26
DecData Models in DBMS: Types, Features, and Applications
A data model in database is a method used to organize and define how data is stored, connected, and accessed. It acts like a blueprint that shows the structure of data and the relationships between different pieces of information. Using a proper data model in database helps ensure that data is well-structured, consistent, and easy to work with.
In this DBMS tutorial, understanding the data model in database design is important for building systems that are efficient, reliable, and scalable. Whether you're developing a small application or a large database system, a good data model helps keep everything clear and manageable
What are Data Models in Database?
Data models in database are frameworks that define how data is stored, organized, and related within a database. They help in creating a clear structure so data can be managed efficiently. These models are essential for designing reliable and easy-to-use databases.
Why do we need data models in a Database?
- Data models help to organize and arrange data in a clear and logical structure.
- They define how different pieces of data are connected to each other.
- Using a data model helps maintain accurate and consistent data.
- It becomes easier to update and manage the database when it is properly modeled.
- Data models make it easier for both developers and non-technical users to understand how the data works.
9 Types of Data Models in DBMS
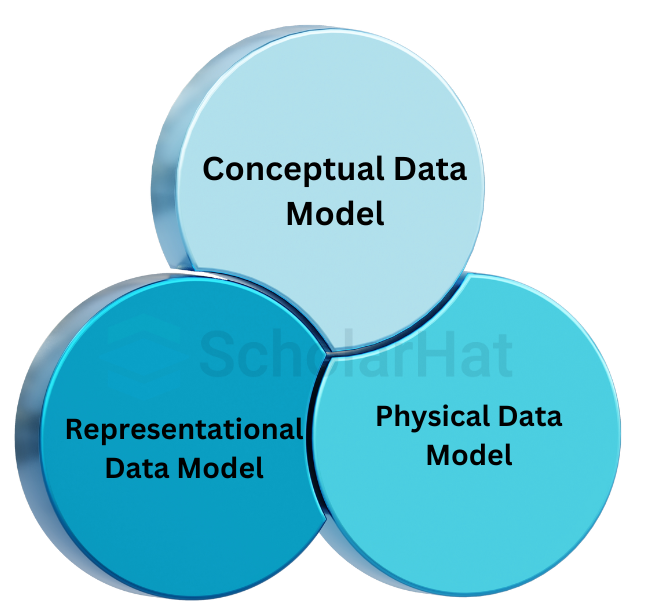
The data model models the data's semantics, consistency requirements, and description. It offers the conceptual tools needed to explain a database's design at every level of data abstraction. There are three main types of Data Models.
There are approximately 9 Types Of Data Models in DBMS :
- Conceptual data model
- Representational Data Model
- Hierarchical Data Model
- Network Data Model
- Object-Oriented Data Model
- Relational Data Model
- Float Data Model
- Semi-Structured Data Model
Let's see the first 3 main Types Of Data Models in DBMS:
Let's see these Data models in DBMS with examples one by one,
1. Conceptual data model
- The conceptual data model in dbms helps understand the database's needs and requirements by providing a high-level description of the database.
- This approach is used during the requirement-gathering phase, which is before the Database Designers begin creating a specific database.
- The entity/relationship model (ER model) is one such common model.
- Entities, relationships, and even properties that database designers utilize are the focus of the E/R model.
- This model helps anyone, including non-computer science(non-technical) users and stakeholders, understand it easily.
Entity-Relationship Model( ER Model)
- This model is built to specify the data and their relationships.
- It is essentially a conceptual design for any database that simplifies creating a data view.
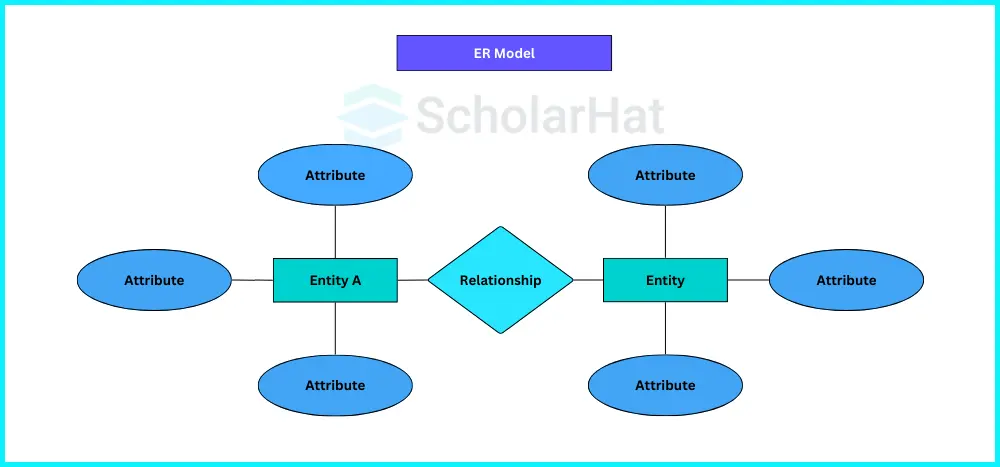
Elements of the ER Model
- Entities: Real-world objects are referred to as entities. It could be a class, name, location, or item. In an ER Diagram, these are shown by a rectangle.
