21
DecAzure Active Directory Explained
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based service used to manage user identities and access. It helps employees sign in securely and access tools like Microsoft 365, Teams, and Azure services. It’s important because it supports single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), which protects accounts from unauthorized access. Organizations use Azure AD to control who can access what, keeping data safe and improving productivity. It’s a key tool for managing access in modern, cloud-based workplaces.
In this Azure Tutorial, we are going to learn Azure Active Directory, including Why do we need Azure Active Directory?, What is Windows Active Directory?, Who utilizes Active Directory?, the Difference Between Azure Active Directory and Windows Active Directory, Service Audience in Azure Active Directory, and a lot more. Azure is powering 40% of global cloud infrastructure. Don’t get left behind—enroll in our Free Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Online Training today!
What is Azure Active Directory?
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based service that helps manage user identities and access to applications. Think of it as a secure gateway that ensures only the right people can log in to systems, apps, and data, whether they’re in the cloud or on your company’s network. With Azure Active Directory, businesses can provide single sign-on (one username and password) for employees, making it easier and safer to work across various platforms and devices.
Why do we need Azure Active Directory?
We use Azure Active Directory for several reasons, which are explained below:
- Secure Access: Azure Active Directory ensures that only authorized people can access sensitive apps and data, protecting businesses from unauthorized logins and security breaches.
- Single Sign-On: It allows users to log in once and access multiple applications without entering their credentials repeatedly, saving time and reducing frustration.
- User Management: Azure AD makes it simple for IT teams to manage employee accounts, such as adding or removing users or assigning specific permissions.
- Supports Remote Work: With Azure AD, employees can securely access company systems and apps from anywhere, which is ideal for remote or hybrid work setups.
- Integration with Other Services: It connects easily with Microsoft 365 and thousands of other apps, making it a seamless tool for businesses of all sizes.
- Improved Productivity: By automating repetitive tasks like password resets, Azure AD helps employees and IT teams focus on more important work.
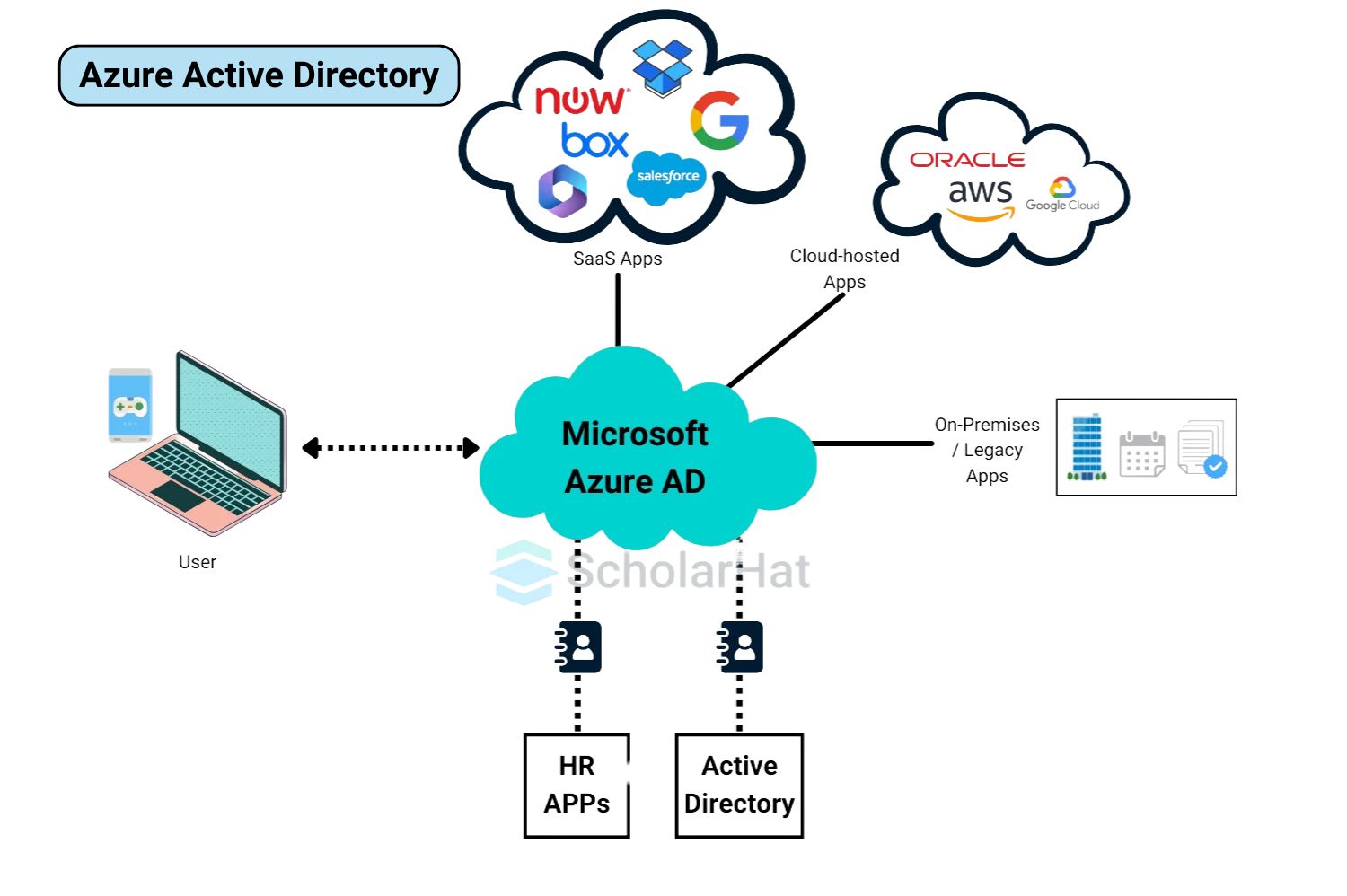
What is Windows Active Directory?
Windows Active Directory is a tool from Microsoft that helps manage users, computers, and devices in a company’s local network. It stores information like who can access certain files or systems. While Azure Active Directory works online in the cloud, Windows Active Directory is used within a company’s physical network.
