11
AprUnderstanding Big Data and Hadoop
The Big Data refers to a collection of large datasets that cannot be stored, processed or analyzed using traditional processes or tools due to limitations of cost or the absence of suitable mechanisms. The issues of Big Data management, maintenance, and analysis became more complex, especially when the volume of data has become very large from multiple data sources.
This requires a Big Data solution which offers real-time data storage, processing or analyzed functionalities for the organizations to extract meaningful, useful, and vital information which helps them to take a decision.

Characteristics of Big Data
In 2001, META Group (now Gartner) analyst Doug Laney specified the data growth challenges and opportunities known as the three dimensions or 3V Dimensions of Big Data.
Volume
Volume refers to the vast amounts of data generated every second. This vast amount of data analyzed by the organization to improve decision-making. Big data solutions typically store and query hundreds of terabytes of data, and the total volume is probably growing by ten times every five years.
For example, Facebook alone generates 25 TB data every day and NYSE spoons 1 billion TB. The storage capacity for storing Big data has been growing fast from terabytes to petabytes and petabytes to zettabytes.
Variety
Variety refers to the different types of data - structured, unstructured and semi-structured data. In the past, all data that was created was structured data which can be fitted in tables or relational databases, such as financial data. But today, 90% of the data that is generated by an organization is unstructured (text, images, video, voice, etc.) data.
The wide variety of data requires the different approaches, techniques, and tools to store or analyze the raw data for the business use. It means applying schemas to the data before or during storage is no longer a practical proposition.
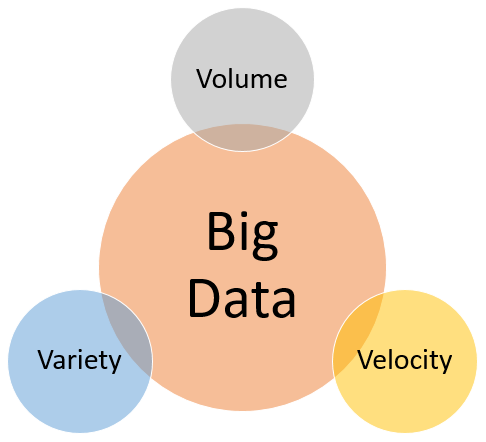
Velocity
Velocity refers to the speed at which the data is generated stored, analyzed and visualized. Big Data solutions allow you to analyze the data while it is being generated (sometimes referred to as in-memory analytics), without ever putting it into databases.
For example, just think of social media like Facebook or Twitter messages going viral in seconds.
In the past, batch processing was the common practice where we receive an update from the database every night or even every week. Computers and servers required substantial time to process the data and update the databases. But in the Big Data era, data is created, analyzed and visualized in real-time or near real-time.
Big Data Challenges
The major challenges associated with Big Data are as follows:
Storage
Cost
Processing
Querying
Sharing
Analysis
Presentation
Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is an open-source software platform used for storage, processing and anlyzing extremely large data sets in a distributed environment using clusters of computers. Hadoop was born form Nutch search engine, created by Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella in 2006 which was inspired by Google's research paper - MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters.

The Hadoop name came from the Doug Cutting's son's yellow plush toy elephant. Hadoop 0.1.0 was released in April 2006 and after many years of development, Hadoop 1.0 was released in November 2012 as part of the Apache project sponsored by the Apache Software Foundation.
Advantages of Hadoop
Scalable
Hadoop is a highly scalable data storage and processing platform, since it uses thousands of nodes in a cluster that operate in parallel. Unlike traditional RDBMS that can't scale to process large amounts of data, Hadoop enables the application to run on thousands of nodes involving thousands of terabytes of data.
Fast
Unlike traditional RDBMS, Haddop's data processing is very fast since it is based on a distributed file system that basically 'maps' data wherever it is located on a cluster. The data analytics tools for data processing on the same servers where the data is located, resulting in much faster data processing. Hadoop is able to efficiently process terabytes of data in just minutes, and petabytes in hours.
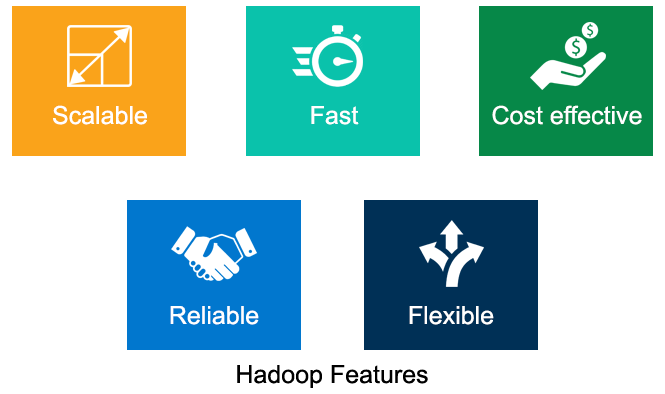
Cost effective
Unlike traditional RDBMS that are extremely expensive to scale in order to process such massive volumes of data, Hadoop is open source and runs on low-cost commodity hardware.
Reliable
The main advantage of using Hadoop is its fault tolerance. When data is sent to an individual node, that data is also replicated to other nodes available in the cluster, which means that if a node fails it will redirect to the remaining nodes in the cluster for data processing.This makes it extremely reliable.
Flexible
Hadoop is flexible in data processing, it means you can process different types of data (structured, unstructured and semi-structured) to generate value from that data. In this way, Hadoop can derive valuable business insights from data sources such as social media, email conversations or clickstream data.
What do you think?
Thank you for your time, I hope you enjoyed this article and found it useful. Please add your comments and questions below. I would like to have feedback from my blog readers. Your valuable feedback, question, or comments about this article are always welcome.