18
AprAzure Firewall - A Comprehensive Guide
Azure Firewall
Azure Firewall is essential to modern cloud network security, acting as a safeguard for Azure Virtual Network resources.The word 'Firewall 'refers to a physical obstacle designed to prevent it from spreading. In the digital world, a firewall offers the same security measures, but it also provides security against network traffic and cyber attacks.
In this Azure tutorial, we will learn crucial concepts related to the Azure firewall, including Firewall Implementation, Firewall setup, Firewall capabilities, Azure firewall vs. NSG, Firewall pricing, Firewall benefits, Firewall use cases, and more.
Why do we need Network Security in the Cloud Computing?
In the Digital world, Network security is imperative in cloud computing because precise data is moved to the cloud. Even though the cloud offers various advantages and security measures like scalability and remote access, it brings new security challenges. The reasons why network security is vital in the cloud era are depicted below:
- Data Security
- Reducing Cyber Threats
- Shared Responsibility Model
- Multicloud Environments
- Compliance
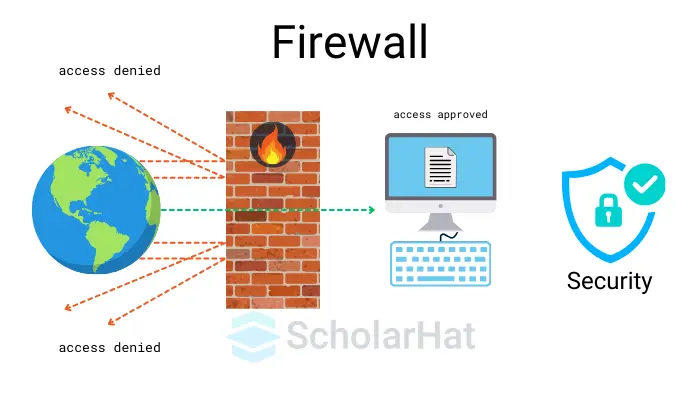
What is the Azure Firewall?
Microsoft Azure Firewall is afast-faced technology tool and a composed security service that guards yourAzure Virtual Networkresources. Itpermits only authorized connections and blocks malicious traffic using threat intelligence. Azure Firewall offers scalability, centralized management, and high availability to ensure protection during failures.
Note: Default Azure Firewall can block all the traffic.
Read More: |
How to set up Azure Firewall?
Here is the complete guidance for setting up Azure Firewall:
1. Preparation
- Identify your needs for protection in your Azure Virtual Network, understand traffic flow, resources requiring security, and your desired security level.
- Create a Resource Group to manage all resources associated with the deployment.
2. Deployment
- Ensure you have a virtual network with subnets :
- Dedicated Azure Firewall Subnet(/26 recommended).
- Workload Subnets(s) for protected resources.
- Set up the Azure Firewall Resource within the Azure Firewall Subnet.
- Allocate a public IP address for the Azure Firewall.
- Create a separate firewall policy resource to define security rules.
2. Configuration
- Specify firewall rules within the policy to allow or deny traffic flow( based on IP address, ports, protocols, and applications (FQDNs).
- Configure a default route in the virtual network to direct traffic to the firewall.
3 Optional Configuration
- Enable threat intelligence for real-time threat filtering.
- Configure web filtering to block access to specific website categories.
- Set up Azure Firewall as a DNS proxy for centralized management and filtering.
- Define custom DNS servers for your virtual network.
- Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) for private addresses to access the internet.
- Implement Forced tunneling (optional) for enhanced outbound traffic security.
4. Testing and Monitoring
- Thoroughly test firewall rules to ensure expected behavior.
- Integrate Azure firewall with Azure Monitor for logging and monitoring network traffic and security.
Implementation of Application Rules and URL Filtering in Azure Firewall
Azure Firewall provides robust capabilities for application rules and URL filtering. Here’s an overview of how to implement these features:
Application Rule Filtering in Azure Firewall
Application rules allow you to control outbound traffic from your Virtual Machines(VMs)to specific FQDNs (Fully Qualified Domain Names) based on the HTTP, HTTPS, and MSSQL protocols.
1. Create an Azure Firewall
- In the Azure gateway, drive to "Create a resource" > "Networking" > "Firewall."
- Configure basic settings, networking, and management.
2. Create an Application Rule Collection
- Go to your Azure Firewall.
- Under "Settings", select "Rules".
- Click "+ Add a rule collection."
