Introduction to ASP.NET MVC
What is MVC?
Model-View-Controller is referred to as MVC. It is a software design pattern that originated in the 1970s. Furthermore, the MVC pattern requires a separation of concerns, which means that the domain model and controller logic are isolated from the user interface (view).
Describe the MVC Design Pattern
The MVC design pattern divides an application into three major components: Model, View, and Controller
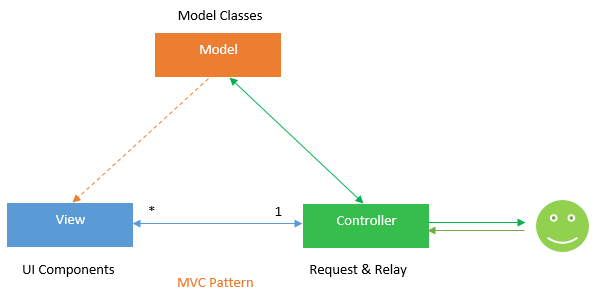
Model
The Model is a collection of classes that describe both the business logic (business model) and the data access activities (data model). It also sets business rules for data, specifying how it can be altered and manipulated.
View
The View represents UI components such as CSS, jQuery, and HTML. It is solely responsible for showing the data received from the controller as the result. This also converts the model(s) to UI.
Controller
The Controller is responsible for processing incoming requests. It gets input from users via the View, processes the data using the Model, and returns the results to the View. Typically, it serves as a liaison between the View and Model.
Describe the MVP pattern
This model is comparable to the MVC pattern, only the presenter has taken the controller role. This design pattern divides an application into three major components: model, view, and presenter.
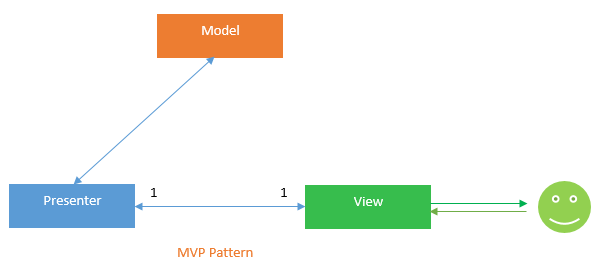
Models
Models are collections of classes that describe the business logic and data. It also sets business rules for data, specifying how it can be altered and manipulated.
Views
Views represent user interface components such as CSS, jQuery, and HTML. It is solely responsible for showing the data obtained from the presenter as the result. This also converts the model(s) to UI.
Presenter
The Presenter handles all UI events on the view's behalf. This receives input from users via the View, processes the data using the Model, and returns the results to the View. Unlike views and controllers, views and presenters are detached and communicate via an interface.
Key Features of the Model-View-Presenter (MVP) Pattern
- The view is interacted with by the user.
- A one-to-one link exists between View and Presenter, meaning only one View is associated with a single Presenter.
- The View contains a reference to the Presenter but no reference to the Model.
- Allows two-way communication between the View and the Presenter.
Describe the MVVM pattern
MVVM is an acronym for Model-View-View Model. This pattern allows for two-way data binding between the view and the view model. This allows for automatically propagating changes from the state-of-view model to the view. Typically, the observer pattern is used to notify changes in the view model to the model.
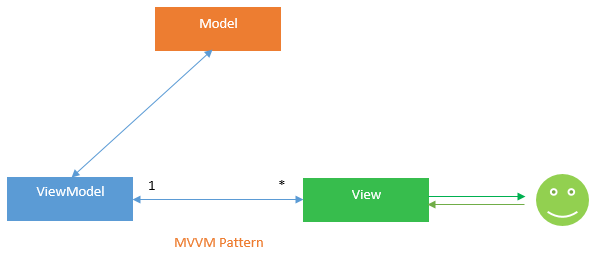
Model
The Model is a collection of classes that describe business logic and data. It also sets business rules for data, specifying how it can be altered and manipulated.
View
The View represents UI components such as CSS, jQuery, and HTML. It is solely responsible for showing the data received from the controller as the result. This also converts the model(s) to UI.
View Model
The View Model exposes methods, commands, and other properties that maintain the view's state, alter the model as a result of actions on the view, and trigger events within the view itself.
Key Features of the MVVP Pattern
- The view is interacted with by the user.
- View and ViewModel have a many-to-one relationship, meaning numerous Views can be mapped to a single ViewModel.
- The view references ViewModel, but ViewModel contains no information about the view.
- Allows View and ViewModel to bind data in both directions.
