18
AprData Structures Sorting: Types and Examples Explained
Sorting in Data Structures
Sorting is a fundamental operation in data structures. It organizes data and optimizes search operations. We have already learned about searching in data structures. We saw that if the data is sorted, it becomes easy to find the required element. So, learning about sorting in data structures can be easy for you while programming.In this DSA tutorial, we are going to understand sorting such as What is Sorting in Data Structures, various types of sorting in data structuresbubble sort, heap sort, selection sort, etc.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of sorting algorithms and their real-world applications, consider enrolling in a Data Structures and Algorithms Course. This course will provide you with expert insights, hands-on practice, and the knowledge required to master DSA concepts and excel in technical interviews.
What is a Sorting in Data Structures?
In simple words, Sorting refers to arranging data in a particular format. Sorting algorithms in data structures refer to the methods used to arrange data in a particular order mostly in numerical or lexicographical order.When we have a large amount of data, it can be difficult to deal with it, especially when it is arranged randomly. In such cases, sorting becomes crucial. It is necessary to sort data to make searching easier. Sorting algorithms can help in organizing data to make it more accessible to work with and even speed up processing times for larger amounts of data.
Types of Sorting Algorithms in Data Structures
- In-place Sorting and Not-in-place Sorting
- Stable and Unstable Sorting Algorithm
- Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Sorting Algorithm
- Comparison and Non-Comparison-based Sorting Algorithm
1. In-place Sorting and Not-in-place Sorting
In-place SortingThese algorithms rearrange the elements within the array being sorted, without using any additional space or memory. In other words, the algorithm operates directly on the input array, modifying its content in place. In-place sorting again has different types as shown in the below figure.
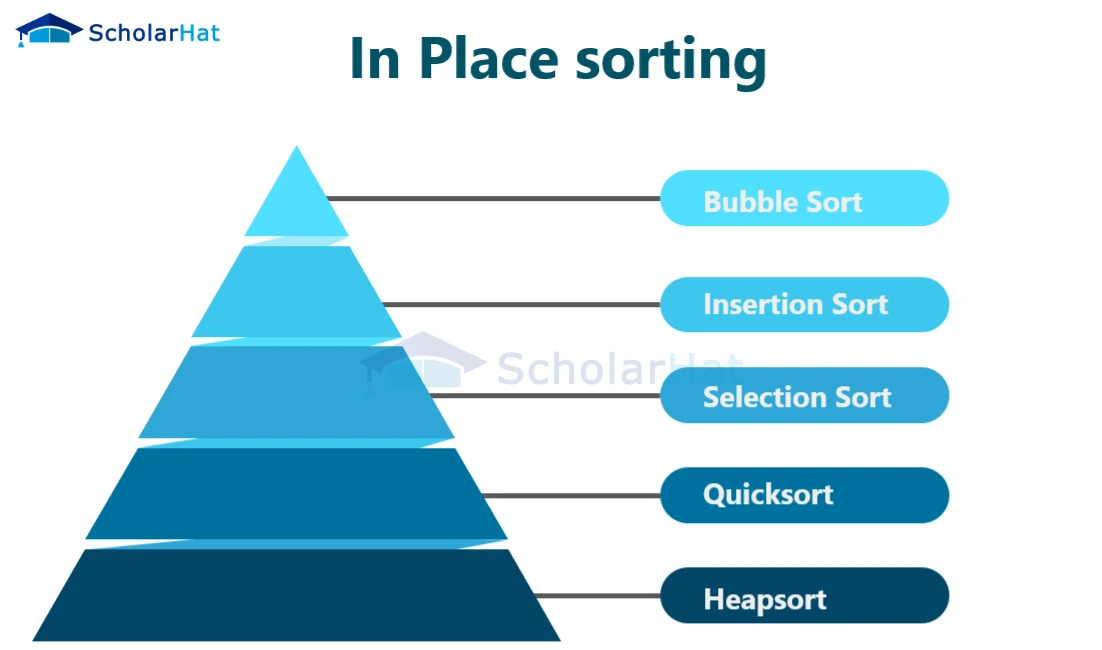
1. Bubble Sort
- Bubble Sort is the easiest and the fundamental sorting algorithm in data structures.
