21
Dec10 Points to Secure ASP.NET Core MVC Applications
10 Points to Secure ASP.NET Core MVC Applications: An Overview
Securing an ASP.NET Core MVC application has become a major concern when we talk about web application. Also, we are aware that framework .net core 2.1 is now under LTS (Long Term Support) releases. So, this framework is more stable and may use to create a large application. In this tutorial, I have explained about 10 points that need to consider before start application development.
Developers with ASP.NET skills earn up to $11,000 more annually. Kickstart your career with our Free .NET Course with Certificate now!
Read More: Top 50 ASP.NET Interview Questions and Answers
1.) Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
What is Cross-Site Scripting?
Cross-Site Scripting is kind of computer security vulnerability found in web application that allows attackers to inject client-side scripts or malicious code into web pages which are viewed by the other users. It is different from another web attack like SQL injection that does not directly target web app. In XSS, mostly attack happened via the input field, query string, request headers.
Types of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities
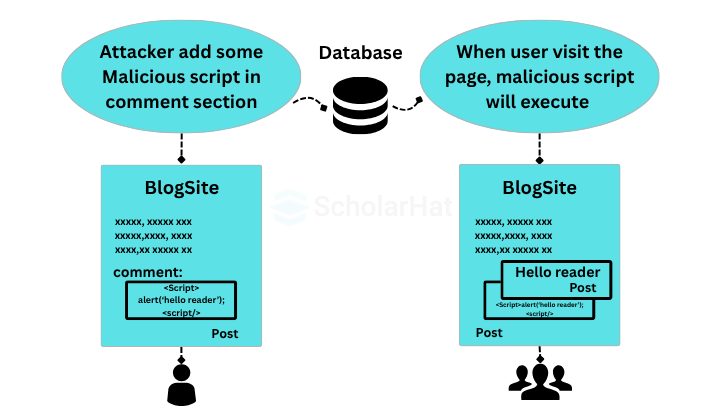
There are mainly three types of XSS vulnerabilities: Reflected XSS, DOM-based XSS, and Stored XSS. Reflected XSS is the most common type of XSS vulnerability. Here, an attacker may inject the payloads (also refer as metadata) to the victim so that the payload script is part of request sent to the webserver and reflected with HTTP response. Document Object Model (DOM) Based XSS is an advanced type of XSS attack and it is possible when the client script generates DOM by using provided data. In stored XSS, the attacker injects the script which stored into the target application permanently. For example, some malicious script can be injected to site in any input field such as comment field and the victim views this page in a browser, the script will run into the browser.
How to prevent XSS
Following are some solutions to prevent XSS.
Sanitizing user input:This is helpful to prevent XSS attack on site that allows HTML markup as input. It means that encode the HTML that is stored. The Razor engine automatically encode all the inputs so that the script part which adds as any field is never executed. The using @ directive, we can apply encoding rule to the variable.
Encoding the URL: Many applications use Query String to transfer the data from one page to another page. The XSS attack can be possible on query string data due to it is not encoded. Using UrlEncode and UrlDecode method of Microsoft.AspNetCore.WebUtilities class, we can encode and decode the URL with ASp.net code 2.0 and above version.
Input Validation: Some time HTML character does make sense for user input. we can put the validation (client and server-side both) that prevent the malicious data that harming a website.
Read More: Why you need ASP.NET Core in your tech stack?
2.) Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
What is Cross-Site Request Forgery?
