18
AprTop 50 Cloud Computing Interview Questions: What You Need to Know
Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers
Cloudcomputing interview questionscan be proven a hat-trick for you preparingfor your upcoming job interviews. Are you nervous and confused about your job interview?, So dear, don't need to go anywhere. This article will provide you with complete knowledge for the interview. It will cover several subjects like various Azure service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), cloud architecture, security, and specialized platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
ThisAzure tutorialprovides you with the solution for your doubts aboutcloud computing by providing theTop 50 Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers.Here, we will categorize these 50 questions into three categories: fresher, intermediate, and experienced. These interview questions are very helpful for you to crack any tech interview.
Top 20 Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
In this section, we will provide you with the Top 20 Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers for freshers.
Ques-1. What is a cloud?
Cloud in the real world refers to an open environment in nature. But in the tech world, A cloud is a network where you can share, access, and manage data over the internet without using any physical devices.
Ques-2. Describe Cloud Computing.
Cloud Computingis a method of utilizing technology that enables individuals and organizations to access and store apps and data online rather than locally on PCs or servers.
Ques-3. Why should we use cloud computing?
We should use cloud computing because it provides several benefits that are:
- Cloud computing allows for easy scaling of resources based on demand.
- Many cloud providers offer robust backup and recovery solutions.
- Users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
- Users can use of AI, machine learning, and analytics without significant investment.
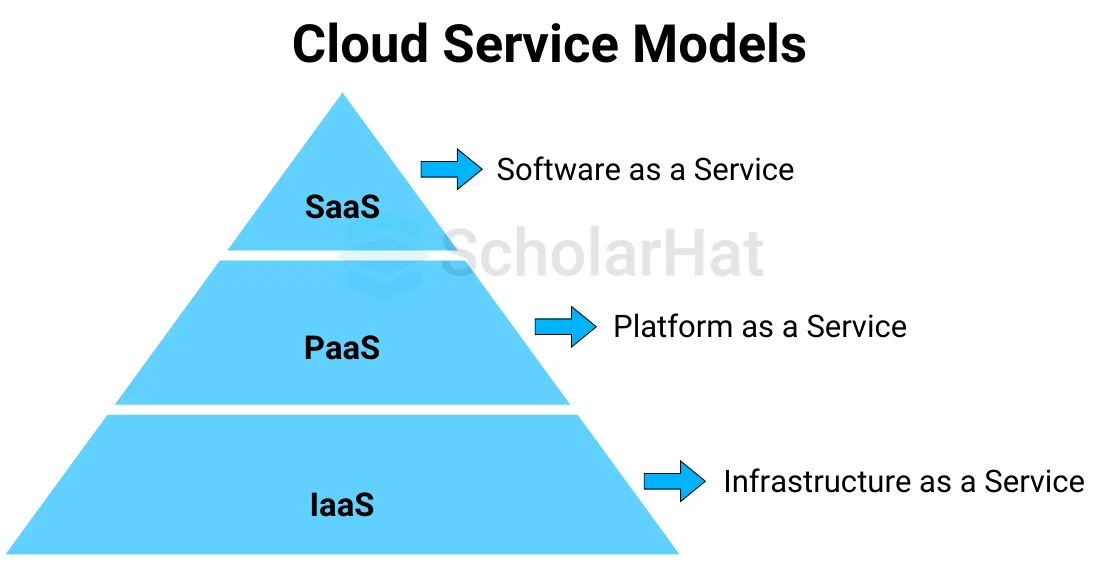
Ques-4. Describe services that are provided by Cloud computing.
Cloud Computing provides different types of services that are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Function as a Service (FaaS)
- Backup as a Service (BaaS)
- Storage as a Service (STaaS)
Ques-5. What are Cloud Delivery Models?
There are several cloud delivery models that are:
1. Public Cloud
Public Cloud is a cloud environment where services are offered to multiple customers over the internet, making resources like storage and servers available on a pay-as-you-go basis from a third-party provider.
2. Private Cloud
Private Cloud is a dedicated cloud infrastructure used exclusively by one organization, offering greater control over security and data but requiring the company to manage and maintain the environment.
3. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud combines public and private cloud environments, allowing data and applications to move between them, providing flexibility, and optimizing existing infrastructure for specific needs.
4. Community Cloud
Community Cloud is a shared cloud infrastructure that serves a group of organizations with similar requirements, enabling collaboration while maintaining specific security and compliance standards for the community.