- In the "Add rule collection" area, set:
- Name: Set a descriptive name for the rule collection.
- Priority: An integer value refers to the priority of the rule collection (lower numbers have higher priority).
- Action: Select "Allow" or "Deny".
3. Add Rules to the Application Rule Collection
- Click "+ Add a rule" to add a rule to the collection.
- Set the following for each rule:
- Name: A descriptive name for the rule.
- Source type: Set this to "IP address" or "Service Tag."
- Source: Specify the source IP addresses or service tags.
- Protocol: Select the protocol (HTTP, HTTPS, or MSSQL).
- Target FQDNs: Specify the FQDNs to which the rule will apply.
4. Deploy the Application Rule Collection
- Save the rule collection, and it will be applied to your Azure Firewall.
URL Filtering in Azure Firewall
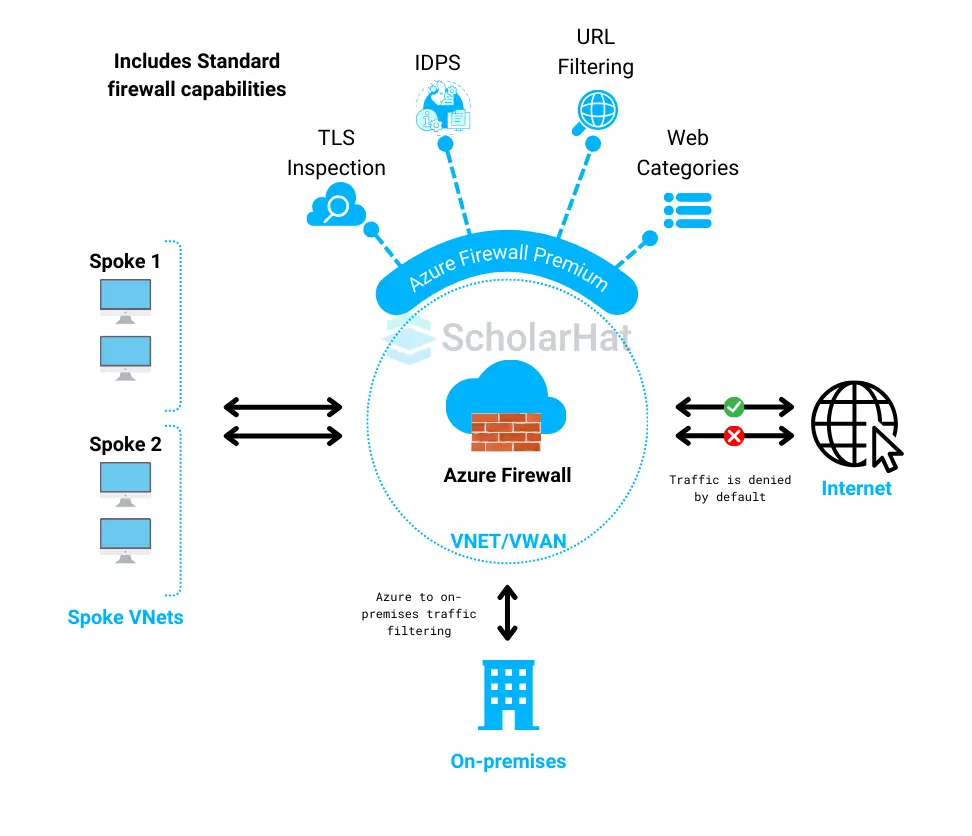
URL filtering allows you to control outbound traffic based on specific URLs and categories. This feature requires enabling Azure Firewall Premium.
1. Upgrade to Azure Firewall Premium
- In the Azure gateway, drive to your actual Azure Firewall.
- Under "Settings", select "Upgrade".
- Follow the prompts to upgrade to Azure Firewall Premium.
2. Create a URL Filtering Rule Collection
- Go to your Azure Firewall Premium.
- Under "Setting," select "Rules."
- Click "+ Add a rule collection."
- In the "Add rule collection" area then, set:
- Name: Set a descriptive name for the rule collection.
- Priority: An integer value refers to the priority of the rule collection (lower numbers have higher priority).
- Action: Select "Allow" or "Deny".
3. Add Rules to the URL Filtering Rule Collection
- Click "+ Add a rule" to add a rule to the collection.
- Set the following for each rule:
- Name: A descriptive name for the rule.
- Source type: set this to "IP address" or "Service Tag."
- Source: Specify the source IP addresses or service tags.
