27
DecData Types in Java : Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Types
Data Types in Java
Data types in Java are a way to classify data to make it easier to understand and work with in programming. They define what kind of value a variable can hold, such as numbers, text, or collections of items. If you’ve worked with data types in Java, you’ll find that other languages follow similar concepts, even if their rules and features vary.
Hence, In this Java tutorial, we'll learn the concepts of Data Types in Java, including primitive and non-primitive data types in Java, in detail. We will also explore various Data types in Java with examples. Also enroll in our Free Java Course and build a strong foundation in Java Programming.
What are Data Types in Java?
- Primitive data type: This particular data type includes float, short, boolean, byte, char, long, int, and double.
- Non-primitive data type: This particular data type includes arrays, interfaces, strings, and classes.
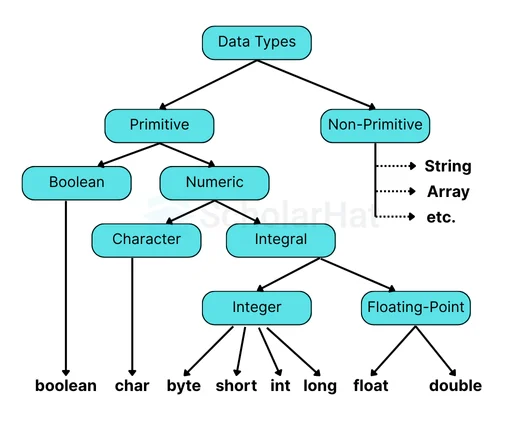
1. Primitive Data Types in Java
Primitive data types in Java are the basic building blocks of data, representing simple values like numbers, characters, and true/false conditions. They are predefined by the language, require minimal memory, and have no additional methods or functionality.
There are 8 types of primitive data, which will be discussed further.
- Integer Types
- Floating Point Types
- Char data type
- Boolean data type
| Data Type | Description | Default Value | Default Size | Range |
| byte | 8-bit signed integer, used to save memory in large arrays. | 0 | 1 byte | -128 to 127 |
| short | 16-bit signed integer, used for saving memory compared to int. | 0 | 2 bytes | -32,768 to 32,767 |
| int | 32-bit signed integer, the most commonly used integer type. | 0 | 4 bytes | -231 to (231) - 1 (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) |
| long | 64-bit signed integer, used when a larger range than int is needed. | 0L | 8 bytes | -263 to (263) - 1 (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807) |
| float | 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point, used for decimal values (less precision than double). | 0.0f | 4 bytes | Approximately ±3.40282347E+38F |
| double | 64-bit IEEE 754 floating-point, used for precise decimal values (default for floating-point). | 0.0d | 8 bytes | Approximately ±1.79769313486231570E+308 |
| char | 16-bit Unicode character, used for a single character/letter. | '\u0000' | 2 bytes | '\u0000' (0) to '\uffff' (65,535) |
| boolean | Stores one of two values: true or false. | false | ~1 bit | true or false |
Read More - Advanced Java Interview Questions
1. Integer Types
Integer types store whole numbers, positive or negative, like 233 or -457, without decimals. There are four data types for storing whole numbers. The choice depends on the numeric value.
- Byte data type
The byte data type is an 8-bit signed two’s complement integer. It can store whole numbers from -128 to 127. Its default value is 0. It is used to save memory in large arrays where memory savings are most required. The byte data type saves space because a byte is 4 times smaller than an integer. It can also be used in place of the int data type.
Syntax
byte variable_name;Example of Byte Data Type in Java
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { byte myNum = 126; System.out.println(myNum); } }Output
126 - Short data type
The short data type is a 16-bit signed two’s complement integer. It can store whole numbers from -32768 to 32767. Its default value is 0. A short data type is 2 times smaller than an integer. It can be used when a small range of integer values is required. We will understand through illustration in the Java Compiler.
Syntax
short variable_name;Example of Short Data Type in Java
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { short myNum = 30000; System.out.println(myNum); } }Output
30000 - Integer Data Type
It is a 32-bit signed two’s complement integer. It is a 4-byte integer type with a range of -2^31 to 2^31-1. Its default value is 0. The int data type is generally used as a default data type for integral values.
