Queue in Data Structure
Duration : 00:04:00
What is a Queue?
Queues are linear structures that allow elements to be inserted from the rear and deleted from the front. The queue elements are ordered in the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) order.

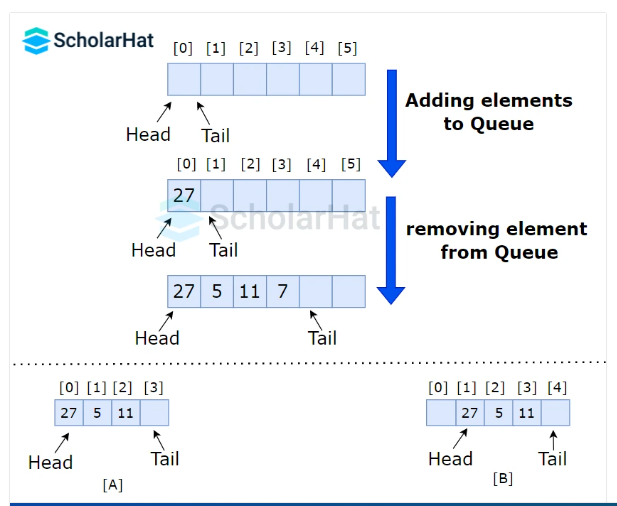
Representation of a queue in data structures
We know that a queue can be accessed from both sides, deleting from the front and inserting from the back or rear.
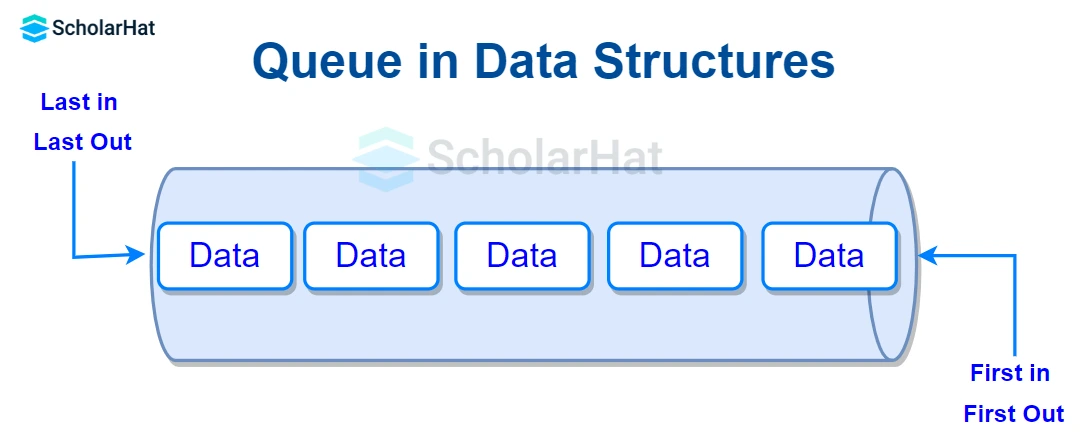
Working of Queue in Data Structures
- Two pointers are marking two ends, FRONT and REAR.
- FRONT records the queue's first element.
- REAR tracks the queue's last member.
- Initially, set the values of FRONT and REAR to -1.
- After that, do the basic operations using the algorithms listed above.
