26
DecDifferences between JDK, JRE, and JVM: Java Toolkit
JDK, JRE, and JVM are essential components of the Java programming environment, each serving a specific purpose.
- JDK (Java Development Kit) is a complete software development kit that provides the tools and libraries required to create, compile, and debug Java applications.
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment) is responsible for providing the necessary environment to run Java programs—it includes the JVM and essential class libraries but lacks development tools.
- JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is the core engine that interprets and executes Java bytecode, making Java programs platform-independent by running them on any system with a compatible JVM.
Together, these three components ensure that Java applications can be developed, executed, and run efficiently across different platforms.
Understanding the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM is essential for anyone learning Java. 95% of Java newbies miss jobs without basic skills. Don’t lose out—Enroll now in our Free Java Course to start strong and land your dream role!
What is JVM?
- JVM is an abstract machine that assists a computer in running Java programs, which include different types of arrays in Java.
- Java virtual machine is the finite engine that anticipates a "run time environment" to generate the code for Java.
- JVM or Java virtual machine is a major part of the "Java Runtime Environment".
- The primary job of the JVM is to convert "bytecode" to "machine language".
- The activities, which are done by JVM, are "Loading", "Linking", and "Initialization".
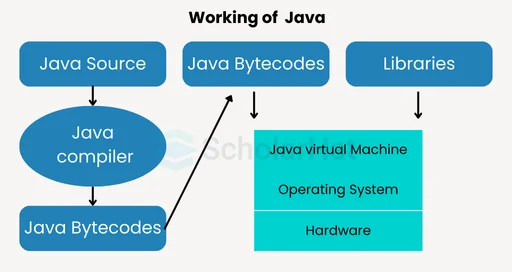
Features of JVM
- It converts byte code into machine language.
- JVM supports core Java functions such as memory management, security, and garbage collection.
- Runs the program using the JRE's libraries and files.
- JVM is a fundamental component of JRE.
- It can run a Java program line by line. It is also known as an interpreter.
- The essential functions of the JVM are to load, link, initialize, and compile the program.
Working of JVM
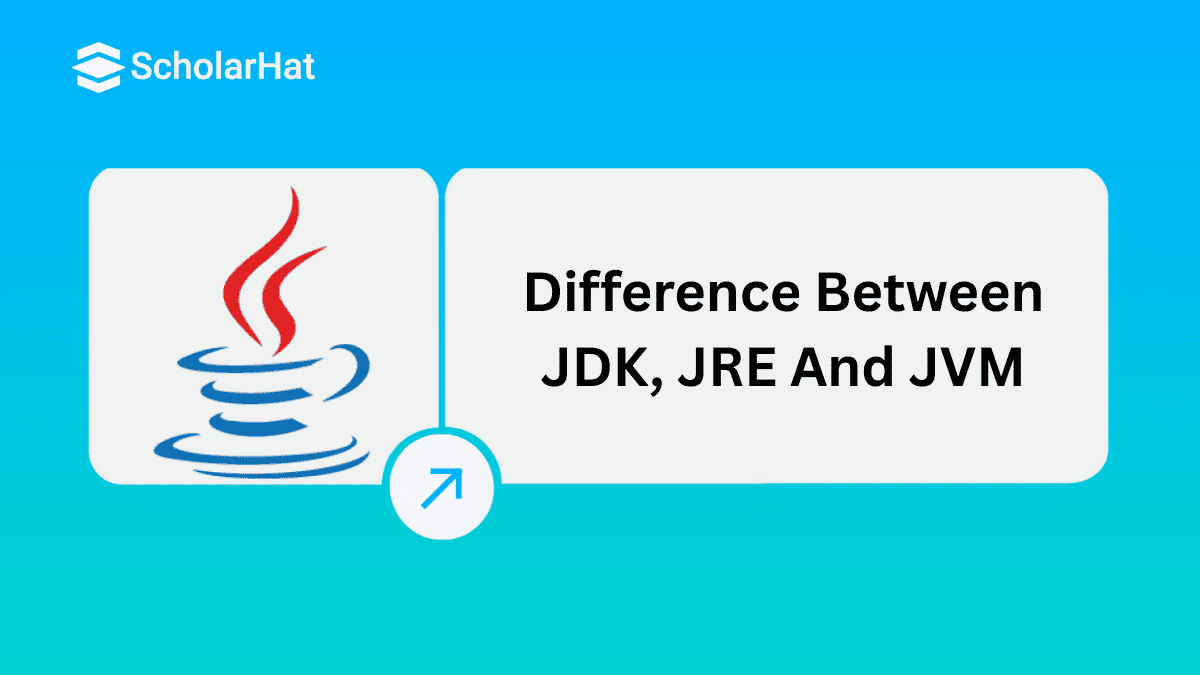
The JVM is the engine that runs Java applications. When you write a Java program, it doesn’t directly run on your computer’s hardware. Instead, it goes through a few steps before it is executed. Let’s understand how JVM works:
- Java code is written in a .java file.