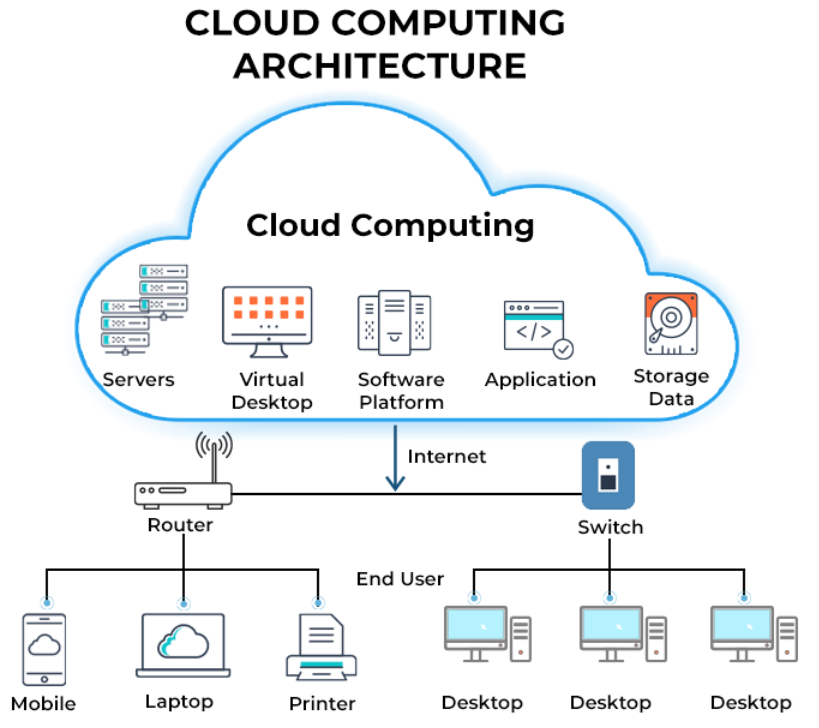
Ques-6. Describe Cloud Architecture layers.
The layers which make up the architecture of the cloud are:
- Physical Layer: Hardware resources like servers and storage in data centers.
- Virtualization Layer: turns real hardware into virtual machines (VMs) through virtualization.
- Infrastructure Layer: Provides computing resources (IaaS) like servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform Layer: Offers platforms and frameworks for app development (PaaS).
- Application Layer: Delivers software applications to users over the internet (SaaS).
- Management Layer: Monitors, automates, and manages cloud resources.
- Security Layer: Implements security measures like encryption, access control, and compliance.
Ques-7. Who are the major performers in Cloud Computing Architecture?
Major Cloud Service performers are:
Ques-8. Describe Hybrid Cloud.
A hybrid cloud is a collection of public and private cloud services, permitting companies to use a public cloud for scalability and flexibility and a private cloud for safe storage of sensitive data. Although it might add some complexity to administration and security, this configuration helps businesses save money and manage resources efficiently.
Ques-9. Who are the major performers in the architecture of cloud computing?
Every performer in the context of cloud computing is an entity (a person or an organization) that participates in a transaction or procedure and/or carries out tasks. The NIST cloud computing reference architecture defines five primary actors:
- Cloud Provider
- Cloud Carrier
- Cloud Broker
- Cloud Auditor
- Cloud Consumer
Ques-10. Describe the Levels of Cloud Storage.
The levels of cloud storage are:
- Object Storage: Itstores data as objects and is ideal for managing unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups.
- Block Storage: Itdivides data into blocks, making it suitable for high-performance, low-latency applications like databases and virtual machines.
- File Storage: Itorganizes data using a hierarchical structure, making it the best option for shared access in collaborative environments.
- Cold Storage: It offers inexpensive storage with delayed access times, specifically designed for data that is infrequently accessed or archived.
- Hybrid Storage:Itprovides flexibility by combining cloud-based storage with on-site storage, allowing businesses to balance cost and performance.
- Multi-cloud Storage: It enhances flexibility and redundancy by utilizing storage from several cloud providers, ensuring better availability and risk management.
Ques-11. Give five names of Cloud computing Databases.
Here are five names of cloud computing databases:
- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
- Google Cloud SQL
- Microsoft Azure SQL Database
- MongoDB Atlas
- Firebase Realtime Database
Ques-12. What is cloud storage?
Cloud Storageis avirtual storage servicewhereyou can store your data, such as photos, videos, and files, on the internet without any hardware requirements.
Quess-13. How many types of cloud computing are there?
There are five types of cloud computing you need to know that are:
- Hybrid Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Multi-Cloud
Ques-14. Describe Edge Computing.
Let's understand edge computing from some points:
- Edge computing is when data is processed close to where it's created, making it faster.
- It eliminates the need to transfer data to centralized cloud servers, enabling quicker real-time answers.
- Edge computing is commonly used in IoT devices, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles for instant processing.
- It helps improve data privacy and security by keeping sensitive data locally and reducing exposure to threats.