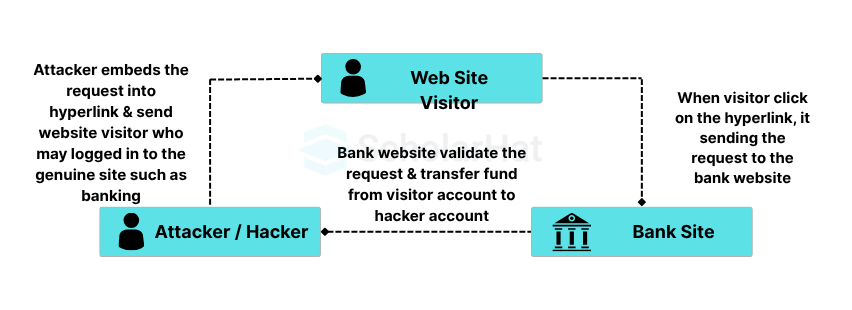
It is also known as Session riding and pronounced as XSRF. In this method of attack, attacker copies forge as a trusted source and send the data to the site. The site processes this information believe that this is coming from a trusted source. This kind of attack can be destroying both client relation and business. The example of CSRF is unauthorized fund transfers, data theft etc.
Mostly this is done through creating a forged site and it internally hits the genuine site and by using already established user session, an attacker is done some malicious activity. For example, a user is transferring fund from one account to another account and trusted connection established between the user and bank site. At the same time user click on malicious like from junked email (that sent by the attacker). Because of the secure session is established between user and bank site, the attacker uses this connection and does some malicious activity such as fund transfer. However, it is vulnerability at the server (web application) side, not an end-user side.
How to prevent Cross-Site Request Forgery
Using tag helper "asp-anti forgery", we can enable/disable anti-forgery for the page. If this tag helper value is set to "true", it means that it enables the anti-forgery for this page. And using ValidateAntiForgeryToken attribute, we can check whether the token is valid or not at server side (controller / action method). It also can be ignored by using “IgnoreAntiforgeryToken” attribute
Example<form asp-controller="Account" asp-action="Login" asp-antiforgery="true" asp-route-returnurl="@ViewData["ReturnUrl"]" method="post" class="form-horizontal">
….
….
</form> 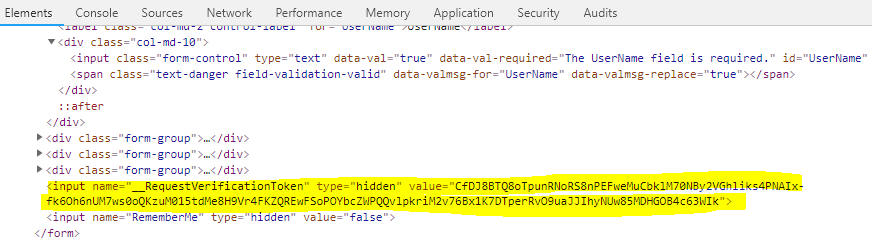
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public class AccountController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Login()
{
return View();
}
[IgnoreAntiforgeryToken]
public IActionResult Method1()
{
return View();
}
} 3.) SQL Injection
What is SQL Injection?
SQL Injection is the most common attack that injects malicious SQL code for database and an unauthorized user can get the information. For example, the user gets the information that he/she did not have the right to visualize using SQL injection. In this attack, a hacker is always trying to inject SQL statement that will get executed on the database and get unassessed data. In this following example code snap, the attacker/hacker can easily do the SQL injection. Here, I have modified the input (id that is visible as a query string), so the system will return all the records of the user instead of a specific user.
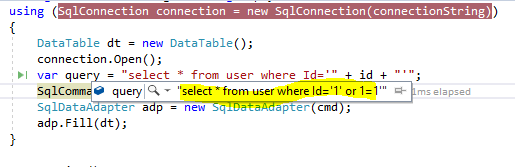
How to prevent SQL Injection
Following are some solutions to prevent SQL Injection.
Use Parameterized Query or stored procedure usingthe parameterized query or stored procedure, we can prevent SQL injection. It is better to use a stored procedure instead of an inline query. If you want to use inline query, we must use a parameterized query to prevent our application from SQL Injection.
SqlCommand cmd1 = new SqlCommand("select * from User where id = @id", connection); SqlParameter param = new SqlParameter(); param.ParameterName = "@id"; param.Value = id; cmd.Parameters.Add(param); … …Use any O/RM (Object-relational mapping) such as Entity Framework O/RM maps SQL object such as a table, view to our domain object such as class. Most of the ORM is to generate a parameterized query internally to fetch the record from the database.
