Wrapper Classes in Java
Wrapper Class
In Java, a wrapper class wraps or contains primitive data types. When we build an object for a wrapper class, it has a field in which we can put primitive data types. In other words, we can convert a primitive value into a class object.
Need for Wrapper Classes
Wrapper classes are necessary for Java because they convert primitive data types into objects, allowing for the alteration of method arguments and providing synchronization in multithreading, which is critical for dealing with objects in Java.util package classes like ArrayList and Vector to store only objects, not primitives.
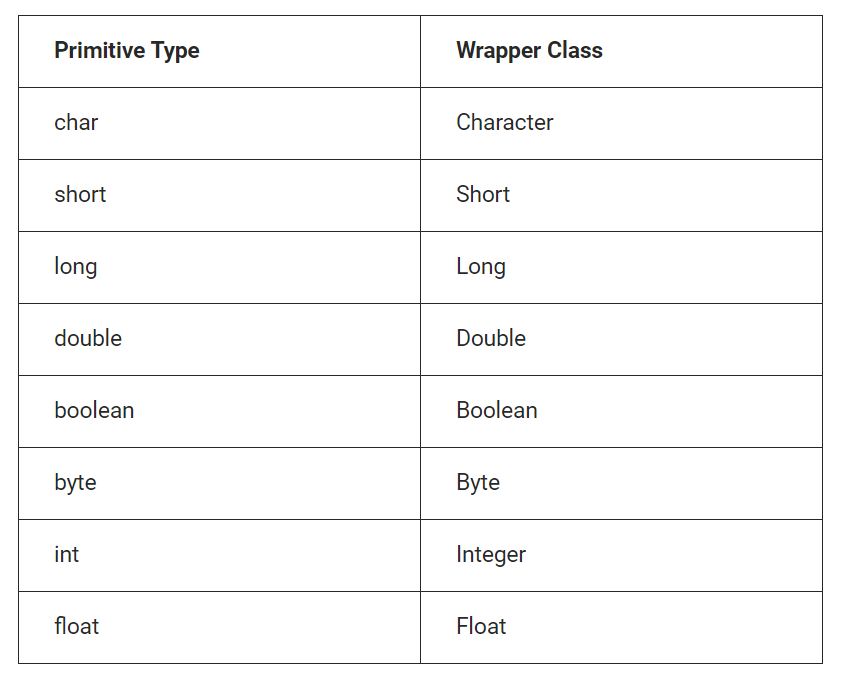
List of Wrapper Classes
Wrapper Classes Uses
The wrapper class is mostly used in Java for:
- Using objects to represent primitive data types
- Storing null values
- Method parameters
- Autoboxing and unboxing
- Converting primitive data types to strings
- Value Comparison
- Perform mathematical operations
Autoboxing
Autoboxing is the process of automatically converting primitive types into the objects of their appropriate wrapper classes.
Unboxing
It is simply the reverse procedure of autoboxing. Unboxing refers to the process of automatically converting a wrapper class object to its corresponding primitive type.
Wrapper Classes Advantages
- Provide data types that are primitive in an object representation.
- Make it easier to convert types.
- Assist in implementing Autoboxing and Unboxing.
Wrapper Classes Disadvantages
- Overhead performance.
- Increased memory consumption.
- Immutable.