- Attributes: An entity's description is referred to as an attribute. In an ER Diagram, these are represented by an ellipse. For a student, it could be their age, roll number, or marks.
- Relationship: Relationships are what establish the connections between various entities.
Key Characteristics of a Conceptual Data Model
- It provides an overview of the business ideas for the entire organization.
- Data models of this kind are created with a corporate audience in mind.
- The conceptual model is created without regard to software or hardware requirements, such as DBMS vendor and technology, or data storage capacity or location.
- Representing data as a user would see it in the "real world" is the main goal.
The Conceptual data models also called Domain models establish fundamental concepts and scope that all stakeholders can use to develop a shared vocabulary.
2. Representational Data Model
- This kind of data model does not describe the physical structure of the database.
- Rather, it is used to represent only the logical portion of the database.
- The representational data model specifically looks into the database's design.
- A relational model is a common type of representational model.
- Relational Calculus and Relational Algebra make up the Relational Model.
- Tables are essentially used in the Relational Model to represent our data and the relationships among them.
- It is a theoretical idea that is put into practice using a physical data model.
- One benefit of using a representational data model is that it offers a framework upon which the physical model may be built.
3. Physical Data Model
- The Relational Data Model is accurately executed with the Physical Data Model in DBMS.
- In the end, every piece of data within a database is physically kept on discs and tapes or other secondary storage devices.
- Files, records, and a few more types of data structures are used to store this.
- It contains all the details on the file formats, database structures, external data structures, and how they relate to one another.
- In this case, tables are essentially saved in memory for effective access.
- Better work on the relational model is necessary before we can develop a good physical model.
- Relational algebra is realistically implemented using Structured Query Language (SQL).
| SQL Server Course |
This data model explains WHY a particular DBMS system would be used to implement the system.
Key Characteristics of a Physical Data Model
- It is designed for a particular DBMS version, site, data storage capacity, or project-specific technology.
- Its Columns contain default values, given lengths, and precise datatypes.
- views, authorizations, access profiles, indexes, primary and foreign keys, etc are defined in it.
Additional Data Models in DBMS You Should Know
1. Hierarchical Data Model
- The hierarchical data model in dbms organizes data in a treelike structure, where each record has a single parent and one or more children.
- This model is ideal for representing data with a clear hierarchical relationship, such as organizational charts or file systems.
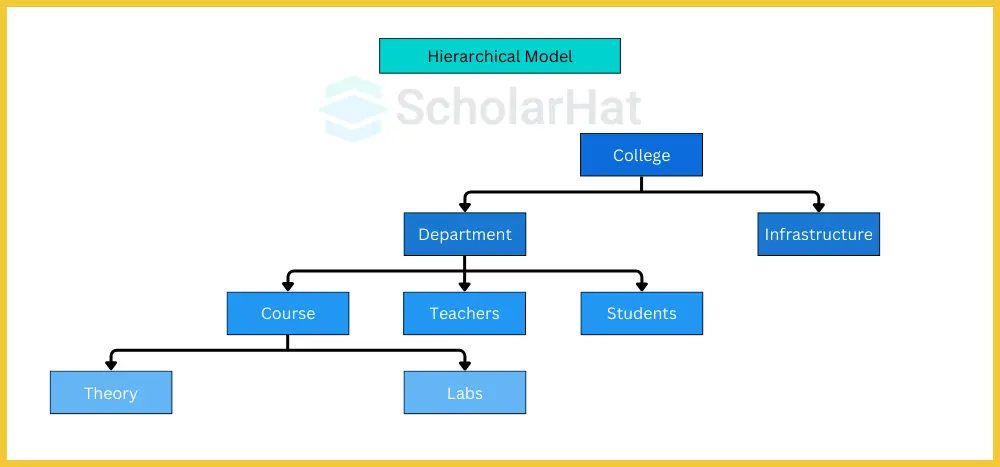
There are 3 main characteristics of Hierarchical Data Model in DBMS these are as follows:
Characteristics:
- ParentChild Relationship: Each node (record) is linked to a single parent.
- Navigational Access: Data retrieval involves navigating through the hierarchy.
- Simplicity: Simple to understand and implement for hierarchical data.
Advantages:
- Efficient for queries that require traversing hierarchies.
- Enforces data integrity through parent-child relationships.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of flexibility: changes in the hierarchy can be complex.
- Difficult to model many-to-many relationships.
2. Network Data Model
- The network data model is an extension of the hierarchical model, allowing multiple parent-child relationships, thus creating a graph structure.
