbol tilde (~). It accepts only one operand or variable and performs the complement operation on it. When we apply the complement operation to any bit, 0 becomes 1, and 1 becomes 0.