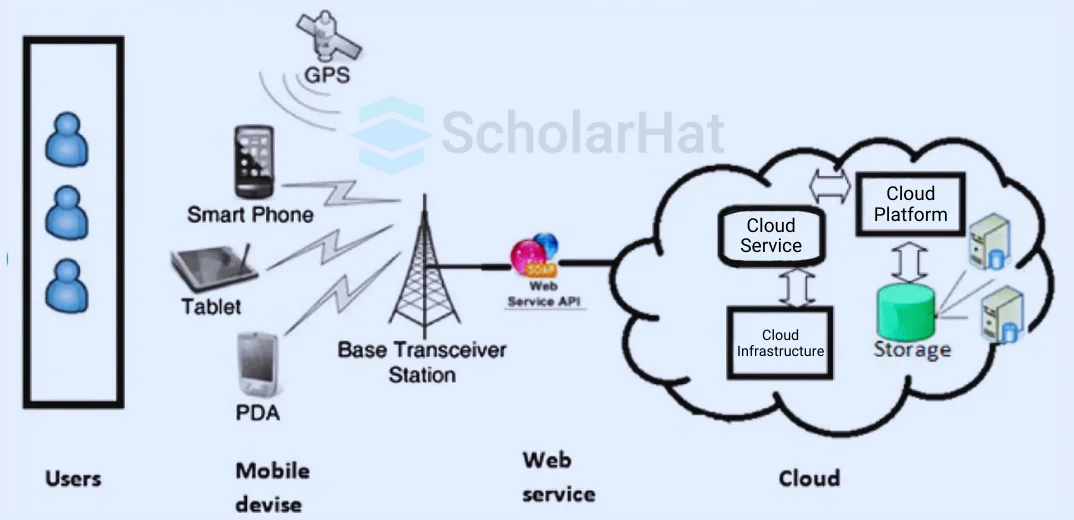
Ques-15. Describe Mobile Cloud Computing.
Mobile cloud computing is a general-purpose requirement. When you access the internet on your mobile phones or tablets, it is called mobile computing.
Ques-16. DescribeCloud computing hypervisor.
A cloud computing hypervisor is software that creates and manages virtual machines (VMs) on physical servers. It allows multiple operating systems to run on a single machine by sharing the underlying hardware resources. This helps cloud providers efficiently use hardware, making it easier to scale and manage computing resources.
Ques-17. What does virtualization mean in cloud computing?
In cloud computing, virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, optimizing resource use and enhancing security through isolation. It also provides scalability and flexibility, enabling fast modifications to computer resources based on demand.
- Virtualization maximizes resource efficiency by allowing independent VMs to operate on a single server.
- It enables easy scaling and deployment of diverse operating systems and applications on the same hardware.
Ques-18. What does multitenancy mean in Cloud computing?
In cloud computing, multitenancy is an architecture design that enables multiple customers to share the same application and infrastructure resources while ensuring their data and configurations remain isolated, promoting efficient resource utilization and cost savings.
Ques-19. what do you mean by elasticity and scalability in Cloud computing?
Elasticity of Clouds
Elasticity is the capacity of a cloud to dynamically compress or expand its infrastructure resources in response to abrupt increases or decreases in demand, allowing for effective workload management. This flexibility reduces the cost of infrastructure.
Scalability of Clouds
Cloud scalability is used to manage the increasing demand in situations where using software or apps effectively also requires high performance. Scalability is frequently employed in situations when a persistent resource deployment is necessary to handle the workload statically.
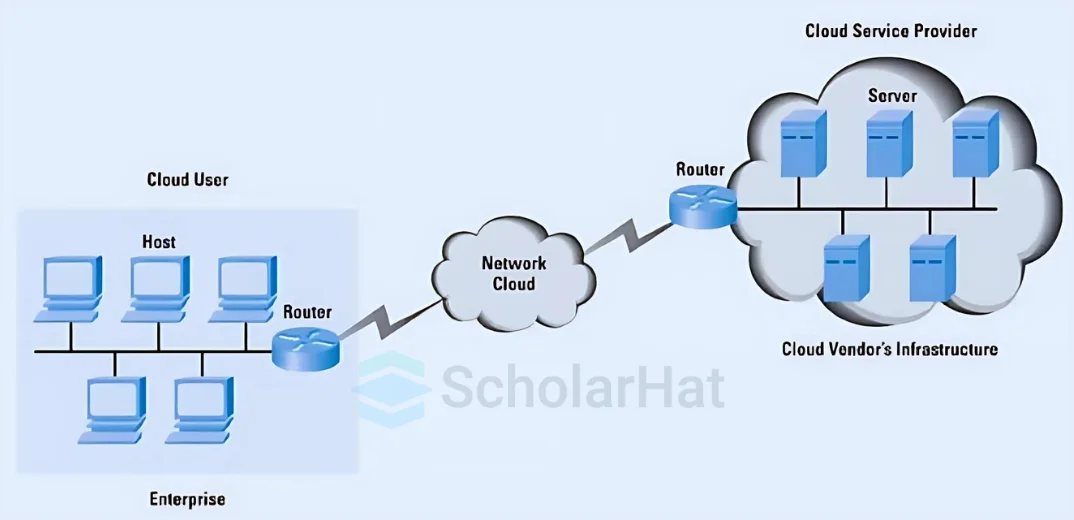
Ques-20. What is the networking in the cloud?
