18
AprEnvironment in AI
Introduction
Understanding the function of the environment in AI systems is essential as artificial intelligence (AI) develops and shapes a variety of sectors. The term "environment" in AI refers to the setting in which AI functions, which might include real-world, digital, and simulated environments. This article, Artificial Intelligence for beginners, will look at the importance of the environment in AI as well as how it affects the effectiveness and long-term viability of AI systems.
What is an environment in AI and why is it important?
The surroundings or circumstances in which an AI system functions are referred to as the environment in AI. It includes the physical environment, digital platforms, and virtualized worlds where AI models and algorithms are used. The environment gives AI systems the context they need to see, think, and decide in an informed manner.
Because it directly affects how AI systems behave and operate, understanding the environment is essential. Different environments offer different opportunities and problems for AI algorithms. AI designers may create systems that can adapt and function well in a variety of situations by understanding the surroundings.
Types of environment in AI: Physical, virtual, and simulated
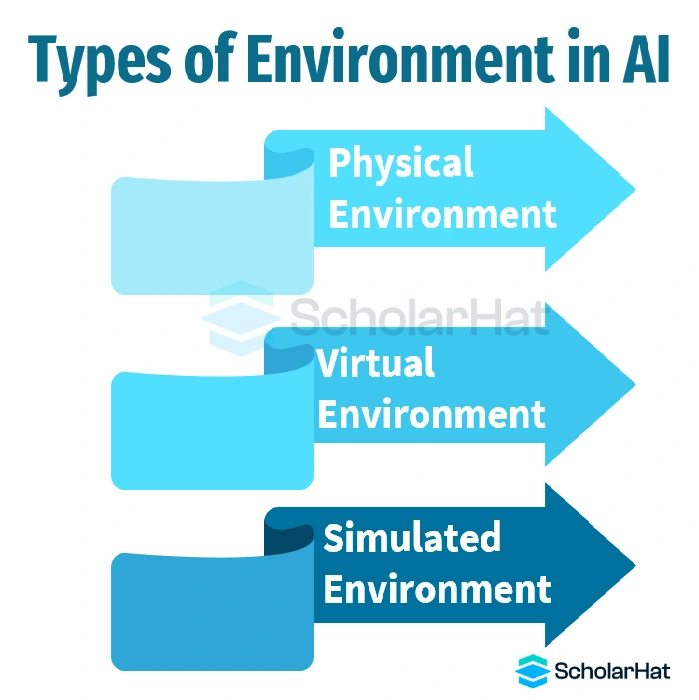
There are three basic types of environment in ai: real-world, virtual, and simulated. Each category has a particular function and raises particular issues for AI system development.
Here are the 3 types:
The Physical Environment
- The tangible reality in which AI systems function is referred to as the physical environment.
- It features authentic environments including houses, workplaces, factories, and outdoor areas.
- When used in real situations, AI systems must use sensors to sense their surroundings and interact with people and objects in a useful way.
- These surroundings frequently provide difficulties like noise, shifting weather patterns, and significant safety risks.
Virtual Environment
- Computer-generated settings that resemble real-world scenes are called virtual environments.
- They make it possible for AI systems to communicate with made-up things and entities.
- Before deploying AI models and testing algorithms in the actual world, virtual environments are frequently used.
- They offer engineers a safe space for testing and allow them to make adjustments to AI systems without worrying about the impact on the real world.
Simulated Environment
- Realistic and highly specialized virtual places are called simulated environments.
- They generate intricate situations that could be risky or impossible to recreate in the real world.
- Simulated environments are especially useful for teaching AI systems in fields like robotics, aerospace, and autonomous vehicles.
- Developers can improve AI systems' adaptability and get them ready for difficulties in the real world by exposing them to a variety of simulated settings.
The goal of artificial intelligence and its implications for the environment
- The creation of intelligent systems that can see, reason, and learn from their surroundings is the aim of artificial intelligence (AI).
- AI has environmental effects that need to be taken into account.
- By streamlining processes, consuming less energy, and enhancing resource management, AI can help the environment.
- Smart grids with AI capabilities can optimize energy distribution, resulting in lower carbon emissions.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in autonomous vehicles can optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and fuel consumption.
- The potential for AI to lead to a greener future exists.
- However, the environmental impact of AI systems must be taken into account throughout development and implementation.
