18
AprTop AI Features You Should Know
AI in today's world powers innovations across industries, enhancing automation, decision-making, and personalization. From chatbots and virtual assistants to advanced data analytics and generative AI, it streamlines tasks and boosts efficiency. AI-driven technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and NLP are transforming healthcare, finance, and education, making processes smarter and more adaptive.
In this AI tutorial, you will learn how AI helps in daily life. It will show you simple examples of AI making tasks easier.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Importance of AI in Today’s World
Top 7 Core Features of AI
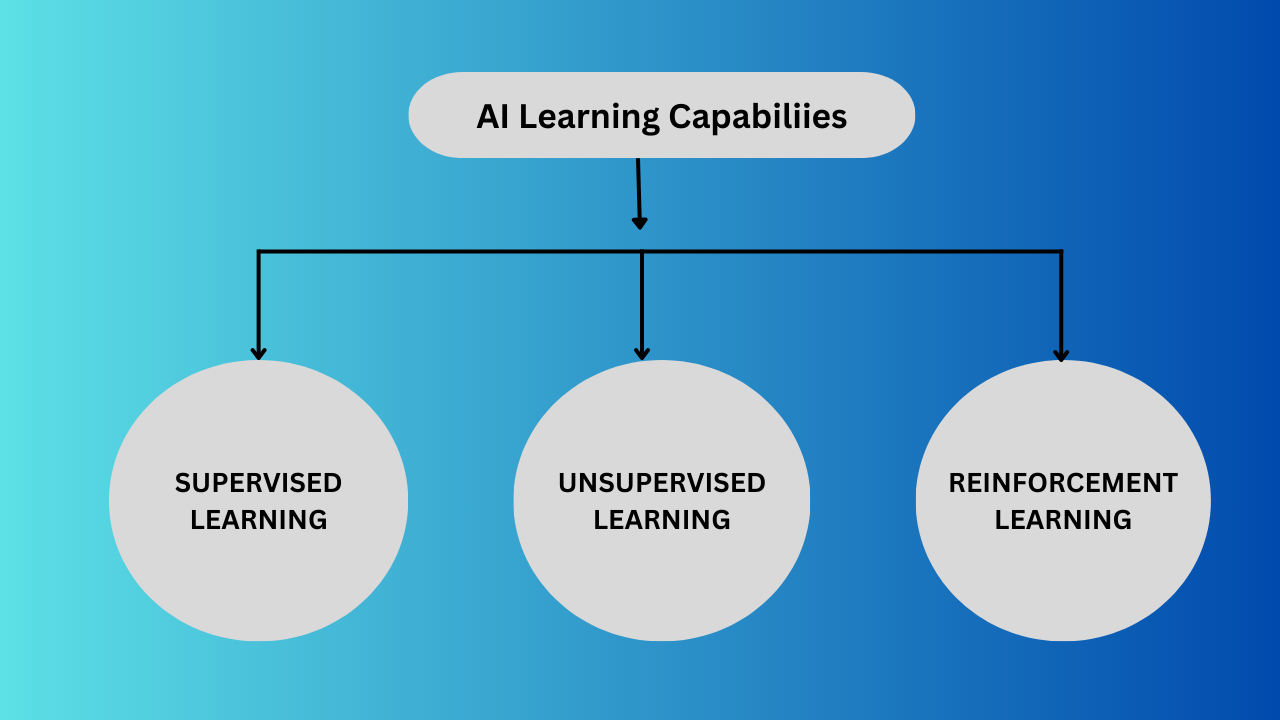
1. Learning Capabilities
| Learning Type | Description | Additional Point | Example |
| Supervised Learning | The AI learns from labeled data, where input-output pairs are provided. | It improves by comparing predictions with actual results. | Email spam detection (classifying emails as spam or not spam) |
| Unsupervised Learning | The AI finds patterns in unlabeled data without predefined categories. | It groups similar data points based on relationships. | Customer segmentation (grouping customers based on buying behavior) |
| Reinforcement Learning | The AI learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties. | It continuously improves by trial and error. | Self-driving cars (learning to navigate roads safely) |
2. Reasoning & Decision-Making
AI can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions. It helps in automation, reducing errors, and improving efficiency in various industries. AI-powered decision-making is widely used in healthcare, finance, and business intelligence.
2.1 Rule-Based Systems & Probabilistic Models
- Rule-based AI follows predefined logic rules for decision-making, ensuring consistent and structured outcomes.
- Probabilistic models handle uncertainty by using statistical methods, making them useful for risk assessment and predictions.
2.2 AI in Problem-Solving (Search Algorithms, Constraint Solving)
- AI uses search algorithms like A* and genetic algorithms for pathfinding, optimization, and strategic planning.
- Constraint-solving AI tackles complex scheduling, resource allocation, and decision-making problems in logistics and operations.