We understand networking in simple words. When many computers and devices connect and start sharing data in a wired or wireless medium, it is called networking.
Top 15 Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers for Intermediate
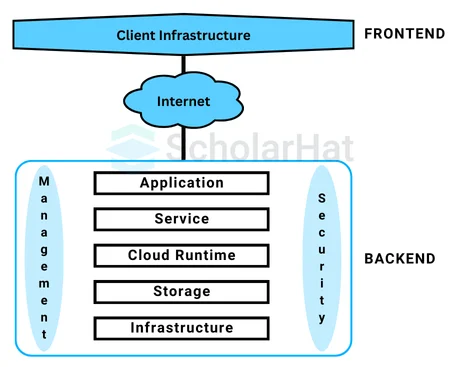
Ques-21. What are the components of cloud computing?
There are four components of cloud computing that are explained below:
1. Front-End Platform
The front endis what you see and use when you access cloud services. It includes the apps, websites, or software that let you interact with the cloud. For example, when you open Google Drive or Dropbox on your phone or computer, you are using the front end.
2. Back-End Platform
The backend is the part of the cloud you don’t see. It includes the servers, storage, and systems that do all the work in the background, like storing your files or running programs. It makes sure your data is safe and available when you need it.
3. Delivery Models
Delivery models are the different ways cloud services are offered. There’s IaaS, which gives you virtual servers and storage; PaaS, which provides a platform to build apps; and SaaS, which is the software you use online, like Gmail or Microsoft 365.
4. Network
The network is how everything in the cloud connects. It links the front end and back end through the internet, allowing you to access your files or services from anywhere in the world, whether you're at home or on the go.
Ques-22. Describe the pros and cons of serverless computing.
Pros of Serverless Computing
- Serverless computing is cost-efficient as you only pay for the resources you really utilize, eliminating idle server fees.
- It automatically scales based on demand, handling traffic spikes without manual intervention.
- Developers should focus on coding, which provides efficient results.
- Server maintenance is no longer required because the cloud provider handles infrastructure management and updates.
- Developers can focus on creating apps since it automatically maintains the underlying infrastructure.
Cons of Serverless Computing
- Cold start latency can be a challenge for serverless operations, potentially delaying the processing of initial requests.
- It may result in vendor lock-in, which makes switching cloud providers for application migration challenging.
- Because of their limited control over the underlying infrastructure, developers may find it difficult to optimize or debug.
- Serverless platforms often impose execution time and memory limits, which may hinder resource-intensive tasks.
- It may not be suitable for real-time or long-running tasks due to potential performance issues.
Ques-23. Which technology enables the cloud?
There are several technologies that enable the cloud that are:
- Broadband Networks
- Virtualization
- Data Centre
- Web Technology
- Multitenant Technology
- Service Technology
Ques-24. Define micro-services in cloud computing.
In cloud computing, microservices are architectural styles in which programs are divided into tiny, self-contained services that interact with one other through APIs, allowing for easier scalability, more flexibility, and quicker deployment of individual components.
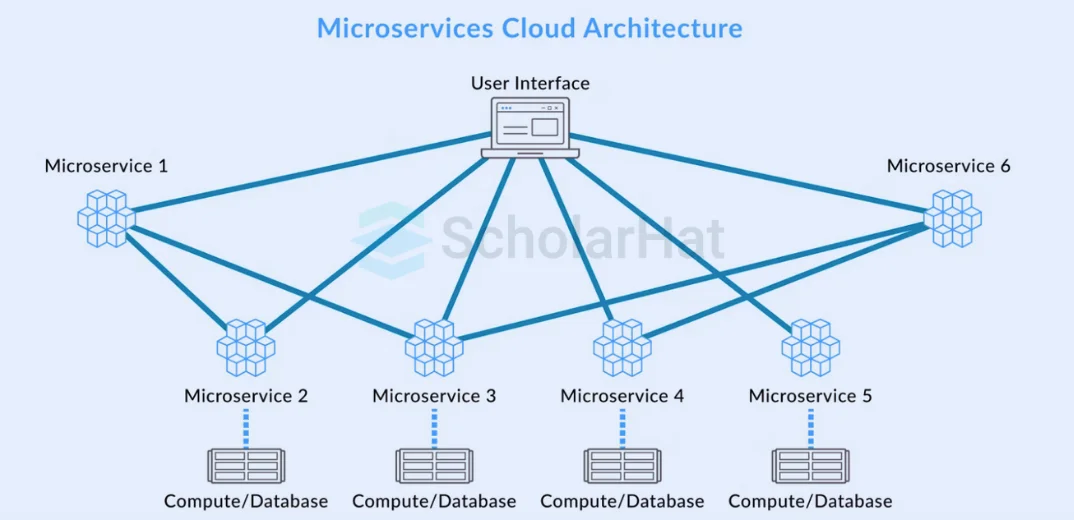
- Because each microservice runs on its own, development and deployment may be done separately.