Why do we need Windows Active Directory?
We use Windows Active Directory for several reasons, which are explained below:
- Centralized User Management: It helps manage all users, computers, and devices from one place, making it easier for IT teams to organize.
- Access Control: You can decide who gets access to certain files, applications, or systems, ensuring security in the network.
- User Authentication: It checks and confirms users’ identities before allowing them to log in, keeping the system safe from unauthorized access.
- Network Organization: It keeps the company’s network well-structured by grouping devices, users, and resources logically.
- Custom Permissions: You can assign specific rights to different users, such as who can read or edit a document, based on their role.
- Offline Use: Since it works within a local network, it doesn’t need internet access, which is helpful for on-site setups.
Windows Active Directory Components
Let's discuss the key components of Windows Active Directory:
1. Domain Services (AD DS)
Domain Services (AD DS) is the core of Active Directory. It stores important information about all users, computers, and other resources in the network. It also decides who can access what and makes sure only authorized people can log in.
2. Domain Controllers
Domain Controllers are special servers that keep all the data in Active Directory. They verify user logins and manage access to resources. Every time someone logs in, a domain controller checks if they have permission to access the network.
3. Organizational Units (OUs)
Think of OUs as folders where you organize your users, groups, and computers. By grouping things together in OUs, IT admins can apply certain rules or settings to all the items in a group, making it easier to manage.
4. Group Policy
Group Policy tool allows IT admins to apply specific settings across all computers or users in the domain. For example, they can set rules for password strength, control which apps can be used, or define security settings to keep the network safe.
Who utilizes Active Directory?
Active Directory is used by:
- Businesses: Companies of all sizes use Active Directory to manage their employees' access to different systems and resources.
- IT Teams: IT professionals use Active Directory to organize, secure, and control access to the company’s network, devices, and applications.
- Large Organizations: Big companies with many users and devices rely on Active Directory to keep everything running smoothly and securely.
- Small Companies: Even small businesses use Active Directory to make sure only the right people can access sensitive information or systems.
Difference Between Azure Active Directory and Windows Active Directory
let's see the difference between Azure Active Directory and Windows Active Directory with various factors
1. Purpose
- Azure Active Directory: A cloud-based service to manage users and apps online.