- This model is suitable for complex data relationships.
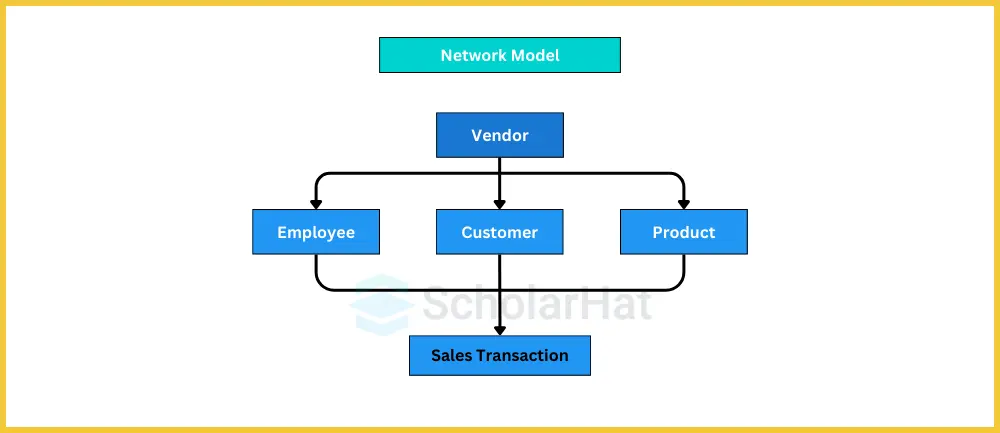
Characteristics:
- Graph Structure: Data is represented as a collection of records connected by links.
- Flexibility: Supports many-to-many relationships.
- Set-based access: Data can be accessed through predefined paths (sets).
Advantages:
- More flexible than the hierarchical model.
- Efficient for complex queries involving interconnected data.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity in implementation and maintenance.
- Navigational access can be cumbersome.
3. Object-Oriented Data Model
- The object-oriented data model integrates object-oriented programming principles into databases, allowing data to be stored as objects.
- This model is suitable for applications requiring complex data representations.
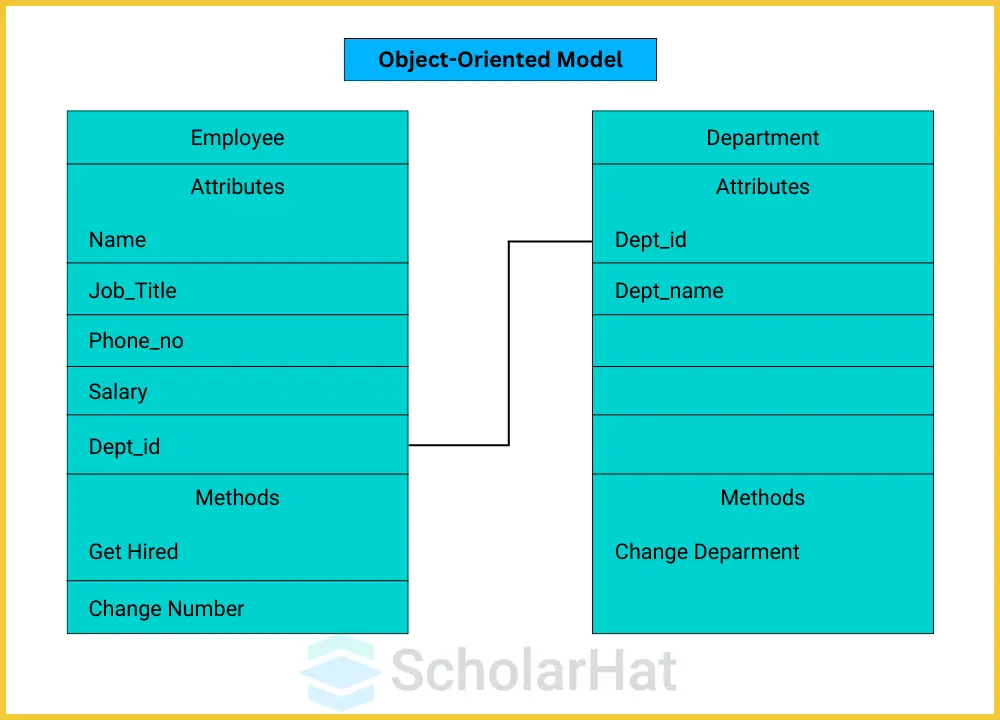
Characteristics:
- Object Structure: Data is represented as objects, similar to object-oriented programming languages.
- Encapsulation: Combines data and behavior (methods) in objects.
- Inheritance: Supports inheritance of properties and methods.
Advantages:
- Seamless integration with object-oriented programming.
- Suitable for applications with complex data structures.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity in implementation.
- It is less useful compared to the relational model.