- Individual services may be scaled in response to demand, maximizing the use of available resources.
- Depending on their unique requirements, various microservices can employ various programming languages or technologies.
- The dependability of the system is increased overall since the failure of one microservice doesn't impact the entire program.
- Smaller codebases make continuous integration and delivery
Ques-25. What is edge computing in the cloud?
By processing data closer to the point of generation (such as Internet of Things devices)rather than depending only on a centralized cloud server,edge computinglowers latency, boosts performance, and increases data handling efficiency.
Ques-26. What does Software as a Service (SaaS) stand for?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud delivery model where software applications are provided over the Internet. Users can access these applications through a web browser without needing to install or maintain them on their devices. SaaS makes it easier to use software on a subscription basis, with updates and maintenance handled by the provider.
Ques-27. What is PaaS, or platform as a service?
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model where users rent hardware and software over the internet. It provides tools for building, running, and managing applications without needing to install or maintain infrastructure. This allows developers to focus on coding rather than setup.
Ques-28. What is Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS) in cloud computing?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers basic infrastructure like servers, storage, and networking, allowing businesses to rent rather than own hardware. Users can scale resources on demand and only pay for what they use.
Ques-29. What is resource pooling architecture in cloud computing?
Resource pooling architecture in cloud computing refers to the concept of combining and allocating physical and virtual resources from multiple servers to serve multiple clients or consumers simultaneously.
- Multi-Tenancy: It allows multiple users to share resources while ensuring data isolation so each user’s data remains private and secure.
- Dynamic Allocation: Itenables real-time allocation of computing, storage, and bandwidth resources based on demand, ensuring efficient use of resources.
- Scalability: Itallows services to scale easily, ensuring that they can handle varying workloads without affecting performance.
- Flexibility: Itprovides access to a wide range of resources, enabling users to configure and customize their environments based on specific needs.
- Cost Efficiency: It minimizes idle capacity, which helps lower service costs compared to traditional models, making cloud services more affordable.
Ques-30. What does Eucalyptus mean in cloud computing?
Eucalyptus (Elastic Utility Computing Architecture for Linking Your Programs To Useful Systems) is an open-source software platform that allows users to create and manage private cloud environments. It provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) capabilities, enabling the deployment of virtual machines, storage, and networking resources in a cloud-like environment.
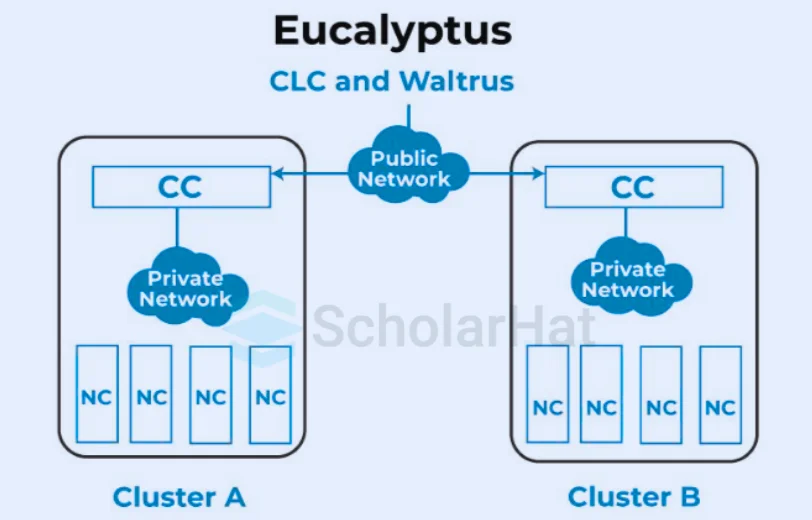
- Interoperability: Eucalyptus is designed to be compatible with Amazon Web Services (AWS), allowing users to transition between their private cloud and AWS easily.
- Flexibility: Users can customize and manage their cloud resources according to their specific needs, making it suitable for various applications and workloads.
- Scalability: The platform allows for the scaling of resources up or down based on demand, providing an elastic computing environment.
- Resource Management: Eucalyptus provides tools for monitoring, managing, and optimizing resource usage within the cloud infrastructure.
