15
MarTypes of Inheritance in C++ with Examples
Types of Inheritance in C++: Overview
In the previous C++ tutorial, we saw the basics of Inheritance in C++. Now, we will move a step forward in our journey of learning OOP concepts in C++ and look at types of inheritance in C++. They constitute an important aspect ofinheritance. For more information, check our C++ Online Course Free.Types of Inheritance in C++
C++ supports the following five types of inheritance:Single inheritanceMultipleinheritanceMultilevel inheritanceHierarchical inheritanceHybrid inheritance
Single Inheritance in C++
When a child/derived class inherits only one base/parent class, it is called asingle inheritance.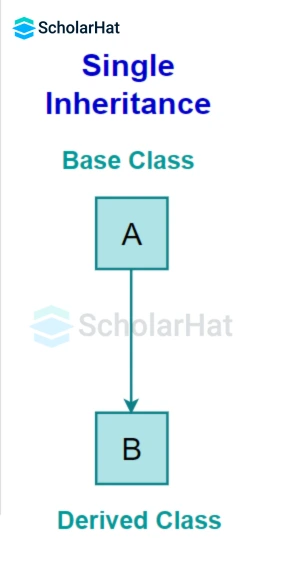
Example to demonstrate single inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle
{
public:
int speed;
void StartEngine()
{
cout << "Engine started." << endl;
}
};
class Car : public Vehicle
{
public:
void Accelerate()
{
cout << "Car is accelerating." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Car myCar; // object of the Car class
myCar.speed = 60; // member of the base class
myCar.StartEngine(); // member function of the base class
myCar.Accelerate(); // member function of the derived class
return 0;
}
Here, the derived class Car inherits a single base class i.e. Vehicle.
Output
Engine started.
Car is accelerating.
Read More - C++ Interview Questions Interview Questions for Freshers
Multiple Inheritance in C++
When a child/derived class inherits from more than one base/parent class, it is calledmultiple inheritance.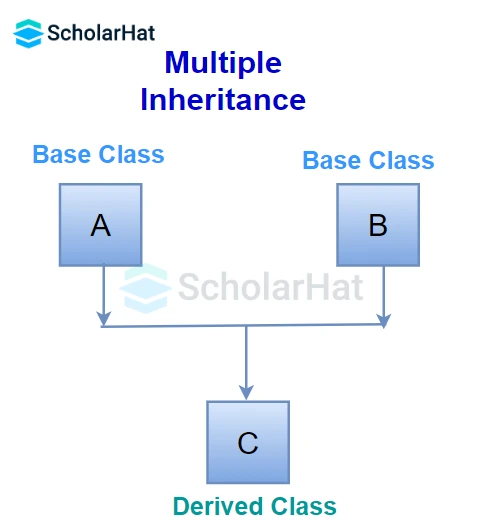
Example to demonstrate multiple inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Birds {
public:
Birds() {
cout << "Birds are of two types" << endl;
}
};
class Oviparous {
public:
Oviparous() {
cout << "Oviparous birds lay eggs." << endl;
}
};
class Sparrow: public Birds, public Oviparous {
public:
void display() {
cout << "I am a sparrow." << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Sparrow h1;
h1.display();
return 0;
}
Here the class Sparrow is derived from base classes Birds and Oviparous. It makes sense because Sparrow is a bird as well as oviparous.
Output
Birds are of two types
Oviparous birds lay eggs.
- Ambiguity in Multiple Inheritance: Suppose, two base classes have the same function. When you call that function using the object of the derived class, the compiler shows an error. It's because the compiler doesn't know which function to call.
Example
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class base1 { public: void display() { cout << "Class base1" << endl; } }; class base2 { public: void display() { cout << "Class base2" << endl; } }; class derived : public base1, public base2 { void view() { display(); } }; int main() { derived d; d.display(); return 0; }Here the method
display()is defined in both base classes,base1andbase2. The derived class methodview()contains the function call todisplay()method. When the objectdof the derived class calls thedisplay()method, the compiler gets confused about whichdisplay()to call, thebase1class or thebase2class. Thus, it throws an error.Output
error: reference to 'display' is ambiguous display();This ambiguity could be resolved in two ways
- using the scope resolution operator
::. In the above example, it can be resolved in two waysclass derived : public base1, public base2 { void view() { base1::display(); // Calling the display() function of class base1 base2::display(); // Calling the display() function of class base2 } };int main() { d.base1::display(); // Function of base1 class is called d.base2::display(); // Function of base2 class is called. }
- The above error would not have occurred if the
display()method had been defined in the derived class as well. In other words, if thedisplay()method had been overridden in the derived class. We will understand this in the Polymorphism in C++ and C++ Function Overriding tutorial.
- using the scope resolution operator
Multilevel Inheritance in C++
When one base class is inherited by a derived class which is further inherited by any other derived class, it is known as multilevel inheritance. Here, a derived class becomes the base class of another derived class. In the end, the last derived class acquires all the members of all its base classes.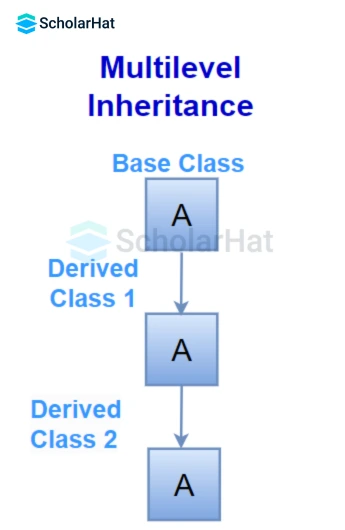
Example to demonstrate multilevel inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class base
{
public:
void display()
{
cout << "Class base1" << endl;
}
};
class derived1 : public base
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "This is the 1st derived class" << endl;
}
};
class derived2: public derived1
{
void view()
{
cout << "This is the 2nd derived class" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
derived2 d;
d.display();
d.print();
d.view();
return 0;
} Here, class derived1 is inheriting the class, base which is further inherited by the derived2 class. The object d of the derived2 class accesses all the methods of the base classes, base and derived1.
