13
MarSwitch Statement in C++: Implementation with Examples
Switch Statement in C++: An Overview
Are you a software programmer looking for an easy way to make decisions in your programs? Look no further than Learn C++ and discover the power ofswitch statement one of the most basic decision-making tools in C++. In this article, we'll explore what makes switch statements so versatile and practical, from how they're set up to how they can be used effectively. Enhance your C++ programming skills and master switch statements with a Free C++ Course With Certificate.
Switch Statement in C++
In the previous, conditional statements in C++ tutorial, we saw the if else-if ladder to check multiple conditions if one or the other fails. The switch statement serves as an alternative to the if else-if ladder. It checks multiple cases for different values of a single variable.
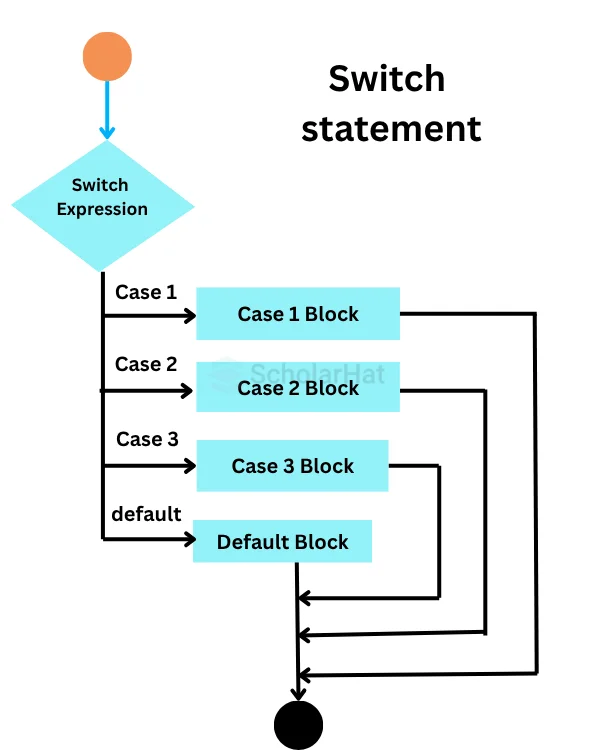
Switch Statement Syntax
switch(expression){
case value1:
//code to be executed;
break; //optional
case value2:
//code to be executed;
break; //optional
......
default:
code to be executed if all cases are not matched;
}
The working of the switch statement goes like this
- It starts with the keyword,
switchfollowed by a set of()containing anexpression. - The expression is evaluated once and compared with the values of each
case. - If any
casematches, the correspondingcasestatement executes. - After the execution of the matching
casestatement, the control comes out of theswitchstatement due to thebreakkeyword. - If no
casematches, thedefaultstatement, if present, gets executed.
Read More - C++ Interview Interview Questions and Answers
Rules for the switch statement in C++
- The
data typeof theswitch expressionmust be of anintegerorcharacter. - All the
case labelsmust be followed by a colon “:”. - The
casevalue must be anintegerorcharacterconstant. - The
breakkeyword is optional, but it can decrease the execution time of your program. It will stop the unnecessary execution of other cases after a match is found.
Note: We will learn thebreak statement in detail in the section, break statement in C++.
Example to demonstrate switch statement in C++ Compiler
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int num;
cout<<"Enter a number:";
cin>>num;
switch (num)
{
case 20:
cout<<"It is 20";
break;
case 30:
cout<<"It is 30";
break;
case 40:
cout<<"It is 40";
break;
default:
cout<<"Not 20, 30 or 40";
}
return 0;
}
The above code checks if the input number, num is 20 or is it 30 or is it 40. If none of the given numbers exist, the default statement gets printed.
Output 1
Enter a number:
20
It is 20
Output 2
Enter a number:
68
Not 20, 30 or 40
Nested Switch Case in C++
There can be several switch statements inside a switch statement. These are called nested switch statements.
Syntax
switch (expression1)
{
case value1:
// Code block for value1
switch (expression2)
{
case valueA:
// Code block for valueA
break;
case valueB:
// Code block for valueB
break;
// More cases for expression2
}
break;
case value2:
// Code block for value2
break;
// More cases for expression1
default:
// Default code block for expression1
}
Example to demonstrate Nested switch case In C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i = 10;
int j = 20;
switch (i) {
case 10:
cout << "the value of i evaluated in outer switch: " << i << endl;
case 20:
switch (j) {
case 20:
cout << "The value of j evaluated in nested switch: " << j << endl;
}
}
cout << "Exact value of i is : " << i << endl;
cout << "Exact value of j is : " << j << endl;
return 0;
} - In the above code, the outer
switchstatement checks the value ofi. - The value of
imatches with thecase 10. So, the corresponding statement gets printed. - Since there's no
breakstatement, it continues to execute the code in the subsequentcase 20block. - Inside the
case 20block, there is anested switchstatement that checks the value ofj. - The value of
jmatches withcase 20in thenested switchblock. So, the corresponding statement gets printed.
Output
the value of i evaluated in the outer switch: 10
The value of j evaluated in nested switch: 20
Exact value of i is : 10
Exact value of j is : 20
Summary
Switch statements in C++ provide a useful alternative to the traditional if statement for making decisions within your code. The syntax of the switch statement is much easier to learn than that of the if...else statement, making it perfect for even novice programmers. As you continue learning about the intricacies of switch statements in C++, remember the tremendous power it gives you not only to control what is inside your program’s box of instructions but also how best to apply those instructions for maximum results.
React.js is powering apps like Netflix and Instagram. Don’t miss out—join our React JS online course and build world-class projects!