- Windows Active Directory: An on-premises tool to manage users and devices in local networks.
2. Technology
- Azure Active Directory: Built for modern cloud use and works over the internet.
- Windows Active Directory: Created earlier for local networks and uses physical servers.
3. Where It Works
- Azure Active Directory: Ideal for remote work and cloud-based apps.
- Windows Active Directory: Best for companies using on-site networks and resources.
4. Security
- Azure Active Directory: Offers advanced tools like single sign-on and multi-factor authentication.
- Windows Active Directory: Provides basic security for local systems.
5. Integration
- Azure Active Directory: Connects easily with online apps and mobile devices.
- Windows Active Directory: Works well with local devices like printers and shared drives.
6. Why They Were Created
- Azure Active Directory: Designed for businesses using cloud services and remote access.
- Windows Active Directory: Made for companies relying on local, on-site networks.
Let's understand the differences in a synchronized way:
| Factors | Azure Active Directory (AAD) | Windows Active Directory (AD) |
| Purpose | Cloud-based identity and access management for applications and services. | On-premises directory service for managing users, computers, and resources. |
| Deployment | Cloud-based, part of Azure services. | On-premises or on a private network. |
| Infrastructure | No on-premises infrastructure is needed; fully managed by Microsoft in the cloud. | Requires on-premises infrastructure, such as domain controllers. |
| Authentication Protocols | Supports modern authentication protocols (OAuth, OpenID Connect, SAML). | Uses legacy protocols like Kerberos and NTLM. |
| Access Management | Manages user access to cloud-based apps and services. | Manages access to on-premises resources, such as servers and network resources. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Built-in support for multi-factor authentication (MFA). | Requires additional configuration or third-party tools for MFA. |
| Directory Types | Primarily used for identities and devices in the cloud. | Used for traditional Windows-based domain services (on-premises). |
| Domain Trusts | Does not require domain trusts as it's based on cloud identities. | Supports domain trusts for managing relationships between domains. |
| Support for Non-Windows Devices | Supports a wide variety of devices, including iOS, Android, and macOS. | Primarily designed for Windows-based devices. |
| Management Interface | Managed via Azure Portal, PowerShell, and APIs. | Managed via Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC), Group Policy, PowerShell. |
Why do we choose Azure AD over Windows AD?
We choose Azure AD over Windows AD for several reasons:
- Access from Anywhere: Azure AD lets you securely log in to apps and data from any location with internet access.
- Perfect for Remote Work: It’s great for teams working from home or on the go without needing to be in the office.
- Better Security: Offers modern tools like single sign-on and multi-factor authentication to keep accounts safe.
- No Servers Needed: Since it’s cloud-based, there’s no need to set up or maintain physical servers.
How Does Azure Active Directory Work?
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) works by managing and securing user identities and access to applications in the cloud. Here’s how it works:
1. User Authentication
When users try to log into an app or service, Azure AD checks their identity. It makes sure the username and password match, and can even use extra steps like multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
2. Single Sign-On (SSO)
Once users log in to Azure AD, they can access multiple apps and services without having to log in again. This is called Single Sign-On, making it easier for users to switch between apps.
3. Access Control
Azure AD gives organizations the power to decide who can access what. IT admins can set up permissions so that users only have access to the apps or data they need, keeping sensitive information safe.
4. Cloud Integration
Azure AD connects with cloud apps (like Microsoft 365 and Salesforce) and on-premises systems. It manages access to both types of resources from a central location.
In short, Azure AD helps organizations keep their users' access secure, simple, and organized, whether they’re working in the cloud or on local systems.
Service Audience in Azure Active Directory
Here’s how different people use Azure Active Directory and how it helps them:
1. IT Administrators
- IT admins use Azure Active Directory to manage users, devices, and access within the organization.
- They can easily control who can access certain apps or systems, ensuring security.
- It helps them automate tasks like password resets and monitor security risks.
2. Application Developers
- Developers use Azure Active Directory to integrate user sign-in and authentication into their apps.
- It allows them to securely manage user identities without handling passwords directly.