3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language, improving communication between humans and machines. It powers applications like virtual assistants, chatbots, and translation services.
3.1 Speech Recognition & Chatbots
- AI-powered speech recognition converts spoken language into text, enabling voice assistants like Siri and Google Assistant.
- Chatbots enhance customer support by understanding and responding to queries, providing instant assistance.
3.2 Text Generation & Sentiment Analysis
- AI generates human-like text using models like GPT, automating content creation for businesses and media.
- Sentiment analysis helps interpret emotions in text and is widely used for market analysis and social media monitoring.

4. Computer Vision
AI can analyze and interpret images and videos for various applications, enabling automation in security, healthcare, and entertainment.
4.1 Object & Image Recognition
- AI identifies and classifies objects in images and videos, which are used in facial recognition and autonomous surveillance.
4.2 Facial Recognition & Emotion Analysis
- AI detects faces, authenticates users, and analyzes emotions for security and psychological studies.

5. Automation & Robotics
AI enhances automation and robotics to improve efficiency in various industries, reducing manual labor and increasing precision.
5.1 Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- RPA automates repetitive tasks in businesses, improving productivity and reducing human errors.
- Industrial robots enhance manufacturing by increasing precision and efficiency in production lines.
5.2 AI in Autonomous Vehicles
- AI enables self-driving cars to perceive surroundings, make decisions, and navigate safely.

6. Generative AI
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence models that create new content such as text, images, music, and code by learning patterns from existing data. It is widely used in chatbots, content creation, and design automation.
6.1 AI-Generated Text, Images & Music
- AI generates human-like text for chatbots, content writing, and storytelling, enhancing automation and creativity.
- AI models create realistic images and music, enabling applications in design, entertainment, and media production.
6.2 AI in Content Creation & Art
- AI assists artists and writers by generating unique content, aiding in design, and enhancing creativity.