What is the ASP.NET MVC?
ASP.NET MVC is an open-source framework for developing online applications allowing clear code separation. It is built on the Microsoft.NET Framework. The ASP.NET MVC framework is Microsoft's most customizable and versatile platform. ASP.NET MVC, built on the MVC pattern, is an alternative to WebForms. It removes support for code-behind pages, server controls, drag-and-drop, postback, view state, and event life cycles.
Why ASP.NET MVC?
ASP.NET MVC offers a simpler architecture for online application development by removing traditional ASP.NET features such as page life cycles & state illusions. It focuses on extensibility, allowing developers to customize views with multiple engines and inject custom logic across the framework, improving testability and ensuring a clear separation of responsibilities between controllers and the ASP.NET runtime.
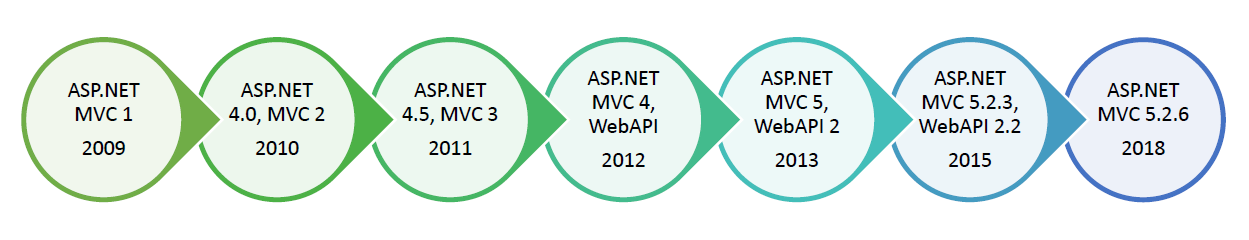
History of ASP.NET MVC
ASP.NET MVC1
Released on March 13, 2009, it works on.NET 3.5 and Visual Studio 2008. MVC Pattern architecture with WebForm Engine, HTML Helpers, Ajax Helpers, routing, and unit testing are some of the key features.
ASP.NET MVC2
Developed on March 10, 2010, it works with Visual Studio 2008 and 2010 with .NET versions 3.5 and 4.0. Strongly typed HTML helpers, templated helpers, Validation DataAnnotations, HTTP Method Verb overrides, areas, and asynchronous controllers are among the enhancements.
ASP.NET MVC3
Released on January 13, 2011, it is based on.NET 4.0 and uses Visual Studio 2010. It included the Razor view engine, improved Data Annotations, Remote Validation, sessionless controllers, a dependency resolver, partial-page output caching, ViewBag, global action filters, and improved JavaScript compatibility.
ASP.NET MVC4
Released on August 15, 2012, ASP.NET MVC4 is compatible with Visual Studio 2010 SP1 and Visual Studio 2012 and operates on.NET 4.0 and 4.5. ASP.NET Web API, better project templates, mobile project templates, display modes, asynchronous controller tasks, bundling, minification, and support for Windows Azure SDK are among the notable additions.
ASP.NET MVC5
ASP.NET MVC5 was released on October 17, 2013, and operates on.NET 4.5, and 4.5.1 with Visual Studio 2012 and 2013. New features include One ASP.NET, ASP.NET Identity, ASP.NET Scaffolding, authentication filters, Bootstrap integration, and the ASP.NET Web API2.
ASP.NET WebForms vs. ASP.NET MVC
| ASP.NET WebForms vs. ASP.NET MVC | ASP.NET WebForms vs. ASP.NET MVC |
| Event Driven development model | MVC Pattern development model |
| Server Controls | Html Helpers |
| Follows Web Forms Syntax | Follows WebForms Razor Syntax |
| ViewState | ViewData, ViewBag |
| Session | Session, TempData |
| File-based Url Mapping | Route-based Url Mapping |
| User Controls | Partial Views |
| Not Open Source | Open Source |
Advantages of ASP.NET MVC
- Separation of Concerns: The program is divided into three parts: Model, View, and Controller, making complexity management easier.
- TDD Support: Improves support for test-driven development.
- Extendable and pluggable: Components are intended to be easily replaced or customized.
- Full Control: Removes View State and server-based forms, providing developers greater control while decreasing server request bandwidth.
- ASP.NET features: It supports provider architecture, authentication, authorization, membership, roles, caching, and sessions.
- URL Routing: A powerful routing technique that generates SEO-friendly and intelligible URLs.