- Azure Active Directory also enables features like single sign-on for users, making it easier for them to access multiple apps with one login.
3. Online Customers
- Customers use Azure Active Directory when they sign in to apps or services that use it for authentication.
- It provides them with a secure, smooth login experience, often using social media accounts or other credentials they already have.
- Azure Active Directory helps keep their personal information safe while accessing different services or applications.
Features and Licensing of Azure Ad or Azure Entra ID
Azure Active Directory Features
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) provides tools to secure and simplify identity management. Here are its key features:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Users can log in once and access multiple apps without needing to log in again.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second step, like a text code or app notification, during login.
- Conditional Access: Allows admins to control access based on conditions like user location, device type, or risk level.
- Self-Service Password Reset: Users can reset their passwords themselves without contacting IT.
- Application Management: Integrates with thousands of apps for easy user access and management.
Azure Active Directory Licensing
Azure AD offers different licensing options based on your needs:
- Free Plan: Includes basic features like user management, SSO for a few apps, and basic security tools.
- Azure AD Premium P1: Offers advanced features like Conditional Access, hybrid identity support, and self-service password reset.
- Azure AD Premium P2: Adds Identity Protection and Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for stronger security and access control.
- Microsoft 365 Plans: Some Microsoft 365 subscriptions include Azure AD features depending on the plan (e.g., Business or Enterprise).
Each plan is designed to match the needs of small businesses, large enterprises, or organizations looking for advanced security.
Azure Entra ID Connect
Azure Entra ID Connect (previously called Azure AD Connect) is a tool that links your on-premises Active Directory to Azure Active Directory. It helps organizations use both local and cloud systems together without issues.
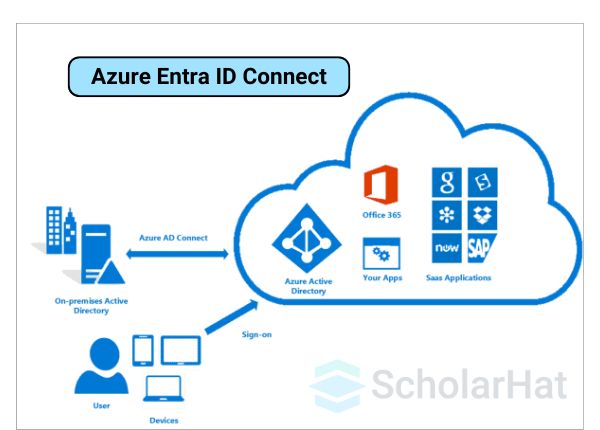
Features of Azure Entra ID Connect
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Users can log in once and access both local and cloud apps without entering their credentials repeatedly.
- Password Sync: Keeps passwords the same across on-premises and Azure AD, so users only need to remember one password.
- Unified Identity: Makes sure users have the same identity for accessing systems in the cloud and on-premises.
- Device Writeback: Let devices registered in Azure AD work with your local Active Directory, supporting both environments.
Why do we use Azure Entra ID Connect?
- It connects your local and cloud systems, making everything work together smoothly.
- Users get a simple login experience, reducing confusion and saving time.
- It ensures secure and consistent identity management for your organization.
In short, Azure Entra ID Connect makes it easier for businesses to manage both on-premises and cloud systems while keeping everything secure and user-friendly.
Azure Active Directory Join
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Join allows devices like laptops, tablets, and desktops to be directly connected to Azure AD, without needing to link them to a traditional on-premises Active Directory. It’s designed for businesses that primarily use cloud services.
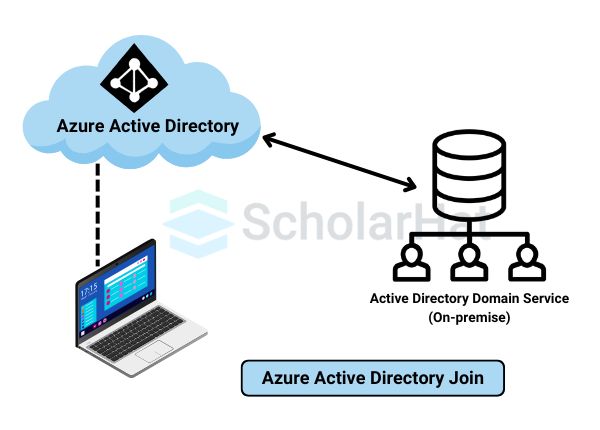
How does Azure Active Directory Join help the engineers?