7. Personalization & Recommendations
Personalization and recommendations enhance user experience by tailoring content, products, or services based on individual preferences, behavior, and data insights. AI-powered recommendations improve engagement and customer satisfaction.
AI in E-Commerce & Streaming Services
- E-Commerce: AI enhances online shopping by providing personalized product recommendations, optimizing search results, and enabling chatbots for customer support.
- Streaming Services: AI analyzes user preferences to suggest relevant movies, music, or shows, improving content discovery and user engagement.
Top 4 Advanced Features of AI
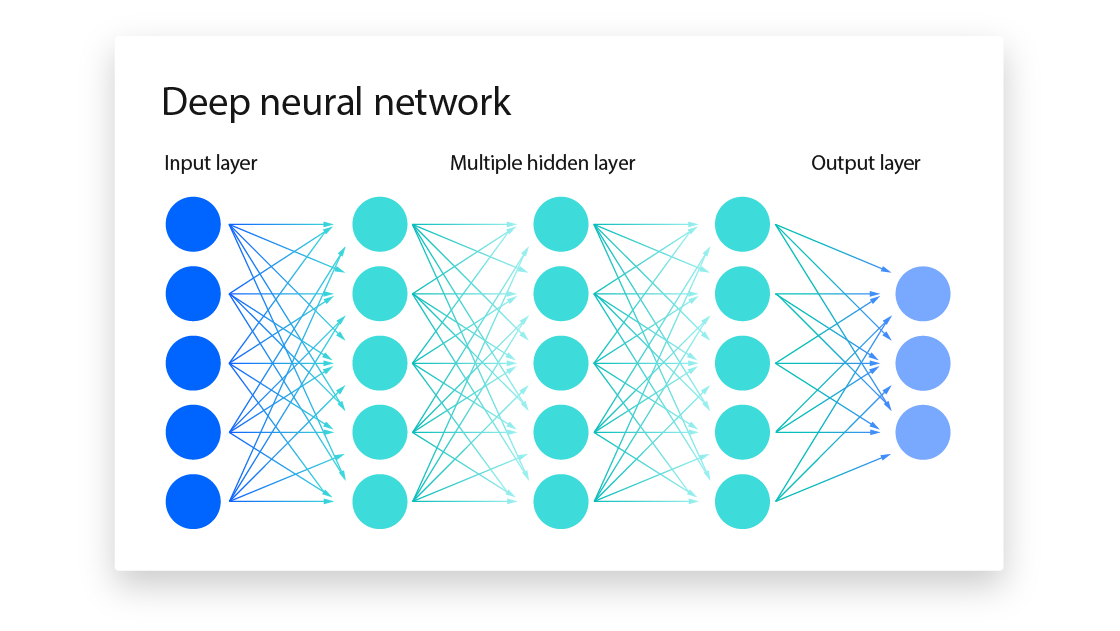
1. Deep Learning & Neural Networks
Deep learning models power modern AI innovations by enabling machines to learn from vast amounts of data and make intelligent decisions. These models mimic the human brain's neural networks to recognize patterns, automate tasks, and improve decision-making.
CNNs, RNNs & Transformers
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) specialize in image processing, enabling applications like facial recognition and medical imaging.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) handle sequential data like speech and text, while Transformers (e.g., GPT, BERT) revolutionize NLP and deep learning applications.
Training & Optimization Techniques
- AI models undergo extensive training using techniques like gradient descent to improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Hyperparameter tuning helps optimize model performance by adjusting learning rates, activation functions, and network architecture.
2. AI in Edge Computing & IoT
AI enhances real-time decision-making in connected devices, reducing latency and improving performance in smart environments. By processing data closer to the source, AI-powered edge computing ensures faster responses and increased efficiency in IoT applications.
AI in Smart Devices & Smart Cities
- AI enhances IoT devices, enabling smart home automation, personalized user experiences, and predictive maintenance.
- In smart cities, AI optimizes traffic management, energy distribution, and public safety through real-time data analysis.
3. Explainable & Ethical AI
AI must be transparent, fair, and accountable to ensure ethical decision-making and avoid biases. Implementing explainable AI (XAI) helps build trust by making AI decisions more interpretable and understandable.
AI Transparency, Bias & Governance
- Ethical AI focuses on creating models that ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability in automated decision-making.
- Governance frameworks help regulate AI systems, reducing biases and ensuring compliance with ethical standards.
4. AI in Cybersecurity
AI strengthens security by detecting threats, preventing fraud, and enhancing digital protection against cyberattacks. It continuously learns from emerging threats to improve defense mechanisms and safeguard sensitive data.
Threat Detection & Fraud Prevention
- AI detects cyber threats by analyzing patterns and anomalies in network traffic to prevent attacks.
- Fraud prevention systems use AI to identify suspicious transactions and enhance security in banking and e-commerce.
Top 4 Future Trends in AI
1. AI & Quantum Computing
AI and quantum computing together are expected to redefine computational capabilities, enabling AI to process vast datasets and complex calculations at speeds unattainable by classical computers. This fusion can significantly impact fields like materials science, climate modeling, and artificial intelligence research itself.
- Advanced AI Models: Quantum computing will help train deep learning models more efficiently by speeding up complex mathematical computations.
- Optimization and Logistics: Businesses will benefit from quantum-enhanced optimization in supply chain management, financial modeling, and risk assessments.
- Breakthroughs in Cryptography: Quantum AI will improve encryption methods and cybersecurity, protecting sensitive data from quantum threats.