Syntax
short variable_name;Example of Int Data Type in Java
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int myNum = 300000; System.out.println(myNum); } }Output
300000 - Long Data Type
The long data type is a 64-bit two’s complement integer. Its value-range lies between -9,223,372,036,854,775,808(-2^63) to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807(2^63 -1). It is used in situations when "int" is not large enough to store the value. Here, you should end the value with an "L". Its default value is 0.
Syntax
long variable_name;Example of Long Data Type in Java
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { long myNum = 15000000000L; System.out.println(myNum); } }Output
15000000000
2. Floating Point Types
This data type is used when there is a requirement for decimal numbers like 2.33, 3.2, etc. There are two data types for storing fractional or decimal numbers.
- Float data type
Float data type in Java has a "single precision 32 bits IEEE 754" floating point. The value of this range is unlimited. The size of the float data type in java is 4 bytes (32 bits). It stores fractional numbers. Sufficient for storing 6 to 7 decimal digits. Its default value is 0.0F. You must end the value with an "f" for floats.
Syntax
float variable_name;Example of float Data Type in Java
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { float myNum = 8.79f; System.out.println(myNum); } }Output
8.79 - Double data type
This data type is a "64-bit Double precision IEEE 754 floating point". The size of the double data type is 8 bytes or 64 bits. It has greater precision than `float'. It also stores fractional numbers. Sufficient for storing 15 decimal digits. Its default value is 0.0d. You should end the value with "d" for doubles. You'll understand completely by executing the code below in the Java Playground.
Syntax
float variable_name;Example of double Data Type in Java
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { double myNum = 78.36d; System.out.println(myNum); } }Output
78.36
Read More - Java Developer Salary
float vs. double
- The precision of a floating point value indicates how many digits the value can have after the decimal point.
- The precision of float is six or seven decimal digits, while double variables have a precision of about 15 digits.
- Therefore, it is recommended to use double for most calculations. However, double takes up twice as much memory as float (8 bytes vs. 4 bytes).
3. Char data type
The char data type is used to store single 16-bit Unicode characters like 'A', '1', or '$'. The character must be surrounded by single quotes. Its value range lies between '\u0000' (or 0) to '\uffff'.
Syntax
char variable_name;
Example of char Data Type in Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char scholarHat = 'S';
System.out.println(scholarHat);
}
}
Output
S
Representing single characters using ASCII values
You can also use ASCII values to display certain characters. Here, these values are not surrounded by quotes (' '), as they are numbers
Example
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char myVar1 = 79, myVar2 = 88, myVar3 = 97;
System.out.println(myVar1);
System.out.println(myVar2);
System.out.println(myVar3);
}
}
Output
O
X
a
4. Boolean data type
The Boolean data type is used to store only two possible values: true and false. It specifies one bit of information, but its "size" can't be defined precisely. Values of type boolean are not converted implicitly or explicitly (with casts) to any other type. This data type is used for simple flags that track true/false conditions.
Syntax
boolean variable_name;
Example of Boolean Data Type in Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean isScholarHat = true;
boolean isEmpty = false;
System.out.println(isScholarHat);
System.out.println(isEmpty);
}
}
Output
true
false
Why is the Size of char 2 bytes in Java?
- In Java, char is 2 bytes (16 bits) because it uses Unicode to support international characters, unlike ASCII, which uses 1 byte.
- Unicode requires 2 bytes to represent over 65,000 characters in various languages.
- Java's fixed 2-byte char simplifies processing and ensures compatibility with the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP). For characters outside BMP, surrogate pairs are used.
- This design enables efficient handling of global text.
2. Non-Primitive Data Types in Java
Non-primitive data types are called reference types because they refer to objects. The value of a variable in a non-primitive data type cannot be stored directly in memory. This particular data stores the address of the variable's memory. Non-primitive types are created by the programmer and are not defined by Java. There are mainly five non-primitive data types, which will be discussed shortly.