- Protocol: Select the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS).
- URL Categories: Specify the URL categories or individual URLs to filter.
4. Deploy the URL Filtering Rule Collection
- Save the rule collection, and it will be applied to your Azure Firewall Premium.
Difference Between Azure Firewall and NSG
| Feature | Azure Firewall | Network Security Groups (NSG) |
| Service type | Managed Firewall Service | Stateful Firewall |
| Service level | Advanced (L3, L4, L7) | Basic (L3, L4) |
| Threat intelligence | Yes | No |
| SNAT/DNAT | Yes | No |
| Application Security | Yes (L7 inspection) | No |
| Cost | Higher | Less |
| Complexity | Higher | Less |
Features and Benefits of Azure Firewall
Azure Firewall is a structured, cloud-based network security service that safeguards your Azure Virtual Network resources. It offers a comprehensive set of features that translate into benefits for your cloud environments.
Features of Azure Firewall
1. High-Availability
- It provides high availability to increase availability uptime to 99.99%.
- You can deploy a Firewall in an Availability Zone at no additional cost, but there is the cost of outbound and inbound traffic data transfer associated with availability zones.
2. Stateful Inspection
- Analyzes ongoing network connections to differentiate between legitimate traffic and potential threats.
3. Multi-layered Threat Protection
- Filters Traffic at layers 3(Network), 4(Transport), and 7(Application) for control.
- Includes application protocol filtering, URL filtering, and even deep packet inspection.
4. Web Application Firewall
- Protects yourAzureWeb Applications for typical web applications from common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site inspection.
5. Multiple Public IP Address
- It can support multiple IP Addresses.
- This enables the following scenarios:
- DNAT:You can translate multiplied standard port instances over your backend servers.
- SNAT: It supports replacing private IP Addresses, port management, and scalability.
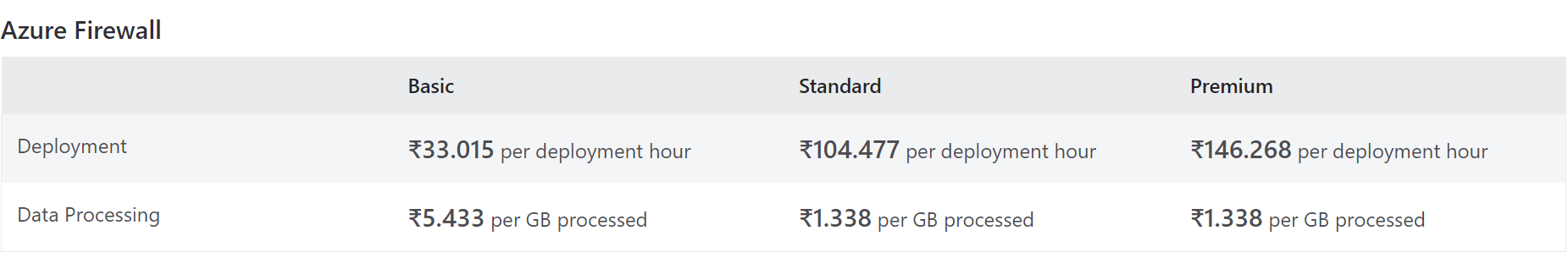
6. Pricing and SLA of Azure Firewall
- Setting up a firewall is easy, with billing involved in fixed and variable fees.
Benefits of Azure Firewall
- It provides advanced threat protection capabilities beyond basic traffic filtering.
- It's simplified management and manages security policies for all your virtual networks.
- It potentially reduces the need for separate on-premises security solutions.
- It scales easily to accommodate growth in your cloud environment.
- It provides insights into network traffic flow and potential threats.
- It helps to meet security compliance requirements for various regulations.
Use cases of Azure Firewall
- Protecting a web application with WAF capabilities.
- Securing a database server.
- Segmenting a virtual network with different security requirements.
- Compartmentalizing development, testing, and production environments.
Conclusion
In the above article, we discussed Azure Firewall, including firewall setup and services used in different industries and business applications. This article will definitely help you understand the steps and regulations to secure your Azure services.
ScholarHat provides various Training and Certification Courses to help you in your end-to-end product development: |
FAQs
- Azure Firewall focuses on protecting your entire virtual network by inspecting traffic at multiple layers.
- Azure WAF shields web applications from web-specific attacks.
- Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) Rules.
- Network Rules
- Application Rules
Take our Azure skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.