26
DecLoop in C with Examples: For, While, Do..While Loops
Loop in C: An Overview
Are you interested in programming but don't know where to start? Have you ever heard the term loop? Looping is one of the key concepts behind programming, and learning how to use Loop in C can open up a new world of code. Gain the foundational skills from this C tutorial and move to the advanced C Language Free Course thatincludes in-depth coverage of loop and other essential programming concepts.
Read More - Top 50 C Interview Questions and Answers
What are Loop in C?
Loops are a block of code that executes itself until the specified condition becomes false. In this section, we will look in detail at the types of loops used in C programming.
What is the Need for Looping Statements in C?
Here are some uses of loops in C:
- Loops allow the user to execute the same set of statements repeatedly without writing the same code multiple times.
- It saves time and effort and increases the efficiency.
- It reduces the chance of getting errors during compilation.
- Loop makes the code readable and easier to understand, especially when dealing with complex logic or large data sets.
- It promotes code reusability.
- Loops help traverse data structures like arrays or linked lists
Types of Loop in C
Let’s get into the three types of loops used in C programming.forloopwhileloopdo whileloop
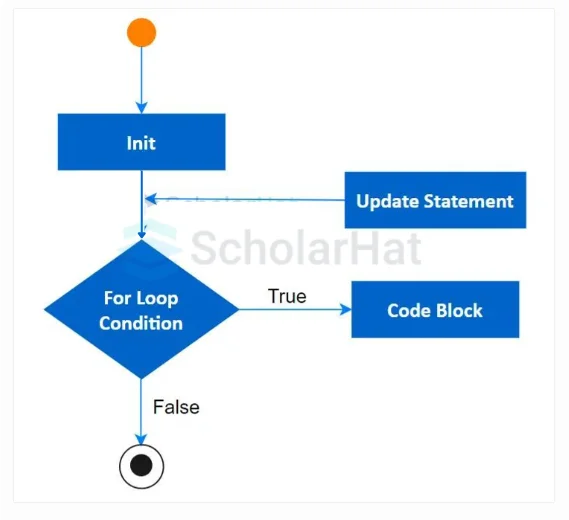
A for loop is a control structure that enables a set of instructions to get executed for a specified number of iterations. It is an entry-controlled loop.
for loop Flowchart
Syntax
for(initialization; test condition; update expression){
//code to be executed
}
- Here, the
initializationstatement is executed first and only once. - The
test conditionis checked, iffalsethe loop terminates - If the test condition is
true, the body of the loop executes - The
update expressiongets updated - Again the
test conditionis evaluated - The process repeats until the
test conditionbecomesfalse.
Example: For loop in C Compiler
// Program to print numbers from 1 to 10
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", i+1);
}
return 0;
}
The above code prints the numbers from 1 to 10 using a for loop in C.
- We know it will take 10 iterations to print 10 numbers so, we have used the
forloop. iis initialized to 0.- The condition
i<10will be checked. It istrue, thereforei+1i.e. 1 gets printed. - Then
iincrements to 1 again the condition,i<10is evaluated. - The process will repeat until
ibecome 10.
Output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
It repeatedly carries out a series of instructions till a condition is true. It is an entry-controlled loop. The
while loop in C is used when we don’t know the number of iterations.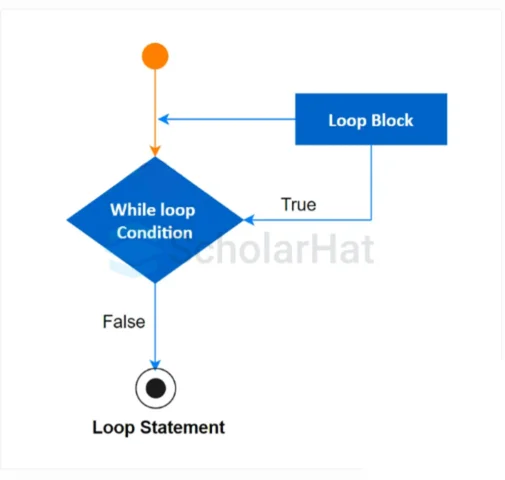
Syntax
while(test condition){
//code to be executed
}
If the test condition inside the () becomes true, the body of the loop executes else loop terminates without execution. The process repeats until the test condition becomes false.
Example: while loop in C
// Print numbers from 1 to 10
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
printf("%d\n", i);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
- In the above code,
iis initialized to 1 before the start of the loop. - The
test condition,i<=10is evaluated. Iftrue, the body of the loop executes. - If the condition becomes
falsein the beginning itself, the program control does not even enter the loop once. - The loop executes until
ibecomes 10.
Output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
It is an exit-controlled loop. It prints the output at least once before checking the condition. Afterwards, the condition is checked and the execution of the loop begins.
Syntax
do{
//code to be executed
}while(test condition);
- The body of the loop executes before checking the condition.
- If the
test conditionistrue, the loop body executes again. - Again the
test conditionis evaluated. - The process repeats until the
test conditionbecomesfalse.
Example: do...while loop in C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
do {
printf("%d\n", i+1);
i++;
}
while (i < 10);
return 0;
}
- The above code prints numbers from 1 to 10 using the
do whileloop in C. - It prints 1 before checking if
iless than 10. - It checks the condition
i<10and executes untilibecomes 10
Output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10