4.) Do the Proper Error Handling
What is Error Handling?
Sometimes, we are not doing proper error handling. So, some of the sensitive information is exposed in term of error such as database object name (table, stored procedure etc.), file location, etc. This kind of information can be used by attacker/hacker to do an attack on the web site.
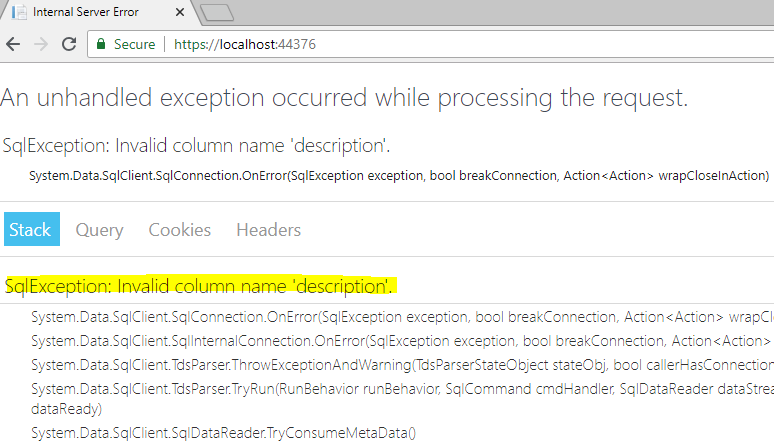
How to prevent
It can be prevented by using creating a custom error page that will display when an error occurred, or we can write the code to do custom error handling. In the first solution, we need to create a page that has a generic message and it needs to be configured Configure method of startup class.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
….
….
….
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
….
….
} 
Alternatively, we can write some custom code to do exception handling such as try-catch block, exception handler or exception filter.
5.) Enforce SSL and use HSTS
What is Enforce SSL and use HSTS?
SSL enables us to establish an encrypted connection between a web server and a browser. It ensures that all the data transmitted between the web server (application) and browser are encrypted and not change during the transition. To secure our application, we can use HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) protocol. There are many advantages using HTTPS such trust, verified data, Integrity of Data, etc.
ASP.net Core 2.1 and later version enable us to create an application that configured over HTTPS. We can also configure HTTPS with ASP.net Core before the .NET core framework 1.1 but it was some difficult to configure. There is an option available to configure our web application over HTTPS when we are creating a web application with Visual Studio. In the template of a web application, HTTPS is enabling for the application.
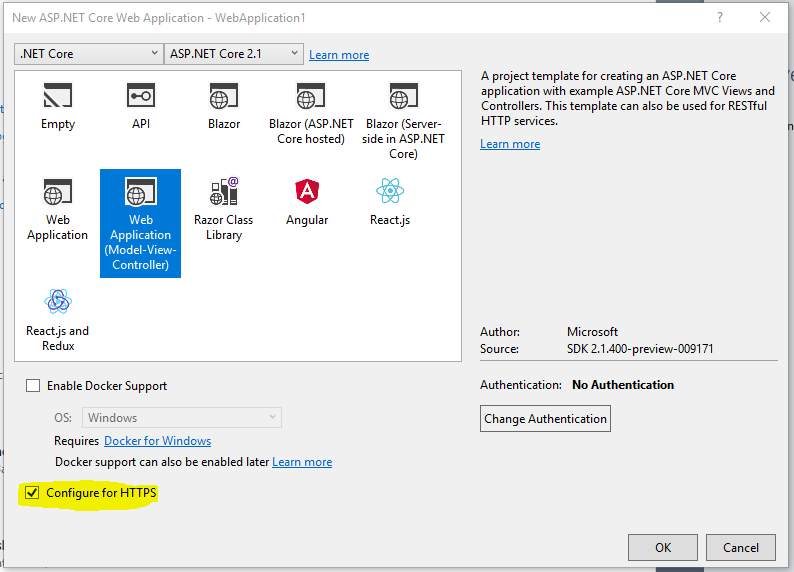
HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security Protocol)
It is a web security policy that protects our web application from downgrade protocol attacks and cookie hijacking. It forces webserver to communicate over an HTTPS connection. It always rejects insecure connections. The Asp.net core templet by default adds HSTS middleware. It is not recommended to use in the development environment as a browser is cache the HSTS header.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
….