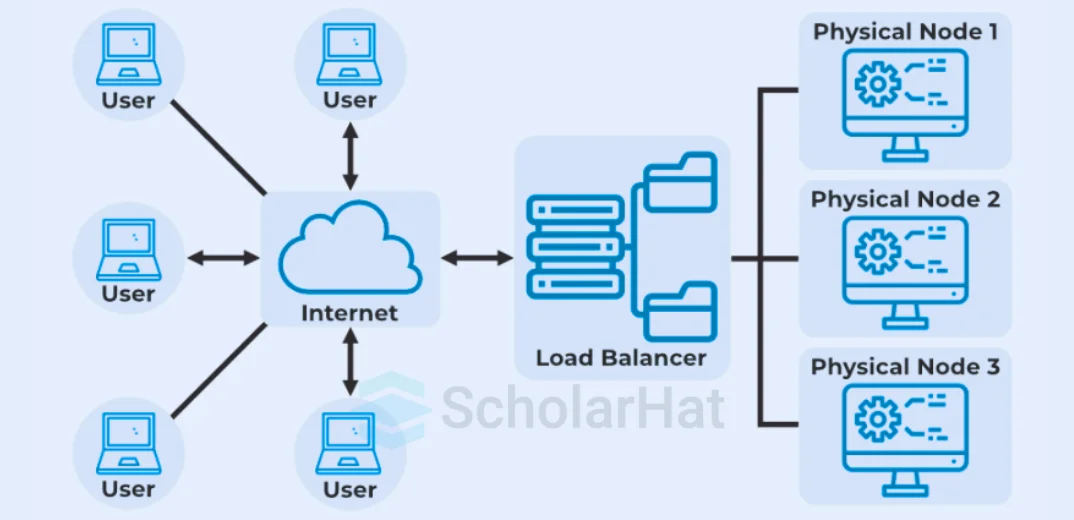
Ques-31. What is load balancing in cloud computing?
Load balancing in cloud computing is the process of distributing incoming traffic and workloads across multiple servers to optimize performance and ensure application availability. Preventing any single server from becoming overloaded enhances resource utilization and maintains responsiveness during peak usage periods.
Ques-32.What is grid computing?
Grid computing is a distributed computing model that connects multiple computers to work together on complex tasks or large data sets by pooling resources across a network. This approach enables efficient processing and analysis of large-scale problems, making it particularly useful in scientific research and simulations.
Ques-33. What is network virtualization in cloud computing
Network virtualization in cloud computing involves creating a virtualized network infrastructure that abstracts physical network components, allowing multiple virtual networks to operate on a single physical network. This approach enhances flexibility, scalability, and resource utilization while simplifying network management and improving application deployment and security.
Ques-34. On which platforms is large-scale cloud computing performed?
Large-scale cloud computing is primarily performed on platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud, which provide extensive infrastructure and services to handle vast computing tasks and data workloads efficiently.
Ques-35. What is the on-demand function in cloud computing?
The on-demand function in cloud computing allows users to instantly access and utilize resources like storage, computing power, or applications as needed without requiring manual setup or provisioning. This ensures flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, as users only pay for what they use.
Top 15 Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
Here, we will discuss the Top 15 Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced.
Ques-36. What are Cloud-native applications in cloud computing?
Cloud-native applications are designed to run specifically in cloud environments, using technologies like microservices, containers, and serverless computing for scalability, flexibility, and resilience. These apps are built to fully utilize cloud resources, making them highly efficient and adaptable to changes in demand.
- Microservices: Microservices break applications into small, independent components for easier development and scaling.
- Containers: Containers package applications with all their dependencies to ensure consistent operation across different environments.
- Serverless: Serverless computing allows developers to run applications without managing infrastructure, automatically scaling based on demand.
- Resilience: Resilience ensures applications can withstand failures and recover quickly, maintaining functionality even during issues.
Ques-37. What does "resiliency" entail in cloud computing?
Resiliency in cloud computing refers to the capability of systems or applications to quickly recover from failures and maintain continuous operations with minimal downtime. This is achieved through mechanisms like data replication, automated failover, and redundancy to ensure service availability.
- Automated Failover: Automated failover allows for seamless switching to backup systems during failures to maintain continuous service.
- Data Replication: Data replication involves copying data across multiple locations to prevent loss and ensure availability.
- Redundancy: Redundancy is the practice of having duplicate resources to ensure service continuity in case of failures.
- Disaster Recovery: Disaster recovery includes strategies to quickly restore operations after major incidents to minimize downtime and data loss.
Ques-38. What kinds of security controls are available for Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing offers several types of security controls to protect data, applications, and infrastructure. These include:
- Preventive Controls: Preventive controls include measures such as encryption, access control, and firewalls to block unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
- Detective Controls: Detective controls involve tools like intrusion detection systems, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), and audit logs to monitor and identify potential threats to the network.
- Corrective Controls: Corrective controls consist of practices such as regular backups, software patching, and incident response plans to recover from security incidents and minimize damage.
- Deterrent Controls: Deterrent controls encompass legal policies and continuous monitoring to discourage malicious activities and promote compliance with security regulations.
Ques-39. How does utility computing get used?
