09
MarAn Introduction to Microsoft Azure global Infrastructure
Azure regions, geographies, and Availability Zones are the foundation of Microsoft global infrastructure which provides high availability, disaster recovery and resiliency. Azure is powering 40% of global cloud infrastructure. Don’t get left behind—enroll in our Free Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Online Training today!
Regions
Azure Region is the physical datacentre placed inside a low-latency perimeter and connected through a dedicated high-bandwidth network connection.
Microsoft Azure has more number of Global regions than any other cloud provider.
Customers can leverage Azure regions to deploy applications where they need to in a flexible manner.
Azure has in total 42 existing regions and 12 more are scheduled to appear very soon.
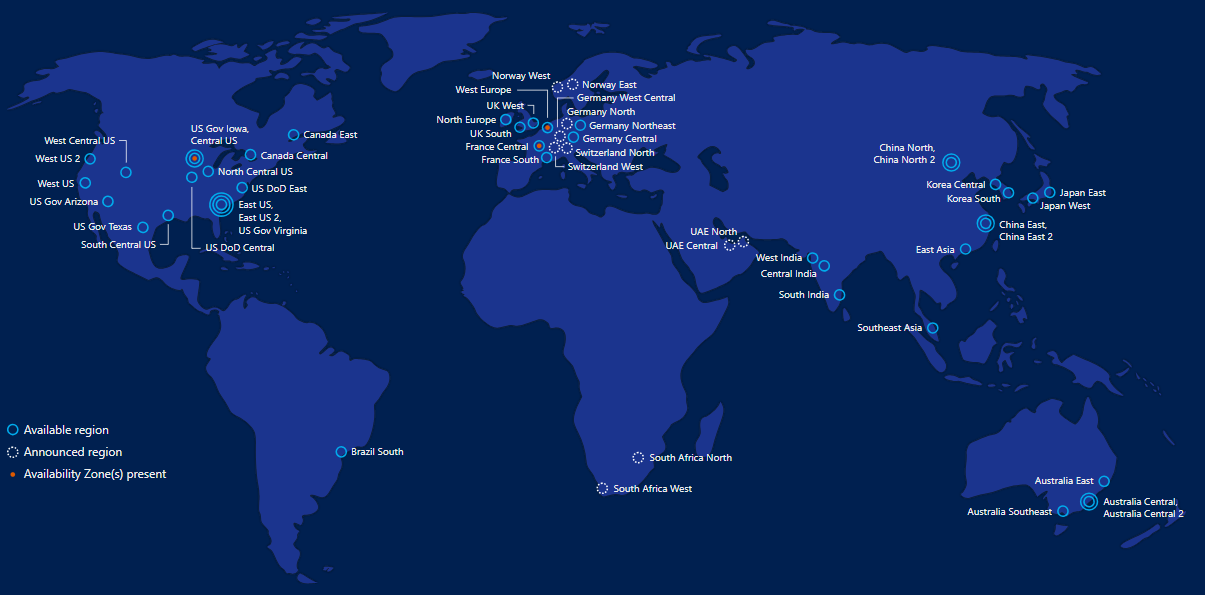
Source : https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/global-infrastructure/regions/
Geographies
A geography is a separate market, typically comprise two or more regions. Geography actually satisfies data residency and compliance requirements.
Customers can meet specific data-residency and compliance requirements to keep their data and applications in one place by using Geographies. Geographies are fault-tolerant infrastructure, to withstand a complete region failure. They are connected through Microsoft’s Azure dedicated high-capacity networking infrastructure. You need to leverage more than one existing regions in a geography to ensure no downtime with your application.
Availability Zones
Availability Zones is made up of one or more datacentre. They are equipped with independent power supply, cooling, and very low-latency network. Availability Zones offer a high-availability service that safeguards your application and database engines from any kind of fault or data centre failures.
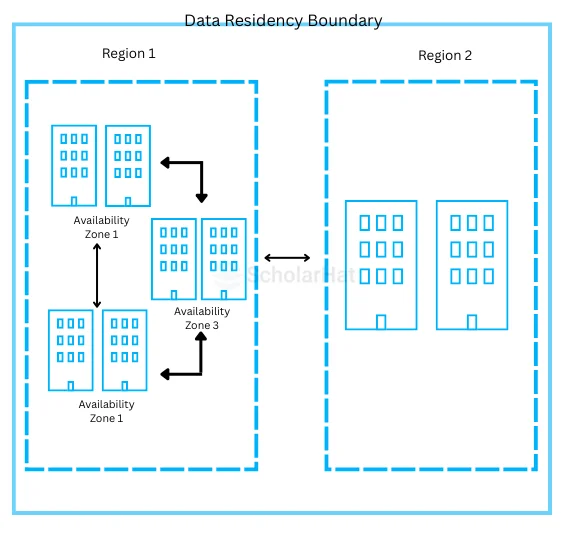
Source : https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/global-infrastructure/regions
Resilience is ensured by maintaining a minimum of three separate zones in all regions which are active. Availability zones are separated within a region which makes your applications deployed on them resistant to the single point of failure in terms of the underlying infrastructure.
Your applications and data across Availability Zones get replicated by Zone-redundant services, to protect them from a single point of failure. Because of this particular feature, Azure boasts of industry best 99.99% uptime for VMs that have two or more instances deployed across two or more Availability Zones in the same Azure region. (There is no additional price for VMs launched in Availability Zone).
Deep dive into Availability Zones
Availability zone inside a Region is created by a combination of fault domain and an update domain. Azure platform recognises your distributed infrastructure over two or more than two Availability zone and whenever you try to update them, Azure make sure that VMs in different zones are not updated at the same time to avoid any kind of downtime or latency.
Highly-available applications can be built by architecting co-locating compute, storage, networking, and data resources within a zone and replicating in other zones.
Availability Zones supporting services fall into two categories:
Zonal services
Resources pinned to a specific zone. (VMs, managed disks, IP addresses)
Zone-redundant services
Where platform replicates automatically across zones. (Storage, Databases)
Use a combination of Availability Zones with Azure region pairs. (BC)
Replicate application and data synchronously using Availability Zones within an Azure Region. (HA)
Replicate your cloud infrastructure asynchronously across Azure Regions. (DR)
Regions that support Availability Zones
Central US
France Central
East US 2
West Europe
Southeast Asia
Services that support Availability Zones
Linux VMs
Windows VMs
VM Scale Sets
Managed Disks
Load Balancer
Public IPs
Zone-redundant storage
SQL DB
Event Hubs
Service Bus
VPN Gateway
ExpressRoute
Summary
Applications architected in the manner where they take advantage of the unique features of Azure global infrastructure e.g. Regions, Geographies and Availability Zones will ensure that your applications will go to remain all the time up, highly available, compliant with local, global laws like GDPR, and with Disaster Recovery agreements. Azure provides you with all the tools, services and platform, now the onus is on you, how well you architect your applications.
In the next 3 years, 75% of developer roles will require Azure expertise. Don’t lag behind. Join our Azure Developer Course now!
Take our Azure skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.