- Simpler Login: Users can log in to their devices with their Azure AD credentials, just like they would for cloud apps like Microsoft 365.
- Seamless Access: Once a device is joined, users can easily access company apps and resources without extra logins.
- Better Security: Azure AD Join ensures that devices follow the organization’s security policies, like requiring strong passwords or device encryption.
- Cloud-First Approach: It’s perfect for businesses that don’t have on-premises servers and rely on Azure or other cloud solutions.
In short, Azure AD Join connects devices directly to the cloud, simplifying access for users while keeping everything secure and managed from one central place.
Attacks on Azure Active Directory
There are 15 possible attacks on Azure Active Directory, and we are understanding each one of them:
1. Phishing
Attackers trick users into entering their usernames and passwords on fake websites or emails, allowing the attacker to steal the login information.
2. Password Spray Attacks:
Attackers try common passwords on many accounts, hoping one will work, often bypassing lockout measures that stop too many failed login attempts.
3. Brute Force Attacks
Attackers use automated software to guess passwords by trying many different combinations until they find the right one.
4. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Attackers intercept communication between a user and Azure AD, stealing login information or altering data without the user knowing.
5. Token Theft
Attackers steal authentication tokens, which are used to verify a user’s identity and use them to access systems without needing a password.
6. Privilege Escalation
Attackers gain higher access levels within Azure AD by exploiting weaknesses or mistakes in security, giving them access to sensitive data.
7. Bait-and-Switch
Attackers impersonate a legitimate website or service, tricking users into logging in to the fake site, which gives the attacker access to their credentials.
8. Social Engineering
Attackers manipulate people, like employees or IT staff, into giving away sensitive information or bypassing security measures.
9. MFA Fatigue
Attackers keep sending multiple multi-factor authentication (MFA) requests to a user in the hope they’ll approve one out of frustration or mistake.
10. Identity Spoofing
Attackers pretend to be someone else by stealing their login details or using stolen authentication tokens to gain access.
11. Token Reuse
Attackers steal authentication tokens from one service and try using them to access other services that use the same system.
12. Application Proxy Misconfigurations
If the Azure AD Application Proxy is set up incorrectly, it can allow unauthorized access to apps that should only be used internally.
13. Access Control Misconfigurations
Weak or incorrect permission settings can give attackers the ability to access sensitive information or perform actions they shouldn’t be able to.
14. OAuth Token Exploits:
Attackers can find and use security flaws in OAuth (a system for letting apps access information) to gain unauthorized access to resources.
15. Insider Threats
Employees or trusted individuals with access to Azure AD can intentionally or accidentally misuse their access to leak sensitive information.
How do we connect and manage the users and groups in Azure AD?
We connect and manage the users and groups in Azure AD by:
- Create Users: You can add new users manually or automatically, giving them a username and password so they can access company apps and resources.
- Manage User Access: You can assign users to different groups or apps to control what they can access, making it easier to manage permissions.
- Create Groups: Groups allow you to organize users (e.g., by department or role) so you can manage them together, like giving all members access to the same apps.
- Update or Remove Users: You can easily update a user’s information (like email or job title) or remove them from Azure AD when they leave the company, keeping things organized and secure.
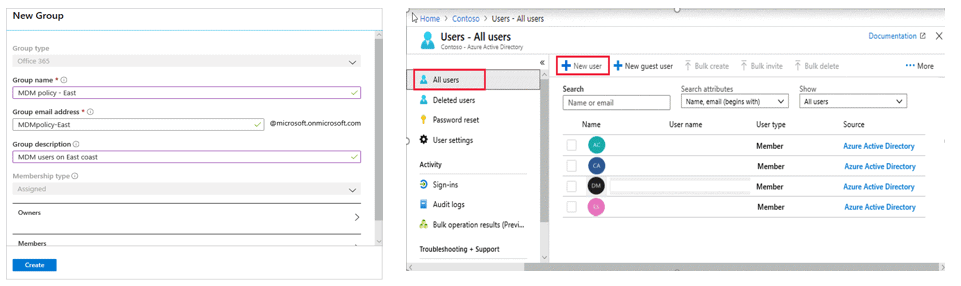
Managing users and groups in Azure AD is a simple way to make sure everyone has the right access and keeps your system organized.