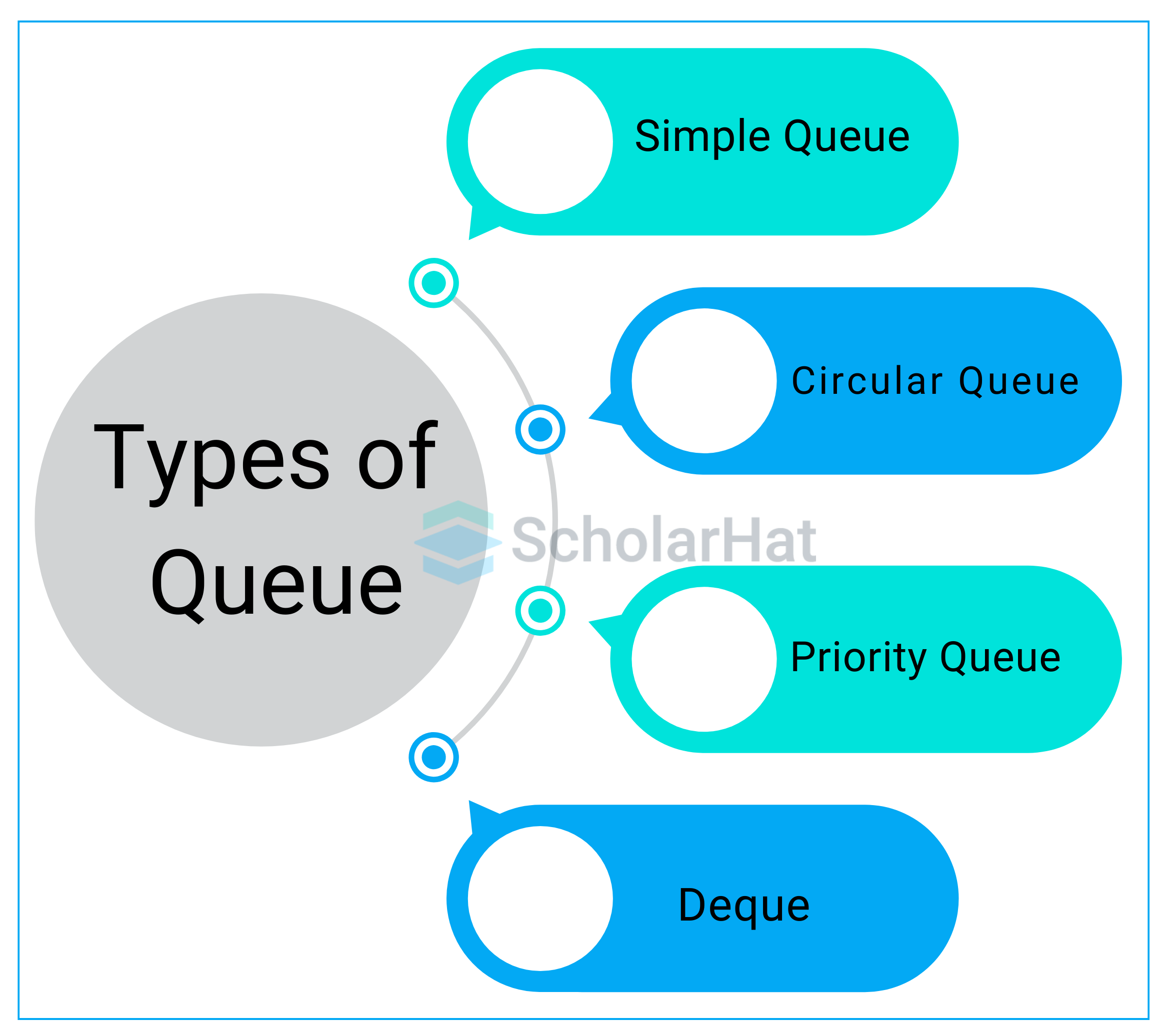
Different Types of Queues in Data Structures
- Simple Queue/Linear Queue: Elements are added at the back and withdrawn at the front, in the FIFO sequence.
- Circular Queue: Similar to a simple queue, except the last member connects to the first, resulting in a circular structure for efficient memory usage.
- Priority Queue: Each element is assigned a priority; the highest priority elements are eliminated first, allowing for prioritized processing.
- Deque (Double-Ended Queue): Elements may be added or withdrawn from both the front and back ends of the queue.
Implementation of Queue
There are two main methods for implementing a queue:
- Array
- Linked List
1. Array
Array-based queues have a fixed size, which means you can only add or remove elements up to the length of the array.
2. Linked List
Linked list-based queues have no defined size, so you can add and remove as many components as you wish.