….
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
….
}
else
{
…
app.UseHsts();
}
….
….
}
There are a couple of options available that can be overridden to configure HSTS. Following are the options
MaxAge : It is the time span that defines the max-age of Strict-Transport-Security header valid. The default value is 30 days.
IncludeSubDomains : It boolean type and if it set to true, Strict-Transport-Security header available for subdomain as well.
Preload : Using this property, we can add preload for Strict-Transport-Security header.
ExcludedHosts : it is a list of hostname will not add the HSTS header
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
….
….
services.AddMvc();
services.AddHsts(options =>
{
options.IncludeSubDomains = true;
options.Preload = true;
options.MaxAge = TimeSpan.FromHours(1500);
options.ExcludedHosts.Add("myDummySite.com");
});
} The default template also adds another middleware that redirects request from non-secure secure HTTP. It uses default redirect status code (307) to redirect the request. We can also configure this middleware based on our requirement. We can override the default option by adding AddHttpsRedirection method to ConfigureService method of startup class. Here we can configure default redirect status code and https port
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
….
services.AddHttpsRedirection(options =>
{
options.RedirectStatusCode = StatusCodes.Status307TemporaryRedirect;
options.HttpsPort = 9001;
});
….
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
….
….
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
….
….
} 6.) XXE (XML External Entities) attack
What is XXE?
XXE (XML External Entity) attack is possible on the application that parses XML input. The possible reason for this attack is XML input contains the reference of the external entity which weakly configured in the XML parser. It may happen due to the disclosure of confidential data, SSRF (server-side request forgery), port scanning by the hacker where the application (XML parser) hosted, denial of service (Dos), etc. Hacker / Attacker can use XML to cause a Denial of Service attack by injecting entities within entities. This type of attack refers to “Billion Laughs Attack”. As a result, the system required more resource to complete the task and due to high utilization server may crash.
How to Prevent XXE Attack
If you are using "XmlTextReader" class to parse the XML, it has property "DtdProcessing" that must be set to Prohibit or Ignore. If we have set DtdProcessing property of XmlTextReader to "Prohibit", the system will throw the exception as DTD (Document Type Definition) is identified and if we have set DtdProcessing property of XmlTextReader to "Ignore", the system will ignore DTD specifications and continue to process the document.
XmlTextReader reader = new XmlTextReader("fileName with path");
reader.DtdProcessing = DtdProcessing.Prohibit;
while (reader.Read())
{
…
…
} 7.) Improper Authentication & session management
What is Improper Authentication & session management?
Sometimes, we do not maintain proper authentication that allows the hacker to steal user credentials in terms of session and cookies. Using this type of user access, a hacker can take complete access to the application. Following are some ways to steal user credentials.
Non-secure connection (without SSL)
Login credential easy hack-able or weak credential
Problem with session such as session-id exposed in URL, the session has a long timeout, etc.
Improper log out from the application (do not kill user session on logout)
After successful login in the web application, some cookies are set to the browser to identify the user that is logged-in. These cookies are always sent to the web server with every request. On logout, we generally remove the session but forget to remove cookies. These cookies may be used by a hacker to do an attack on the web server. Default cookie name for the .net core web application is “.AspNetCore.Session” and this default cookie does not specify the domain. Using session option, we can override the cookie setting.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
….
services.AddSession(options =>
{
options.Cookie.Name = ".MyApplication.Session";
})
….