Advantages of using Azure Active Directory
Here are the advantages of using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) in simple bullet points:
- Access from Anywhere: You can securely access apps and resources from anywhere, as long as you have an internet connection.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Once you log in, you can access all your apps without needing to log in again, saving time and hassle.
- Better Security: Azure AD provides features like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and real-time threat detection to keep your accounts and data safe.
- Easy to Manage: IT admins can easily manage users, groups, and access from a central place, which makes everything more organized.
- Integration with Microsoft Services: It works seamlessly with Microsoft services like Office 365, Azure, and other cloud apps.
- Supports Hybrid Environments: Azure AD can work alongside your on-premises systems, allowing a mix of cloud and local resources.
- Scalable: Whether you have a small business or a large enterprise, Azure AD can easily grow with your needs.
- Cost-Effective: It reduces the need for on-premises hardware and maintenance, saving money on physical infrastructure.
Top Most Certification Courses on Azure by Scholarhat
| Courses | Links |
| Azure AI Engineer Certification Training | Click Here |
| Azure Developer Certification Training | AZ-204 Certification | Click Here |
| Azure Cloud DevOps Engineer Certification Training | Click Here |
| Azure AI/ML and GenAI Engineer Certification Training Program | Click Here |
How to Access Azure Resources
To access the Azure Resources, we should:
- Sign In with Azure Directory: Log in to the Azure portal using your Azure Active Directory credentials.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Azure Directory assigns roles to control who can access specific resources.
- Access via Azure Portal: Go to the Azure portal, where you can view and manage all your Azure resources securely.
- Use Azure CLI or PowerShell: Advanced users can use command-line tools to interact with resources through Azure Directory authentication.
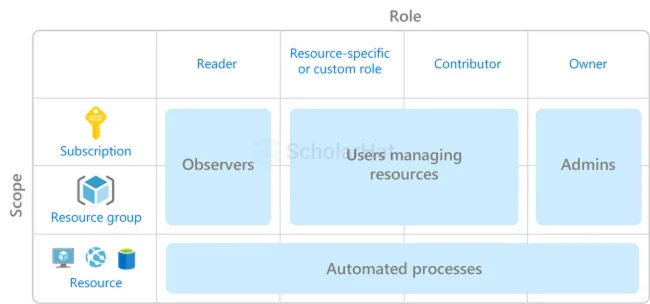
These steps ensure secure and simple access to your Azure resources through Azure Active Directory.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Azure Active Directory simplifies identity and access management for both cloud and on-premises systems. It provides secure login features like Single Sign-On and multi-factor authentication, improving security and ease of use. Overall, Azure AD ensures businesses can manage user access efficiently while keeping everything secure.
In the next 3 years, 75% of developer roles will require Azure expertise. Don’t lag behind. Join our Azure Developer Course now!
Practice with the following MCQs
Q 1: What is the primary purpose of Azure Active Directory?
Q 2: Which of the following is NOT a feature of Azure Active Directory?
Explanation: Azure Active Directory provides features like Single Sign-On, Application Proxy, and Multi-Factor Authentication, but it does not manage traffic load balancing, which is handled by Azure Load Balancer.
Q 3: What is the default domain name provided by Azure Active Directory?
Explanation: Azure Active Directory assigns a default domain name in the format domainname.onmicrosoft.com when you create a tenant.
Q 4: Which protocol is primarily used by Azure Active Directory for authentication?
Explanation: Azure Active Directory uses modern authentication protocols like OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect for secure user authentication and authorization.
Q 5: What is an Azure AD tenant?
Explanation: An Azure AD tenant is a dedicated and trusted instance of Azure Active Directory that is created automatically when an organization subscribes to a Microsoft cloud service.
FAQs
Take our Azure skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.