- Data centers and other AI equipment can use a substantial amount of energy.
- A sustainable and ecologically friendly strategy must balance the advantages of AI with steps to reduce energy use.
AI and sustainability: How can AI contribute to a greener future?
AI has the potential to make a significant contribution to a better future of AI by tackling environmental issues and encouraging sustainability. Here are some examples of how AI might benefit society:
- Optimization of Energy: AI can reduce energy use in a variety of industries, including construction, transportation, and manufacturing. Machine learning algorithms can analyze massive volumes of data to spot inefficiencies in the use of energy and make suggestions for changes. AI can assist in lowering carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices by optimizing energy use.
- Observation of the Environment: AI has the potential to be extremely useful in regulating and monitoring the environment. For example, AI systems can examine sensor and satellite data to track animal populations, detect deforestation, and monitor the quality of the water and air. This knowledge can help with sustainable resource management and conservation activities.
- Waste Management: By maximizing waste collection routes, spotting recycling opportunities, and anticipating waste generation patterns, AI can improve waste management procedures. AI can help create a circular economy and lessen the environmental impact of trash disposal by boosting recycling and minimizing waste.
- Adaptation to and Prediction of Climate: To improve climate prediction models and deepen our understanding of climate change, AI can analyze enormous amounts of climate data. With the right information, communities and governments may choose effective adaptation measures and lessen the effects of climate change in sensitive areas.
Durable AI
The durability of AI systems in varied contexts must be ensured to maximize their efficiency. The ability of AI systems to function consistently and dependably in a variety of settings and scenarios is referred to as durable AI. Considerations for creating robust AI systems include the following:
- Robustness to environmental variation
- Transfer learning and generalization
- Always Learning and Adapting
Examples of AI applications in environmental conservation
Numerous case studies show how AI could help in environmental preservation. These instances demonstrate how AI may effectively handle environmental issues and advance sustainability.
- Wildlife Protection: AI systems have been employed to keep an eye on and safeguard threatened animals. Using camera trap photos as an example, AI algorithms can analyze conservation efforts by identifying and tracking certain species. Using this technology, researchers may gather information on wildlife populations and create specialized conservation plans.
- Management of Forests: By examining satellite photos and other data sources, AI can help manage and monitor forests. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems can offer insightful information for sustainable forest management by identifying trends of deforestation, forecasting forest fires, and mapping biodiversity.
- Protection of the Ocean: Marine mammal species like whales and dolphins can be found and tracked using AI systems that analyze underwater sound data. Researchers can use this data to analyze migration trends, gauge population health, and guide conservation efforts.
Best practices for developing AI systems that are environmentally friendly
Here are some top recommendations for encouraging environmentally friendly practices in AI development:
- Efficiency in Energy Use: Think about energy efficiency when creating AI systems. Reduce energy usage during inference and training by optimizing algorithms and hardware. For AI infrastructure, think about low-power computer choices and investigate renewable energy sources.
- Careful Data Management: Responsibly manages data to reduce the need for processing and storage. Prioritise data security and privacy to guarantee that AI systems adhere to the rules of morality and the law. Reduce the requirement for computing by using data compression & filtering methods.
- Lifecycle Evaluation: Evaluate the environmental impact of AI systems by performing a lifecycle analysis. Throughout the entire life cycle, take into account elements like energy consumption, resource use, and waste generation. Utilize this evaluation to pinpoint areas that require development and introduce sustainable practices.
- Cooperation and Information Exchange: Encourage cooperation and knowledge exchange among AI experts to hasten the creation of eco-friendly AI systems. To promote creativity and group learning, share best practices, research findings, & case studies.
Resources for further learning and practice
Online tutorials and courses: Explore Additional Learning and Practice Resources with us at https://www.scholarhat.com/training/artificial-intelligence-certification-training. There are numerous online tutorials and courses available that specifically focus on Artificial Intelligence.
Summary
It is essential to recognize the promise of AI while taking into account how it may affect the environment as technology develops. For the development of resilient and sustainable AI systems, it is critical to comprehend the function of the environment in AI and its ramifications. AI can help create a greener future by maximizing energy use, monitoring the environment, and supporting sustainable practices.
It is essential to create robust AI systems that can change with the times and respond to various situations. We can reduce the environmental impact of AI systems by taking best practices for environmental sustainability into account during AI development and deployment.