Output
Class base1
This is the 1st derived class
This is the 2nd derived class
Hierarchical Inheritance in C++
If more than one derived class inherits a single base class, a hierarchy of base classes is formed and so it is known as hierarchical inheritance.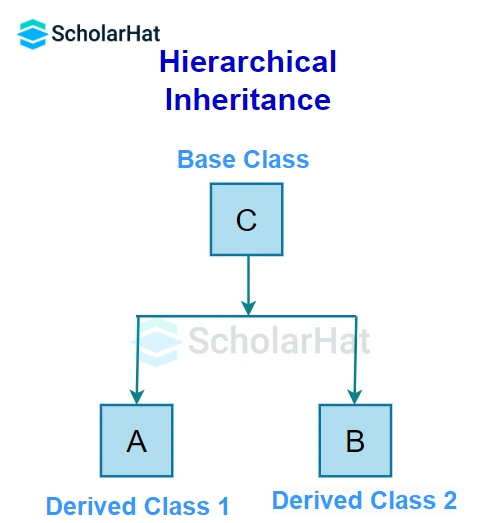
Example to demonstrate hierarchical inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Birds {
public:
void type() {
cout << "I'm an oviparous bird" << endl;
}
};
class pigeon: public Birds{
public:
void name1() {
cout << "I am a pigeon." << endl;
}
};
class Sparrow: public Birds {
public:
void name2() {
cout << "I am a sparrow." << endl;
}
};
int main() {
pigeon p; // object of pigeon class
cout << "\npigeon Class:" << endl;
p.type(); // base class method
p.name1();
Sparrow h; // object of Sparrow class
cout << "\nSparrow Class:" << endl;
h.type(); // base class method
h.name2();
return 0;
} Here, both the pigeon and Sparrow classes are derived from the Birds class. As such, both the derived classes can access the type() function belonging to the Birds class.
Output
pigeon Class:
I'm an oviparous bird
I am a pigeon.
Sparrow Class:
I'm an oviparous bird
I am a sparrow.
Hybrid Inheritance in C++
It is the combination of more than one type of inheritance i.e hybrid variety of inheritance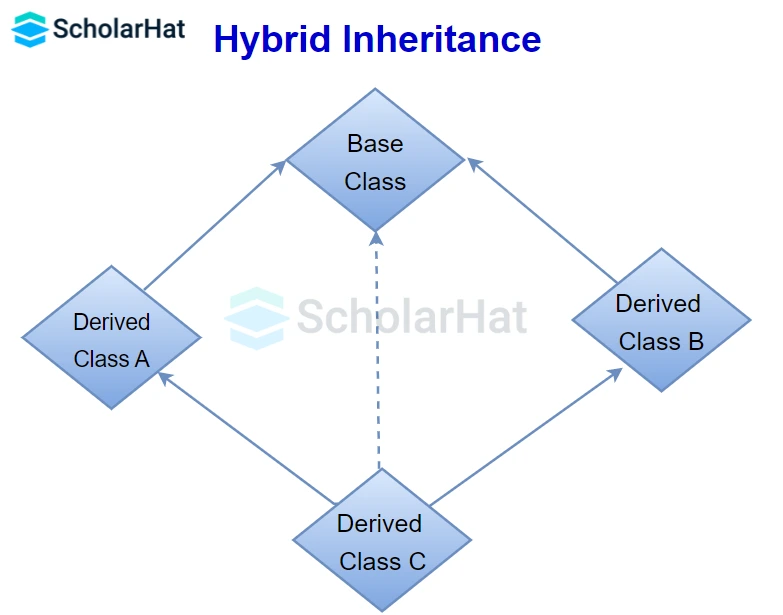
Example to demonstrate hybrid inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Birds {
public:
Birds() {
cout << "Birds are of two types" << endl;
}
};
class Oviparous : public Birds {
public:
Oviparous() {
cout << "Oviparous birds lay eggs." << endl;
}
};
class Sparrow {
public:
void name2() {
cout << "I am a sparrow." << endl;
}
};
class HybridSparrow : public Oviparous, public Sparrow {
public:
void display() {
name2();
cout << "HybridSparrow class is a combination of Oviparous and Sparrow." << endl;
}
};
int main() {
HybridSparrow h1;
h1.display();
return 0;
}
- In the above code, class
Oviparousinherits from classBirds. This is a single inheritance. - The class
HybridSparrowinherits from both classOviparousand classSparrow. This is multiple inheritance. - The
Oviparousclass inheritsBirdsclass which is further inherited by theHybridSparrowclass. This is a multilevel inheritance.
Output
Birds are of two types
Oviparous birds lay eggs.
I am a sparrow.
HybridSparrow class is a combination of Oviparous and Sparrow.
Summary
Here, we have completed all types of inheritances in C++. Go through the article very sincerely to understand each type in detail. For more information, check our C++ Certification course.The average React.js developer earns ₹15–25 LPA, but seniors earn more. Don’t wait—Enroll in our Reactjs Certification Course and unlock top-tier roles!