- Arrays
- Strings
- Strings
- Object
- Interfaces
- Enum
1. Arrays
An array is a group of identically typed elements kept in consecutive memory regions. Multiple values of the same type can be stored and accessed using a single variable name.
Syntax
data_type array_name[array_size];There are two types of arrays in Java, which are:
- Single-dimensional array: It is a collection of elements of the same data type that are stored in a contiguous block of memory.
- Multi-dimensional array: It is an array that contains one or more arrays as its elements.
For more details on arrays: Arrays in Java
2. Strings
The String data type represents sequences of characters. Strings are represented by various alphabets surrounded by double quotes.
Syntax
<String_Type> <string_variable> = “<sequence_of_string>”;
Demonstration of String Data Type in Java Online Editor
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String greeting = "Welcome to ScholarHat";
System.out.println(greeting);
}
}
Output
Welcome to ScholarHat
Read Java Strings in detail: What is String in Java - Java String Types and Methods (With Examples)
3. Class
A class is a user-defined model or prototype from which objects are made. It stands for the collection of attributes or operations that are shared by all objects of a particular type. To create a class, use the keyword class.
Syntax
access_modifier class
{
data members;
methods;
}
Example of a Class in Java
public class ScholarHat {
int x = 5;
}
Read More: What is Class in Java?
4. Object
An object represents real-life entities and is the fundamental building block of object-oriented programming. In Java, an object is created from a class. To create an object of a class, specify the class name, followed by the object name, and use the keyword new.
Demonstration of an Object in Java in Java Online Compiler
public class ScholarHat {
int x = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScholarHat myObj = new ScholarHat();
System.out.println(myObj.x);
}
}
Output
50
Read More: What is an Object in Java?
5. Interfaces
Interfaces are collections of "abstract methods." To achieve abstraction, Java follows an interface mechanism. The interface data type contains "constants," "default methods," "static methods," and "nested type."
Example of an Interface in Java
interface ScholarHat {
public void contentwriters(); // interface method (does not have a body)
public void seo(); // interface method (does not have a body)
}
Read More: Abstraction in Java
Enum
Example
enum Day {
MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY, SUNDAY
} Why is Enum Non-Primitive?
1. Not Built-In Primitive: Primitive types in Java (e.g., int, char, float) are built-in and hold basic values. Enum is not a built-in type but a custom-defined type that extends the java.lang.Enum class.
2. Behavior Like a Class: Enum in Java is internally represented as a class. You can add methods, fields, and constructors to an enum.
enum Day {
MONDAY, TUESDAY;
public void display() {System.out.println("This is " + this);
}
} 3. Memory Allocation: Enums do not store values directly like primitive types but are reference types stored in the heap.
4. Supports Object-Oriented Features: Enums can have methods, fields, and implement interfaces, which are characteristics of objects, not primitives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Data types in Java are the foundation of how information is stored and processed in the language. With Java's wide range of data types, you can handle everything from simple numbers and characters to complex structures efficiently. By understanding data types in Java, you’ll write cleaner, faster, and more reliable code with ease!
Consider our Full-Stack Java Developer Certification to enhance your Java skills. Also, Top Java developers are already moving into Architect roles. Don’t be left behind—upgrade now with our Java Solution Architect Training.
Practice Yourself with the Following MCQs
Q 1: Which of the following is a primitive data type in Java?
Explanation: In Java, int is a primitive data type, while String, Object, and ArrayList are reference types.
Q 2: What is the size of the float data type in Java?
Explanation: The float data type in Java is a 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point type used to store decimal numbers.
Q 3: Which of the following data types can store a single 16-bit Unicode character?
Explanation: The char data type in Java can store a single 16-bit Unicode character, making it suitable for storing individual characters.
Q 4: Which data type is used to store a value of true or false in Java?
Explanation: The boolean data type in Java can hold only two possible values: true or false, and is used for logical operations.
Q 5: What is the default value of a double variable in Java?
Explanation: The default value of a double variable in Java is 0.0 because it is a floating-point type.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.