4. Relational Data Model
The most widely used model is the relational model. According to this concept, data is kept in two-dimensional tables. Data is organized into rows and columns. Tables are the cornerstone of a relational paradigm. For this reason, in the model, the tables are referred to as relations.
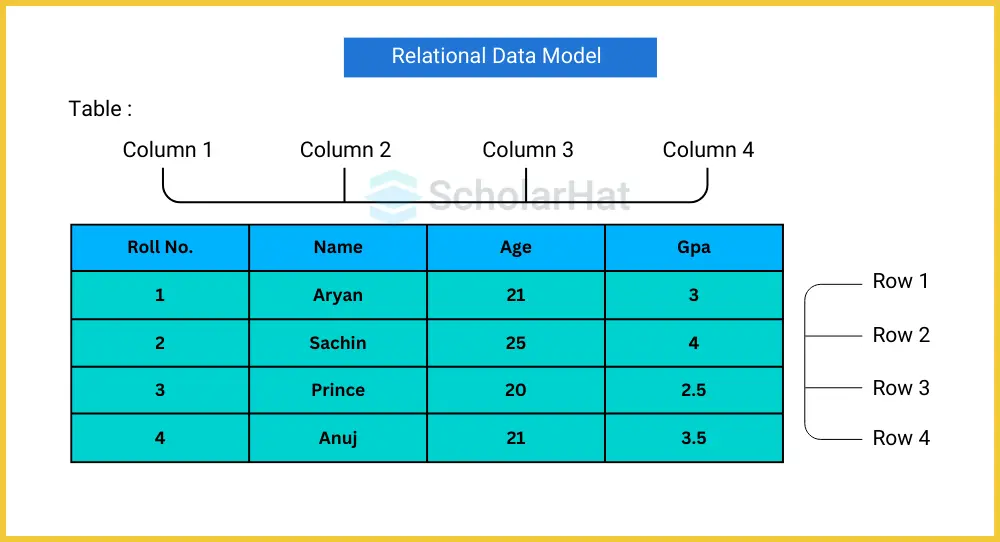
Characteristics
- Triples: The term "tuple" refers to each row in the table. Every row contains every detail pertaining to a single, unique instance. The information about each individual in the following example is filled in a row; for example, the first row includes information about Ramesh.
- Field: A field or quality The characteristic that characterizes a table or connection is its attribute. The values of the attributes have to be in the same domain. The characteristics of an Employee in the example below, such as their address, age, and employee ID, are called attributes.
| Names | employee ID | Phone_No | Address | AGE |
| Ramesh | 34 | 9876542745 | Pune | 32 |
| Arya | 27 | 9234754888 | Mumbai | 22 |
| Kumari | 16 | 8798456123 | Pune | 25 |
| Vishva | 23 | 8865341298 | Pune | 33 |
Advantages
- Scalable: The user may easily add as many rows and columns as they would like to this model.
- Structural independence: It is feasible to change the database's structure without also changing how information is accessed. Structural independence is achieved if we can change the database structure without affecting the DBMS's capacity to access data.
Disadvantages
- Hardware Overheads: This paradigm requires more potent processors and data storage devices in order to mask complexity and simplify user interfaces.
- Improper Design: Users can access data without understanding how it is stored because the model is incredibly simple to generate and use. As a result of the design's simplicity, a poor database could be created, and when the database grows, its growth might stall.
5. Float Data Model
- In basic terms, the float data model is made up of a two-dimensional array of data models without any duplicate parts.
- This data model has one limitation: the tables cannot be too large to hold a lot of data.
6. Semi-Structured Data Model
- Semi-structured data models handle the information in an adaptable manner.
- Certain entities can have more qualities than others, and vice versa.
- Basically, this is a flexible place to express data.
Advantages of Data Models in DBMS
- We can accurately represent data with the use of data models.
- It assists us in reducing data redundancy and locating missing data.
- Data models best provide data security.
- The physical database should be constructed using the data model, which should have sufficient detail.
- The information in the data model can be used to define table relationships, main and foreign key relationships, and stored procedures.
Disadvantages of Data Models in DBMS
- It might occasionally be challenging to comprehend the data model in the case of an extensive database.
- In order to use physical models, you need to be proficient with SQL.
- Modifications to even minor structural changes necessitate alterations to the entire application.
- A set language for data manipulation does not exist in DBMSs.
- Understanding the physical properties of data storage is necessary to construct data models.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate data model in DBMS is crucial for optimizing data storage, retrieval, and management. Each model has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of applications. Understanding these models allows database designers and developers to create efficient and scalable database systems tailored to specific needs.
| Similar Articles |
| Different Types of SQL Keys |
| Introduction to SQL Server |
| SQL Server Insert, Retrieve, Update, Delete Operations using Stored Procedures |
FAQs
Take our Dbms skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.