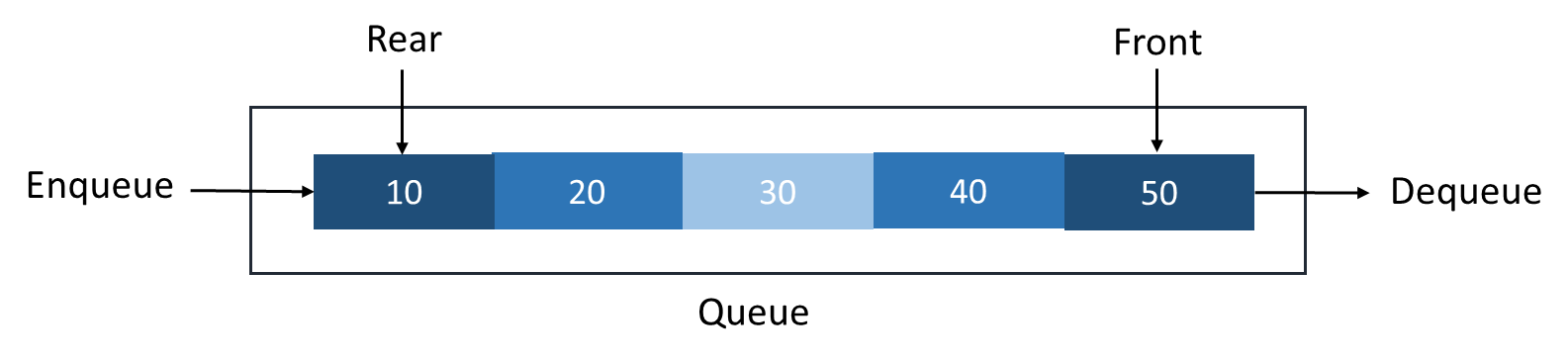
Basic Operations of Queue
- Enqueue: Insert an element at the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove an item from the queue's front.
- IsEmpty: Determine whether the queue is empty.
- IsFull: Determine whether the queue is full.
- Peek: Retrieve a value from the front of the queue without removing it.
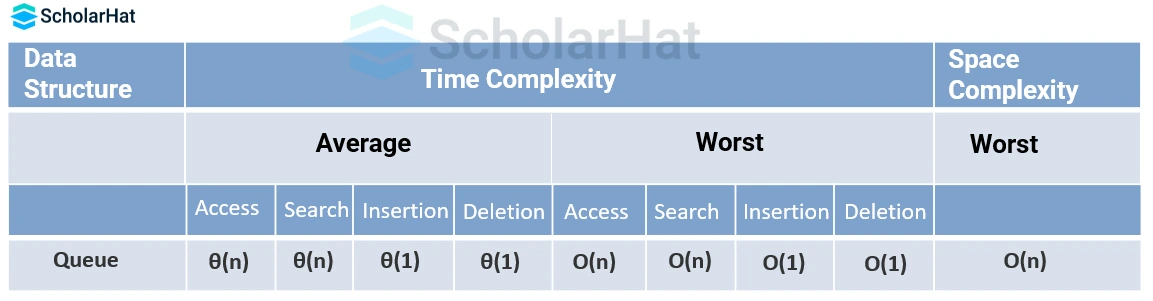
Complexity Analysis of Queue Operations
Applications of Queue
- Multi-programming: Multi-programming involves organizing many programs in the main memory as queues.
- Network: Network Queues are utilized in devices such as routers.
- Job Scheduling: The execution of tasks in a predetermined order using queues.
- Synchronization: Data transmission queues between processes (such as IO buffers and pipes).
- Interrupts: Managing in real-time systems.
- Shared resources: Queues are waiting lists for shared resources.
- Data structure operations: Queue utilized in BFS and tree traversal for the input sequence.
Advantages of Queue
- Efficient data processing: Use a queue to process data in the order it is received.
- Resource management: Resource management refers to the queue used to manage shared resources.
- Buffering: A queue for storing incoming data (for example, a network device buffering data packets).
- Memory management: A queue for allocating and releasing memory chunks consecutively.
Disadvantages of Queue
- Limited flexibility: Queues are completely FIFO, with no room for prioritization.
- No random access: Only the first piece is available; the rest must be removed, which limits access efficiency.
- Overhead: Maintaining queue orders incurs costs, particularly for huge lineups.
- Limited size: Some queues are fixed in size, making it difficult to handle big data sets.
- No search operation: Queues lack search functionality and rely only on sequential removal to get elements.
Still have some questions? Let's discuss.
CONTACT US