- It works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order.
- Until the entire list is sorted, Bubble Sort iteratively goes through the list, compares nearby elements, and swaps them if they are out of order.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Bubble Sort in Data Structures. |
2. Insertion Sort
- Insertion sort is a sorting algorithm in which the unsorted elements are transferred one at a time to the right position.
- It inserts each element of the array into its proper place.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Insertion Sort in Data Structures |
3. Selection Sort
- It repeatedly locates the smallest element in the array's unsorted portion and inserts it at the start.
- Until the full array is sorted, this is done.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Selection Sort in Data Structures |
4. Quick Sort
- Quick Sort is a divide-and-conquer method that divides an array into two sub-arrays, one with elements fewer than the pivot and one with elements more than the pivot.
- It operates by choosing a "pivot" element.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Quick Sort in Data Structures |
5. Heap Sort
- In Heap sort, The input array is initially transformed into a binary heap data structure by heap sort.
- The greatest element from the heap, which is always at the root, is then continually removed, and the heap is rebuilt until the array is sorted.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Heap Sort in Data Structures |
Not-in-place Sorting
These algorithms require space that is more than or equal to the elements being sorted to store intermediate results. Common examples of not-in-place sorting algorithms include:
1. Merge Sort
- A Merge sort is a divide-and-conquer technique.
- It separates the input array into smaller sub-arrays sorts them and then combines the sorted sub-arrays to create a final sorted array.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Merge Sort in Data Structures. |
2. Counting sort
- Counting Sort is a quick and effective sorting algorithm that doesn't rely on comparisons to arrange numbers in a particular range.
- In order to ascertain each element's location in the sorted output, it counts the instances of each distinct element.
- This method, which offers linear time complexity, (O(n + k)), where (n) is the number of elements and (k) is the range of the input values, can be especially useful when the range of values is not appreciably more than the number of elements.
| Read More: Counting Soft In DSA |
3. Radix Sort
- Integers are sorted using the non-comparative Radix Sort algorithm, which groups digits by their place value and sorts them from least to most significant.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Radix Sort in Data Structures. |
