18
AprC Programming Assignment Operators
What is an Assignment Operator in C?
Assignment Operators in C are used to assign values to the variables. They come under the category of binary operators as they require two operands to operate upon. The left side operand is called a variable and the right side operand is the value. The value on the right side of the "=" is assigned to the variable on the left side of "=". The value on the right side must be of the same data type as the variable on the left side. Hence, the associativity is from right to left.
In this C tutorial, we'll understand the types of C programming assignment operators with examples. To delve deeper you can enroll in our C Language Free Course.
Before going in-depth about assignment operators you must know about operators in C. If you haven't visited the Operators in C tutorial, refer to Operators in C: Types of Operators.
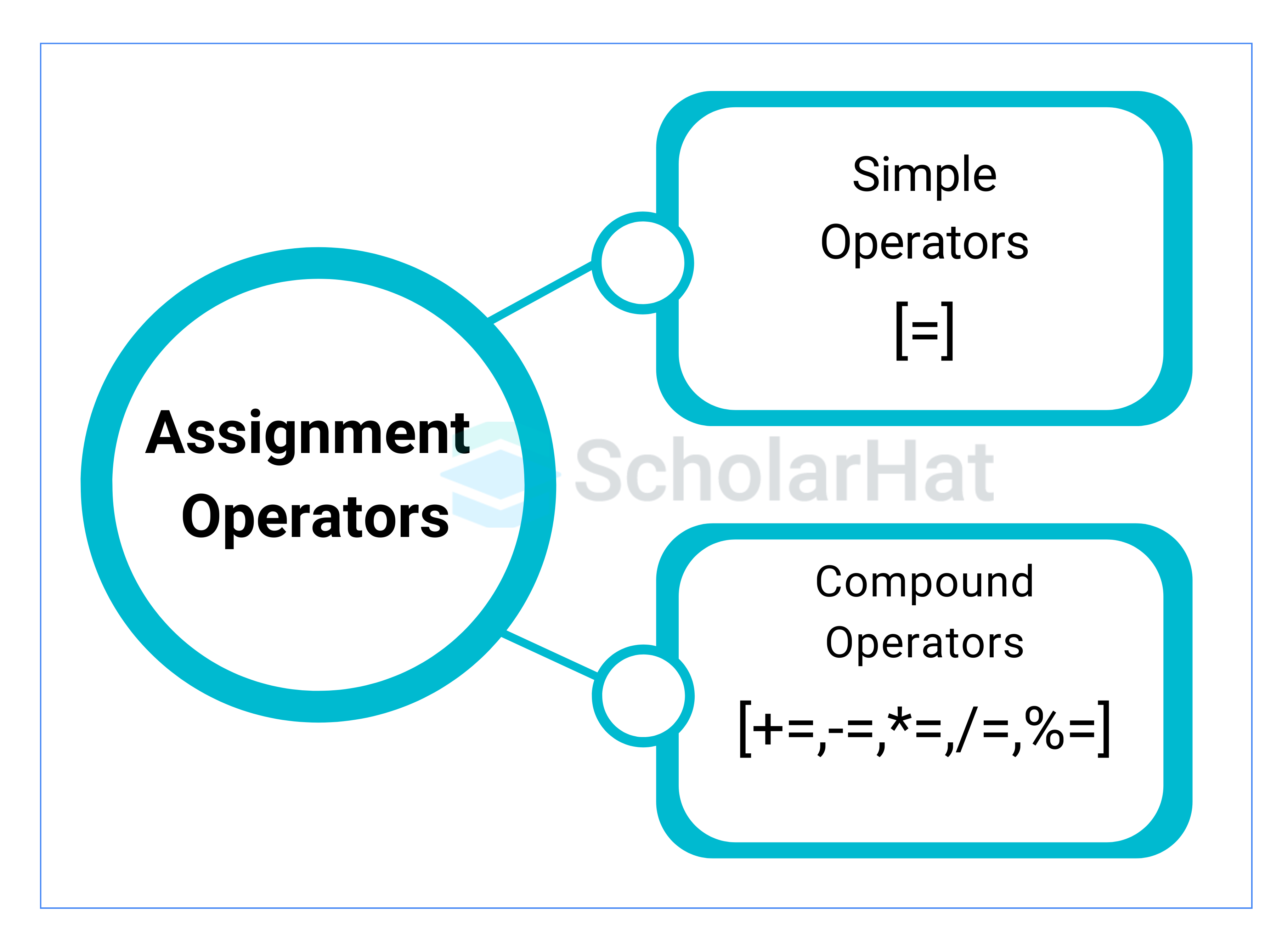
Types of Assignment Operators in C
There are two types of assignment operators in C:
| Read More: Top 50 C Interview Questions and Answers |
1. Simple Assignment Operator (=)
This assigns the value on the right-hand side (RHS) to the variable on the left-hand side (LHS). You can use a literal, another variable, or an expression in the assignment statement.