Utility computing is utilized in the following ways:
- On-Demand Provisioning: On-demand provisioning allows users to access computing resources as needed without making upfront hardware investments.
- Pay-As-You-Go: The pay-as-you-go model bills customers based on actual usage, promoting cost-effective budgeting.
- Scalability: Scalability enables users to scale resources up or down to match fluctuating demands easily.
- Dynamic Allocation: Dynamic allocation adjusts resources in real-time to accommodate varying workloads effectively.
- Reduced Management: Reduced management through outsourcing computing resources allows businesses to focus on core activities instead of infrastructure management.
Ques-40. What are cloud computing system integrators?
Cloud computing system integrators are organizations or professionals that specialize in combining various cloud services and technologies to create cohesive and efficient cloud-based solutions tailored to meet specific business needs.
They play a crucial role in the adoption and implementation of cloud computing by providing expertise in areas such as:
- Cloud Strategy Development: Cloud strategy development involves assessing business needs and designing a cloud plan that supports organizational goals.
- Integration of Cloud Services: Integration of cloud services connects various cloud services and on-premises systems to create a unified IT environment.
- Migration Services: Migration services help move data, applications, and workloads from on-premises environments to the cloud smoothly.
- Customization and Development: Customization and development focus on building new applications or adjusting existing software to use cloud features effectively.
- Ongoing Support and Management: Ongoing support and management provide maintenance and monitoring to ensure that cloud solutions perform well.
Ques-41. Could you provide an example of an extensive database and cloud provider?
Sure! One example of a large database is Amazon Aurora, which is a relational database service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Key Features of Amazon Aurora
- High Performance: Amazon Aurora is designed for high throughput and low latency, providing up to five times the performance of standard MySQL databases.
- Scalability: Aurora automatically scales storage up to 128 TB and can handle millions of queries per second effortlessly.
- Availability: It offers built-in replication across multiple availability zones to ensure high availability and durability.
- Compatibility: Aurora supports both MySQL and PostgreSQL, making it easy to migrate existing applications.
Ques-42. What is the difference between cloud and traditional data centers?
The differences between Cloud and traditional data centers are:
| Factors | Cloud Data Centers | Traditional Data Centers |
| Deployment | Virtualized and can be deployed quickly | Requires physical setup and installation |
| Scalability | Easily scalable on-demand | Limited by physical hardware constraints |
| Cost Model | Pay-as-you-go pricing | Fixed costs with capital expenditure |
| Maintenance | Managed by the cloud provider | Requires in-house IT staff for maintenance |
| Resource Allocation | Dynamic resource allocation | Static allocation of resources |
| Security | Shared security responsibilities with the provider | Full control over security measures |
Ques-43. How many types of data centers in the cloud do we use?
There are several types of data centers in cloud computing, each serving different needs and purposes. Here are the main types:
1. Public Data Centers
Public data centers are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers, such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. These centers share resources among multiple customers, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses.
2. Private Data Centers
Private data centers are owned and operated by a single organization, providing dedicated resources just for them. This setup enhances security and control, allowing companies to manage their data and applications more effectively.
3. Hybrid Data Centers
Hybrid data centers combine elements of both public and private data centers. They allow data and applications to be shared between the two, providing flexibility and scalability for organizations as their needs change.
4. Community Data Centers
Community data centers are shared by several organizations that have common concerns, such as compliance and security. They offer a cost-effective solution for specific communities, helping them to meet their shared requirements.
5. Edge Data Centers
Edge data centers are located closer to end-users to reduce latency and improve response times. They support applications that require real-time processing and low latency, making them ideal for IoT devices and other fast-paced services.
6. Multi-Cloud Data Centers
Multi-cloud data centers utilize resources and services from multiple cloud providers. This approach enhances flexibility and helps organizations avoid vendor lock-in, allowing them to choose the best services for their needs.
Ques-44. What is the VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the Internet. VPNs are commonly used to protect private web traffic from snooping, interference, and censorship. Here are some key features of VPNs:
- Data Encryption: VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it unreadable to unauthorized users and enhancing data security.
- Secure Remote Access: VPNs enable users to connect to a private network remotely, allowing access to resources and data securely from anywhere.
- IP Address Masking: By routing your internet connection through a VPN server, your actual IP address is hidden, providing anonymity and privacy online.
- Bypass Geolocation Restrictions: VPNs allow users to access content that may be restricted or blocked in their geographical location by connecting to servers in other regions.
- Improved Security on Public Wi-Fi: Using a VPN while connected to public Wi-Fi networks helps protect against potential security threats, such as data theft and hacking.
Ques-45. What services does the Windows Azure operating system offer?
Windows Azure (now Microsoft Azure) is a cloud computing platform offering a wide range of services, including infrastructure, platform, and software services, to build, deploy, and manage applications. It supports various programming languages, frameworks, and tools.