} The solution is very simple: remove the cookies are successful logout, use secure HTTP to secure cookies and session.
//Remove session
HttpContext.Session.Clear();
// Removing Cookies
CookieOptions option = new CookieOptions();
if (Request.Cookies[".AspNetCore.Session"] != null)
{
option.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-1);
Response.Cookies.Append("Myapplication.Session", "", option);
} If you are working with built-in identity membership, so “SignOutAsync” method of SignInManager class will take care about removing all your cookies after logout.
public async Task<IActionResult> Logout()
{
await signInManager.SignOutAsync();
…
…
}
As described in the preceding section, SSL enables us to do make secure communication connection between server and client so that any data that transited between server and client are encrypted. There are some cookie options need to set to secure cookies and session
HttpOnly: It indicates whether client-side code able to access the application cookies or not. If it is set to HttpOnlyPolicy. Always, the client-side script is not able to access the application cookies.
Secure: It indicates whether cookies are transmitted using SSL (over HTTPS) only. If it is set to true (internally), the cookies are only transmitted over SSL connection. It can set to true by using CookieSecurePolicy.Always and CookieSecurePolicy.SameAsRequest option.
SameSite: It is the same site mode for cookies.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
…
…
app.UseCookiePolicy(new CookiePolicyOptions
{
HttpOnly = HttpOnlyPolicy.Always,
MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.Strict,
Secure = CookieSecurePolicy.SameAsRequest
});
…
}
8.) Improper Authorization
What is Improper Authorization?
Authentication is a process of checking the identity of the user accessing our application. Most of the application has log in feature and application validate user identity against any trusted source such as database or external login providers (i.e. Facebook, Gmail, Twitter, etc.). This process is called Authentication. Authorization is the process of validating privileges to access a resource of the application. After a successful login to the application, authorization mechanism checks whether a login user has privileges to access the application resource.
Using “Authorize” attribute we can turn on the authorization for any controller or individual action method. Sometimes, due to the laziness of developers, they miss to put authorize check of controller or action and, they bypass the authorization in the same case. It causes the security hole in the web application. Sometimes, developers also miss putting proper authorization for the controller or action method. For example, some of the pages can be accessed by the unauthorized role user due to improper role-based authorization.
Solution
The solution is very straight forward, make sure authorization works as expected before web application moves to the production environment. ASP.net core has a very rich model for authorization such as Policy-based authorization, claim-based authorization, etc., we can use these models in the complex scenario to authorization.
9.) Do not use components with Known Vulnerabilities
Nowadays, we are using many third-party JavaScript libraries in our development of web application. It is just impossible to develop an application without such libraries. These libraries may have security flaws which make a web application vulnerable. The most common security vulnerabilities with-in JavaScript includes CSRF, XSS, buffer overflows, etc. As describe a preceding section of this article, XSS allows a hacker to put malicious code into the trusted page and this code will execute in the user's browser. CSRF allows the hacker to utilize a user’s browser session as a trusted source and send the other sites. Buffer overflow occurred when hacker sent very large data to the site that hold by web site resulting web site maybe crash.
For the JavaScript library, there is full prove documentation that lists down all the vulnerabilities. There is some public site, they log the vulnerabilities for the popular JavaScript framework or plugin. For example, jQuery’s vulnerabilities are list down on the CVE website.
Solution
Do not download any plugin or library from an untrusted source. Use trusted source such as npm. It may reduce the chance of including a malicious or modified component
Do not use any untrusted library in the application
Always use an updated version of the library (it may fix some critical security defect in the latest version)
Always remove unused plugin, files, component from the application
Monitor the library's Vulnerabilities from the source such as NVD and CVE
Here, I have talked about JavaScript library, but there are many security vulnerability incidents are a log for the server-side framework.
10.) Version Discloser
What is Version Discloser?