Example of Simple Assignment Operator
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x;
x = 30;
printf("The value of x is: %d\n", x);
return 0;
} In this example, we have assigned the value 30 to the variable x using the assignment operator (=).
Output
30 | Read More: Expressions in C Programming - Types of Expressions in C ( With Examples ) |
2. Compound Assignment Operators
In addition to the = operator, you can combine arithmetic and bitwise operators with the = symbol to form an augmented or compound assignment operator.
There are five combinations of arithmetic operators with the assignment operator, "=". Let's look at them one by one.
| Operator | Operator Name | Description |
| += | addition assignment | It adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| -= | subtraction assignment | It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| *= | multiplication assignment | It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand |
| /= | division assignment | It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| %= | modulo assignment | It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. |
Example of Augmented Arithmetic and Assignment Operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 20;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
a += 20;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
a -= 20;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
a *= 20;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
a /= 20;
printf("Value of a is %d\n", a);
return 0;
} Output
Value of a is 20
Value of a is 40
Value of a is 20
Value of a is 400
Value of a is 20 There can be five combinations of bitwise operators with the assignment operator, "=". Let's look at them one by one.
| Read More: Bitwise Operators in C: AND, OR, XOR, Shift & Complement |
| Operator | Operator Name | Description |
| &= | bitwise AND assignment | It performs the bitwise AND operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| |= | bitwise OR assignment | It performs the bitwise OR operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| ^= | bitwise XOR assignment | It performs the bitwise XOR operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| <<= | bitwise left shift assignment | Shifts the bits of the variable to the left by the value on the right |
| >>= | bitwise right shift assignment | Shifts the bits of the variable to the right by the value on the right |
Example of Augmented Bitwise and Assignment Operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x=2, y=10;
y <<= x;
printf("Value of y is %d\n", y);
y %= x;
printf("Value of y is %d\n", y);
y &= x;
printf("Value of y is %d\n", y);
y >>= x;
printf("Value of y is %d\n", y);
y |= x;
printf("Value of y is %d\n", y);
y ^= x;
printf("Value of y is %d\n", y);
return 0;
}
Output
Value of y is 40
Value of y is 0
Value of y is 0
Value of y is 0
Value of y is 2
Value of y is 0
Practice Problems on Assignment Operators in C
1. What will the value of "x" be after the execution of the following code?
int x = 50;
x += 5;
x -= 3;
The correct answer is 52. x starts at 50, increases by 5 to 55, then decreases by 3 to 52.
2. After executing the following code, what is the value of the number variable?
int number = 73;
number >>= 1;
number <<= 2;
The correct answer is 144. After right-shifting 73 (binary 1001001) by one and then left-shifting the result by two, the value becomes 144 (binary 10010000).
Benefits of Using Assignment Operators
- Simplifies Code: For example, x += 1 is shorter and clearer than x = x + 1.
- Reduces Errors: They break complex expressions into simpler, more manageable parts thus reducing errors.
- Improves Readability: They make the code easier to read and understand by succinctly expressing common operations.
- Enhances Performance: They often operate in place, potentially reducing the need for additional memory or temporary variables.
Best Practices and Tips for Using the Assignment Operator
- Use Compound Assignment Operators for Clarity and Efficiency
While performing arithmetic operations with the same variable, use compound assignment operators
x += 5; // Clear and concise compared to x = x + 5; - Initialize Variables When Declaring
int count = 0; // Initialization - Avoid Complex Expressions in Assignments
a = (b + c) * (d - e); // Consider breaking it down: int temp = b + c; a = temp * (d - e); - Avoid Multiple Assignments in a Single Statement
// Instead of this a = b = c = 0; // Do this a = 0; b = 0; c = 0; - Consistent Formatting
int result = 0; result += 10; - Use Parentheses for Clarity
When mixing assignments with other operations, use parentheses to ensure the correct order of evaluation.
Example
x = (y + z) * w;