The key services provided are:
- Virtual Machines: Azure Virtual Machines provide scalable, on-demand computing resources that allow users to run applications and workloads in a virtualized environment.
- Azure App Services: Azure App Services is a platform for hosting web applications, RESTful APIs, and mobile backends, enabling developers to build and deploy applications quickly and easily.
- Azure SQL Database: Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service that offers high availability, scalability, and built-in intelligence for applications requiring robust data management.
- Azure Storage: Azure Storage provides secure and scalable cloud storage solutions, allowing users to store and access large amounts of data with high durability and performance.
Ques-46. What are data centers with Containerization?
Datacenters with containerization refer to modern data centers that utilize container technologies to enhance efficiency, scalability, and resource management. Containers package applications and their dependencies into lightweight, isolated units, allowing them to run consistently across different environments.
- Resource Efficiency: Containers share the host OS, reducing overhead compared to virtual machines.
- Portability: Applications can be easily moved between different environments (e.g., development, testing, production).
- Scalability: Containers can be rapidly scaled up or down based on demand.
- Isolation: Each container operates independently, ensuring stable and secure application deployment.
Ques-47. Which kinds of Data Centers have low density?
Low-density data centers are facilities designed to house fewer servers or IT equipment per square foot, prioritizing cooling efficiency, space, and ease of maintenance. These data centers generally operate with lower power consumption and heat output per rack.
- Traditional Data Centers: Traditional data centers are older facilities that typically have lower rack densities due to the use of legacy equipment or limitations in cooling technology.
- Edge Data Centers: Edge data centers are smaller facilities located closer to users, designed to handle less equipment while providing localized processing and reducing latency.
- Disaster Recovery Data Centers: Disaster recovery data centers are primarily used for backup purposes, where fewer resources are actively deployed, ensuring that data and applications can be quickly restored in case of an incident.
- Government or Institutional Data Centers: Government or institutional data centers are often built with a focus on reliability rather than density, resulting in more spread-out setups to meet stringent security and operational requirements.
Ques-48. How does Rate-Limiting work?
Rate limiting controls the amount of traffic a server or API can handle by restricting the number of requests from a client within a given time frame. It helps prevent abuse, ensures fair use, and protects the system from being overwhelmed.
The mechanisms of Rate Limiting are as follows:
- Fixed Window: The fixed window algorithm limits requests within set time intervals, such as 100 requests per minute.
- Sliding Window: The sliding window algorithm dynamically resets the request count based on the timing of the last request, providing more granularity.
- Token Bucket: In the token bucket algorithm, requests are allowed as long as tokens, representing capacity, are available and replenished at a fixed rate.
- Leaky Bucket: The leaky bucket algorithm processes requests at a steady rate, similar to the token bucket, ensuring smoother traffic flow.
Ques-49. What is encapsulation in cloud computing?
In cloud computing, encapsulation refers to the abstraction and isolation of services, data, or resources into a secure and independent "container" that hides the implementation details from the user. Encapsulation allows users to interact with cloud services through a defined interface without needing to understand the underlying infrastructure, technologies, or processes.
- Abstraction: Users access services without knowing the backend complexity.
- Security: Encapsulation helps isolate resources, protecting them from unauthorized access.
- Modularity: Components are packaged independently, improving scalability and maintenance.
- Simplicity: Encapsulation simplifies cloud service usage, allowing focus on functionality rather than implementation.
Ques-50. How does Cloud Computing Use Resource Replication?
In cloud computing, resource replication involves creating multiple copies of data, applications, or services across various physical or virtual locations to ensure high availability, fault tolerance, and load balancing. This redundancy helps the cloud infrastructure deliver reliable performance and minimizes downtime in case of failure.
Here are the several ways to use resource replication:
- Data Replication: Data replication involves storing copies of data across multiple data centers to prevent loss during failures.
- Service Replication: Service replication runs multiple instances of an application to distribute load and improve responsiveness.
- Geo-Replication: Geo-replication stores resources in different geographical locations for faster access and disaster recovery.
- Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes user requests across resources to ensure smooth performance during high demand.
| Download this PDF Now - Cloud Computing Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat |
In conclusion, we get the chance to learn about the Top 50 Cloud Computing Interview Questions for freshers, intermediate, and experienced. I hope this article will help you with your tech interview preparations. By learning this, you can enhance your conceptual ability in cloud computing. If you want to make your career in the cloud era, ScholarHat provides you with job-oriented training courses inMicrosoft Azure Cloud Architectand Azure DevOps Certification Course.
FAQs
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Account hijacking: When attackers gain control of cloud accounts.
- Insecure APIs: Vulnerabilities in APIs that connect to cloud services.
- Insider threats: Malicious actions from people within the organization.
- Cloud Storage: Refers to saving data to an off-site storage system managed by a third party (e.g., Google Drive, AWS S3).
- Cloud Computing: Involves using remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data rather than local servers or computers.
Take our Azure skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.