2. AI in Healthcare & Finance
AI is transforming both healthcare and finance by improving efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making. In healthcare, AI enhances diagnostics, patient care, and drug discovery, while in finance, it strengthens fraud detection, risk management, and investment strategies.
2.1 Healthcare Applications of AI
AI-Powered Diagnostics
- AI-driven imaging analysis helps detect diseases like cancer, stroke, and heart conditions early.
- AI models predict potential illnesses based on patient history and genetic data.
Drug Discovery & Development
- AI accelerates the drug discovery process by analyzing molecular interactions.
- AI-driven simulations help identify promising compounds for new medicines.
Personalized Medicine & Treatment Plans
- AI customizes treatment based on a patient’s genetic profile and medical history.
- AI helps doctors predict patient responses to different drugs.
AI in Surgery & Robotics
- AI-assisted robotic surgery enhances precision, reducing risks and recovery time.
- AI-powered virtual assistants help surgeons with real-time recommendations.
Telemedicine & AI Chatbots
- AI chatbots provide initial consultations, answering patient queries instantly.
- AI enhances remote patient monitoring, reducing hospital visits.

2.2 Finance Applications of AI
Fraud Detection & Cybersecurity
- AI detects fraudulent transactions by analyzing spending patterns.
- AI-powered security systems prevent identity theft and financial fraud.
Risk Management & Credit Scoring
- AI assesses credit risk by analyzing financial behaviors and transaction history.
- AI models predict potential market fluctuations to minimize risks.
Algorithmic & High-Frequency Trading
- AI-driven trading bots analyze stock market data for better investment decisions.
- AI helps hedge funds predict market trends with data-driven insights.
Automated Financial Services (Robo-Advisors)
- AI-powered robo-advisors offer personalized investment strategies.
- AI helps in portfolio management and financial planning.
Customer Support & AI Chatbots
- AI chatbots assist customers with banking queries and transaction processing.
- AI automates loan applications and financial consultations.
3. AI in the Metaverse & Virtual Reality
AI plays a crucial role in shaping the Metaverse and Virtual Reality (VR) by enhancing user interactions, creating realistic environments, and personalizing experiences. AI-driven avatars, intelligent NPCs (Non-Player Characters), and immersive simulations make virtual worlds more engaging and interactive.
3.1 Applications of AI in the Metaverse & VR
AI-Generated Digital Avatars
- AI creates lifelike avatars with realistic facial expressions and emotions.
- AI enhances avatars by learning user behavior and adapting responses in real time.
Immersive & Adaptive Environments
- AI analyzes user interactions to modify virtual environments dynamically.
- AI-driven world-building tools generate realistic 3D landscapes and objects.
AI-Powered NPCs (Non-Player Characters)
- AI enables NPCs to respond intelligently to user actions, improving game realism.
- AI-powered characters in training simulations help in education and professional development.
Content Creation & Personalization
- AI automates the creation of 3D assets, reducing the time required for designing virtual spaces.
- AI personalizes VR experiences by adapting content based on user preferences.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Realistic Conversations
- AI-driven chatbots enhance communication within the Metaverse.
- NLP enables real-time translations, allowing users from different languages to interact.
AI in Virtual Training & Simulation
- AI-powered VR training helps professionals in industries like healthcare, military, and aviation.
- AI-driven simulations provide realistic real-world scenarios for skill development.
Facial Recognition & Emotion Analysis in VR
- AI detects facial expressions in real time to make interactions more engaging.
- AI-enhanced VR systems can adjust content based on the user's emotional state.

4. AI & Human Collaboration (Copilots, AI Assistants)
AI is transforming the way humans work by acting as co-pilots and assistants in various fields. AI-powered tools enhance productivity, automate repetitive tasks, and provide intelligent suggestions, allowing humans to focus on more complex and creative work. These AI assistants are widely used in software development, content creation, customer support, and business decision-making.
4.1 Applications of AI in Human Collaboration
AI-Powered Copilots for Developers
- Tools like GitHub Copilot assist programmers by suggesting code snippets and automating repetitive coding tasks.
- AI-powered code review and debugging enhance software development efficiency.
AI Assistants in Content Creation
- AI tools like ChatGPT, Grammarly, and Jasper help generate and refine written content.
- AI-generated images, videos, and music assist designers and artists in creative projects.
AI in Business & Decision-Making
- AI-powered analytics tools help businesses make data-driven decisions.
- AI chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer queries and automate workflows.
AI in Healthcare Assistance
- AI helps doctors analyze medical reports and suggest treatment options.
- Virtual health assistants provide personalized health recommendations and reminders.
AI in Education & Training
- AI-powered tutors provide personalized learning experiences for students.
- AI assists educators by automating grading and generating customized lesson plans.
AI in Customer Support & Virtual Assistants
- AI chatbots like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant provide instant responses to user queries.
- AI-driven virtual agents assist in handling complex customer service interactions.
AI in Design & Creativity
- AI tools like Adobe Sensei help designers create visuals and enhance digital artwork.
- AI assists in music composition, video editing, and 3D modeling.