4. Bucket Sort
- It divides the input array into a defined number of buckets, distributes the items across the buckets, sorts each bucket, and then concatenates the sorted buckets to get the sorted array.
- We'll see this algorithm in detail in the section,
| Read More: Bucket Sort in Data Structures. |
Read More - Data Structure Interview Questions for Freshers
- Stable and Unstable Sorting Algorithm
- Stable Sorting Algorithm
It maintains the relative order of elements with equal values in the original data set i.e. if two elements have the same value, the algorithm will sort them in the same order as they appear in the original data set. Some examples of stable sorting algorithms are Merge Sort, Insertion Sort, and Tim Sort.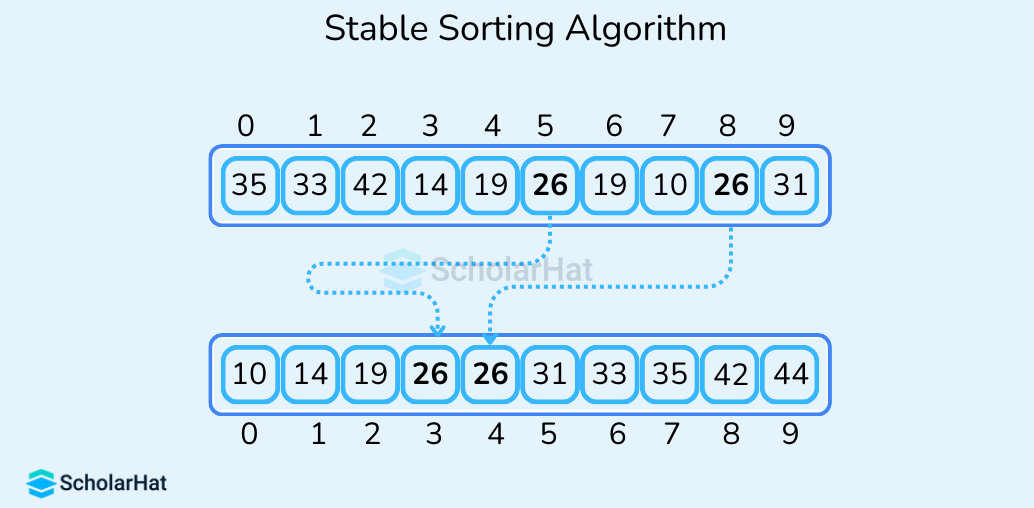
- Unstable Sorting Algorithm
These algorithms do not guarantee to maintain the relative order of elements with equal values in the original data set i.e. the order in which elements with the same value appear in the sorted output may not be the same as their order in the original data set. Some examples of unstable sorting algorithms are Quick Sort, Heap Sort, and Selection Sort.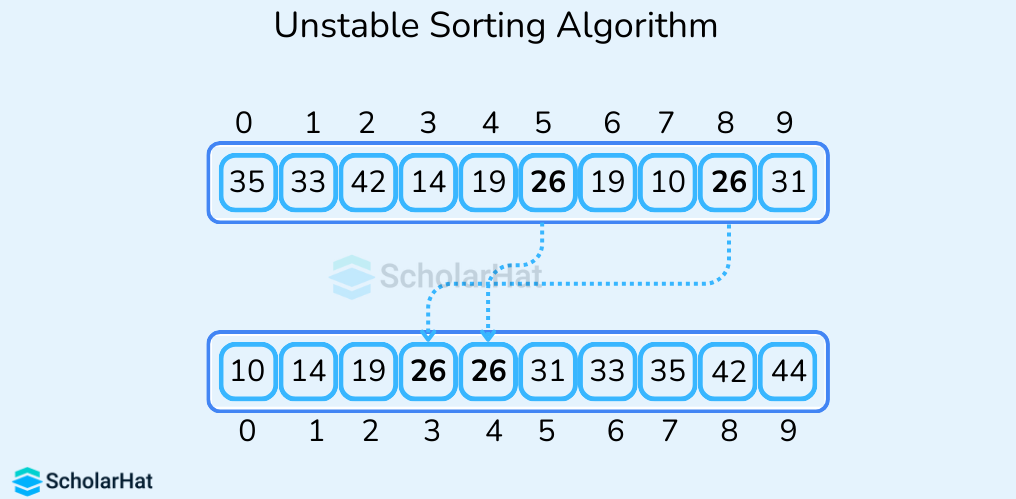
- Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Sorting Algorithm
- Adaptive Sorting Algorithm
These algorithms are adaptive because they can take advantage of the partially sorted nature of some input data to reduce the amount of work required to sort the data. For example, suppose a portion of the input data is already sorted. In that case, an adaptive sorting algorithm can skip over that portion of the data and focus on sorting the remaining elements. Some examples are insertion sort, bubble sort, and quicksort.- Non-Adaptive Sorting Algorithm
These algorithms are non-adaptive because they do not take advantage of any partial ordering of the input data. They try to force every single element to be re-ordered to confirm whether they are sorted or not. Some examples are selection sort, merge sort, and heap sort.- Comparison and Non-Comparison-based Sorting Algorithm
- Comparison-based Based Sorting Algorithms
These compare elements of the data set and determine their order based on the result of the comparison. Examples include bubble sort, insertion sort, quicksort, merge sort, and heap sort.- Non-Comparison based Sorting Algorithms
They are the sorting algorithms that sort the data without comparing the elements. Examples include radix sort, bucket sort, and counting sort.Some other Sorting algorithms
- Shell sort
- Tim Sort
- Comb Sort
- Pigeonhole sorting
- Cycle Sort
- Cocktail Sort
- Strand sort
- Bitonic Sort
- Stooge Sort
- Tag Sort
- Tree sort
- Cartesian Sort
- Odd-Even Sort / Brick Sort
- 3-way Merge Sort
- Gnome sort
- Cocktail shaker sort