06
FebHow to Write Your First C++ Program: Detailed Explanation
First C++ Program and its Syntax: An Overview
C++ is a versatile and strong programming language that has been present for decades, powering everything from video games to operating systems.But wait, where do you even begin? Do not worry. Developing your first Hello World in C++ program is easier than you think. Let us take it one step at a time.Writing Your First C++ Program in Steps.
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
- A C++ Compiler:Other examples include GCC, Clang, or MSVC. IDEs like Code::Blocks, Dev-C++, or Visual Studio are great options as they include a compiler.
- A Text Editor or IDE: Tools like Visual Studio Code or JetBrains CLion work well for writing and debugging C++ code.
Steps to Write Your First C++ Program
1. Create a New File
Open your IDE or text editor and create a new file. Save it with the extension .cpp (e.g., hello_world.cpp).
2. Write the Code
Here’s a simple C++ program that prints "Hello, World!" to the console:
#include <iostream>
// The main function: Entry point of the program
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; // Print message to the console
return 0; // Indicate that the program ended successfully
}Explanation:
#include <iostream>: Includes the library to use input and output features likestd::cout.int main(): The starting point of every C++ program.std::cout: Used to print output to the console.<<: The insertion operator, directs data tostd::cout.std::endl: Ends the line and flushes the output buffer.return 0: Indicates that the program was executed successfully.
3. Compile the Program
Using a Command Line (GCC Example):
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Navigate to the directory containing your file (
hello_world.cpp). - Compile the program using:
g++ hello_world.cpp -o hello_world
This generates an executable file named hello_world.
In an IDE: Click on the Build or Compile button. The IDE will handle the compilation process for you.
4. Run the Program
Using the Command Line:
./hello_worldIn an IDE: Click on the Run button, and the program output will appear in the console window of the IDE.
Expected Output
Hello, World!Begin your 1st C++ Program
- Again, Open any text editor or IDE and create a new file with any name and a .cpp extension. e.g. HelloWorld.cpp
- Open the file and enter the below code in the C++ Compiler:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello, World!" << endl; return 0; } - Compile and run the code
Output
Hello, World!- With the help of
cout, our program printed the sentence “Hello world” on the screen. There can be as manycoutstatements as you want in your program.#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "Hello, World!" << endl; cout << "This is my first program" << endl; return 0; }Output
Hello, World! This is my first program - The
endlmanipulator is used to insert a new line. That's why each output is displayed in a new line. - The
<<operator can be used more than once if we want to print different variables, strings, and so on in a single statement. return 0indicates the end of themain()function.- The closing curly bracket
}is used to end themain()function. - Have you noticed
;after each line of code in themain()function? It is necessary to put it after each line of code. In C++ every line ends with a;. If you forget to put a;, it will show you a compile-time error. - C++ ignores white spaces but we use it to make the code more readable.
User Input in C++
In C++,cin takes formatted input from standard input devices such as the keyboard. The cin object is used along with the extraction operator, >> for taking input.Example of User Input in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
cout << "Enter a number: ";
cin >> a; // Taking input
cout << "The number is: " << a;
return 0;
}
The above C++ code is usedcin to take an integer input from the user. The input is stored in the variable a.
You will see variables and data types in the upcoming tutorials, Variables in C++ Programming and Data Types in C++
Output
Enter a number: 85
The number is: 85
- You can even use
std::cininstead of cin if you don't want to use the statement,using namespace std;.#include <iostream> int main() { int a; std::cout << "Enter a number: "; std::cin >> a; // Taking input std::cout << "The number is: " << a; return 0; } - You can even take multiple inputs using a single
cinstatement#include <iostream> int main() { int a, b; std::cout << "Enter two numbers: "; std::cin >> a >> b; // Taking inputs std::cout << "The numbers are: " << a << "," << b; return 0; }
Output
Enter two numbers: 10 20
The numbers are: 10, 20
Top 5 Programs to Practice C++ As a Fresher
1. Program to Add Two Numbers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num1, num2, sum;
cout << "Enter the first number: ";
cin >> num1;
cout << "Enter the second number: ";
cin >> num2;
sum = num1 + num2;
cout << "The sum of " << num1 << " and " << num2 << " is " << sum << "." << endl;
return 0;
}Sample Output
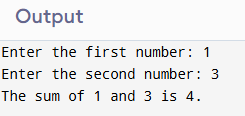
2. Program to Swap Two Numbers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b, temp;
cout << "Enter the first number: ";
cin >> a;
cout << "Enter the second number: ";
cin >> b;
// Swapping using a temporary variable
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "After swapping, first number: " << a << ", second number: " << b << endl;
return 0;
}
Sample Output
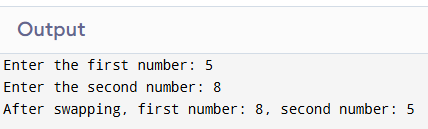
3. Program to Check Whether a Number is Even or Odd
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> num;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
cout << num << " is even." << endl;
} else {
cout << num << " is odd." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Sample Output
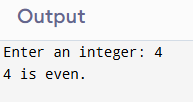
4. Program to Calculate the Sum of Natural Numbers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, sum = 0;
cout << "Enter a positive integer: ";
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
sum += i; // Add current number to the sum
}
cout << "The sum of the first " << n << " natural numbers is " << sum << "." << endl;
return 0;
}Sample Output
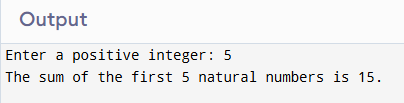
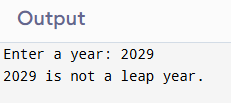
5. Program to Check Leap Year
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int year;
cout << "Enter a year: ";
cin >> year;
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) {
cout << year << " is a leap year." << endl;
} else {
cout << year << " is not a leap year." << endl;
}
return 0;
}Sample Output
Summary
After getting through this article you must have at least got an idea to write a basic C++ program. You'll learn all the concepts of coding in C++ in the upcoming tutorials. For more practice try various simple programs in CPP for that Just follow this tutorial in a sequence. If you want to deepen your understanding of C++ programming skills, consider enrolling in our C++ Certification.FAQs
This line outputs the text Hello, World! to the console. Here’s how it works:
- std::cout: Refers to the standard output stream.
- <<: The insertion operator, used to direct data to std::cout.
- "Hello, World!": The message to be displayed.
- std::endl: Ends the current line and flushes the output buffer, ensuring the text is displayed immediately.