The request and response object contains may information such as to request method, remote address, server X-Powered-By, etc. Some of them are very sensitive such as X-Powered-By, Server etc. They must not disclose to the end-user because the attacker may use this information to do attack. It may possible that some framework version may encounter security Vulnerabilities and using these Vulnerabilities, an attacker may break our system.
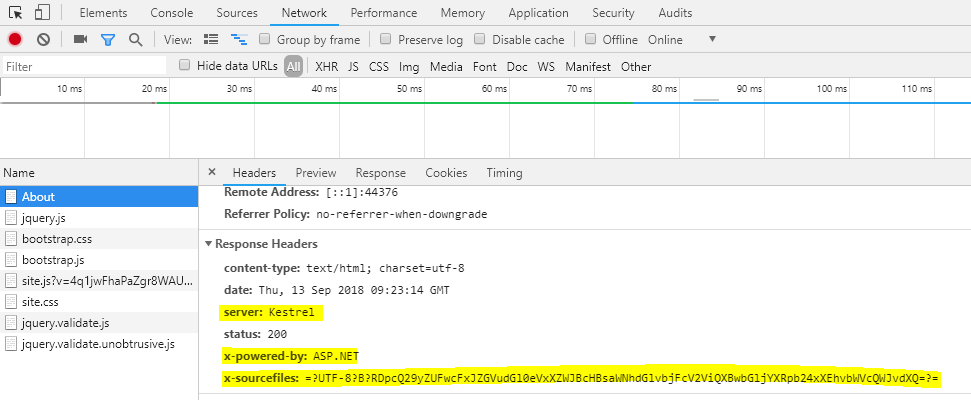
As seen in above snap, we can get information such as a server, X-Powered-By and X-sourcefiles. The Server property indicates which server is used to host application, the X-Powered-By indicate the information about the framework and X-SourceFiles is only available in debugging modules in IIS / IIS express.
Solution
Removing headers that contain sensitive information. We can remove server header by setting up AddServerHeader to false where we configure the server. In following an example, I have to remove server header from Kestrel server.
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseKestrel(c => c.AddServerHeader = false)
.UseStartup<Startup>(); 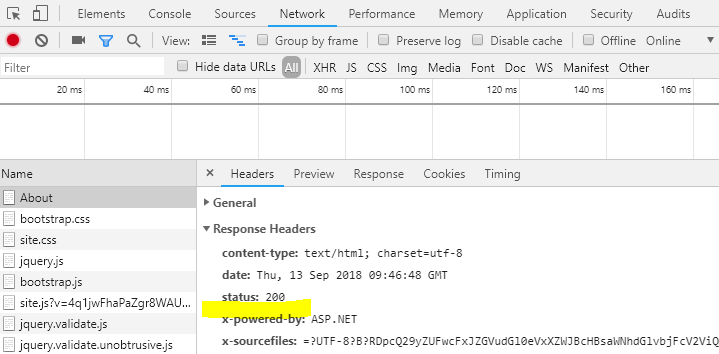
We can remove X-Powered-By header either by using web.config or from IIS setting.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<httpProtocol>
<customHeaders>
<remove name="X-Powered-By" />
</customHeaders>
</httpProtocol>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
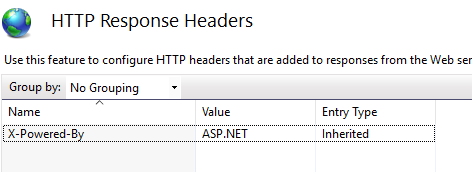
Summary
In this article, I tried to cover the top 10 possible attacks on our Asp.net core application and how to prevent our application from such attack.
By 2026, 80% of enterprise applications will rely on .NET Core. Stay ahead—enroll in our ASP.NET Core Online Training today!
FAQs
- Implement authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Encrypt data with HTTPS
- Validate input data and encode the output data.
- ASP.NET Core's built in AntiXSS library
- Content Security Policy
- Validation and Sanitization methods
- Forms Authentication
- Windows Authentication
Take our Aspnet skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.