Artificial Intelligence Vs. Machine Learning Vs. Deep Learning
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
| Definition | The broad field of intelligent systems mimicking human behavior. | The subset of AI focuses on data-driven learning. | Subset of ML using deep neural networks. |
| Data Requirement | Works with structured rules and minimal data. | Requires large datasets for training. | Needs massive datasets for high accuracy. |
| Complexity | Can be simple (rule-based) or complex (self-learning). | More complex as it learns from data. | Highly complex, with multi-layered neural networks. |
| Human Intervention | Can be rule-based and needs human input. | Learned with some supervision. | Learns autonomously with minimal intervention. |
| Examples | Chess-playing AI, robotics, smart assistants. | Recommendation systems, fraud detection. | Self-driving cars, facial recognition, NLP chatbots. |
| Read More: Artificial Intelligence Certification Course |
How to Get Started with AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries, automating tasks, and enhancing decision-making across various domains. Whether you're a student, professional, or enthusiast, getting started with AI requires a structured approach.
So, let's explore the step-by-step guide to beginning your AI journey.
Step 1: Learn the Basics of AI
- Understand what AI is and its real-world applications.
- Study different types of AI: Narrow AI, General AI, and Super AI.
- Read about AI use cases in healthcare, finance, automation, etc.
Step 2: Learn a Programming Language (Python)
- Start with Python as it is widely used in AI development.
- Learn essential libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Scikit-learn.
- Practice basic coding and algorithms.
Step 3: Develop a Strong Mathematical Foundation
- Study Linear Algebra (Vectors, Matrices, Eigenvalues).
- Learn Probability & Statistics (Mean, Variance, Distributions).
- Understand Calculus (Derivatives, Gradient Descent).
Step 4: Learn Machine Learning Concepts
- Study Supervised Learning (Regression, Classification).
- Explore Unsupervised Learning (Clustering, Dimensionality Reduction).
- Learn about Neural Networks & Deep Learning.
Step 5: Work on AI Projects
- Build small AI projects to gain hands-on experience.
- Example projects:
- Fraud Detection System
- Image Recognition System
- Medical Diagnosis with AI
Step 6: Learn Deep Learning & AI Frameworks
- Deep Learning architectures like CNNs, RNNs, and Transformers.
- Learn frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Work on advanced AI applications like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision.
Step 7: Join AI Communities & Stay Updated
- Read AI research papers, blogs, and follow industry leaders.
- Participate in AI competitions on Kaggle and Google AI Challenges.
- Stay updated with AI trends, news, and breakthroughs.
Learning AI Fundamentals & Tools
You need to learn the basics and important tools to get started with AI.
- AI Fundamentals: Learn Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning, NLP, and Computer Vision.
- Programming Languages: Python, R, Java, and C++ for AI applications.
- AI Tools & Libraries: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-Learn, OpenCV, and NLP tools like NLTK & spaCy.
- Hands-on Practice: Work on projects like chatbots, image classifiers, and recommendation systems.
| Read More: Libraries in Python |
Conclusion
AI features have greatly enhanced various industries by improving efficiency, accuracy, and automation. With capabilities like data analysis, natural language processing, and machine learning, AI continues to drive innovation and provide solutions that simplify tasks and improve decision-making processes.
FAQs
- AI can automate repetitive tasks, like data entry, scheduling, and document verification
- AI can work independently and autonomously
- AI can process large amounts of data quickly
- AI can find patterns and relationships in data
- AI can learn from outcomes to improve performance
- AI can help solve complex problems
- AI can help with planning and decision-making
- AI can help with reasoning and perception