- The Java compiler (java c) converts it into bytecode (.class file).
- JVM loads the bytecode using the Class Loader.
- The Bytecode Verifier checks the code for security and correctness.
- The Execution Engine runs the bytecode:
- It uses an Interpreter or JIT Compiler to convert bytecode into machine code.
- The Garbage Collector automatically manages memory by removing unused objects.
- This process makes Java platform-independent – the same code can run on any system that has a JVM.
Limitations of JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
- Platform Dependent Implementation – JVM must be different for Windows, Linux, etc.
- Slower Performance – Not as fast as native languages (e.g., C++) due to bytecode interpretation.
- Limited Low-Level Control – No access to memory addresses or hardware like C/C++.
- Memory Overhead – JVM requires significant memory and resources.
- Needs Proper Configuration – Improper JVM settings can cause memory leaks or crashes.
- Crashes If Misused – Malformed bytecode or poorly managed resources can crash the JVM.
What is JRE?
- JRE or Java runtime environment is an important part of the "Java development kit" and it has another feature of loops in Java.
- The source code of Java is compiled and converted into byte code in this Java Runtime Environment.
- To run any bytecode, one needs to have access to JRE.
- Java Runtime Environment behaves like a layer on the top of any operating system.
- JRE is very commonly available on devices, and it is also free of cost including "Java class libraries", "specific tools", and "a standalone JVM".
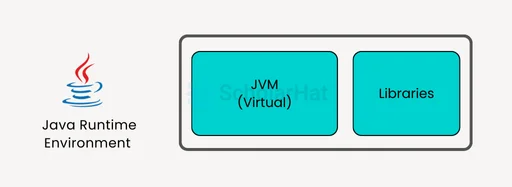
Features of JRE
- JRE is a collection of tools that assist the JVM run. It also provides a few deployment tools, such as Java Plug-in and Java Web Start.
- A user can efficiently run Java code with only JRE. However, JRE does not allow you to write the program.
- JRE includes integration libraries such as JDBC (Java Database Connectivity), JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface), and RMI (Remote Method Invocation).
- Along with JVM, it includes a virtual machine client for Java HotSpot.
Working of JRE
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) provides the necessary environment to run Java applications.
- When you run a Java program, the JRE uses the JVM to execute the compiled bytecode.
- It provides all the core libraries, classes, and files needed during runtime.
- The JVM, inside the JRE, loads the bytecode, verifies it, and then executes it using either an interpreter or JIT compiler.
- The JRE ensures smooth interaction between the Java program and the underlying operating system.
Limitations of JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
- Cannot Write or Compile Code – No compiler (javac) or dev tools included.
- Heavy for End Users – Bulky for users running small or single-purpose apps.
- Frequent Updates Required – Regular updates are needed for security and compatibility.
- Limited for Advanced Tasks – Can’t handle development, testing, or debugging.
- No Customization – Fixed runtime setup with minimal flexibility.
- Dependent on JVM Version – Compatibility issues may occur if the JVM version mismatches with the compiled bytecode.
Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions For Freshers Read More - Advanced Java Multithreading Interview Questions
What is JDK?
- JDK or Java development kit is an objective-oriented software demerit that helps to develop applications in Java.
- JDK offers a collection of libraries and tools that are necessary for the development of Java-based applications.
- Java development kit has its own private "Java virtual machine" and other resources that are valuable for the development of any Java application.
- JDK contains a Java runtime environment, a Java compiler, an interpreter, an achiever, and many more.

Working of JDK
The JDK is a software development kit used to build, compile, and run Java applications. It includes:
- Source Code Writing: You write your Java program in a .java file using an editor or IDE (like Eclipse or IntelliJ).
- Compilation (javac): The JDK provides javac (Java compiler) to convert the source code into bytecode (.class file).
- Execution (via JRE): The JDK also includes JRE, which contains the JVM to execute the bytecode.
- Developer Tools:
i) java c – compiler
ii) java – launcher to run code
iii) java doc – to create documentation
iv) jdb – debugger
Limitations of JDK (Java Development Kit)
- Large File Size – Takes up more storage due to additional tools and libraries.
- Complex for Beginners – Many tools and commands can be confusing.
- Manual Setup Required – Environment variables (JAVA_HOME, PATH) must be configured manually.
- Not for End Users – Contains tools unnecessary for users who only run apps.
- Frequent Version Updates – Developers need to regularly update JDK for the latest features.
- Compatibility Issues – Using different versions of JDK and JRE may lead to runtime errors.
Read More - Java Web Developer Salary
Difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM (JDK vs JRE vs JVM)
| JDK | JRE | JVM |
| Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development kit used to develop Java applications. | Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is a software package that provides Java Virtual Machine (JVM), class libraries, and other components to run applications in Java. | Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is an abstract machine that provides an environment for the execution of Java bytecode. |
| JDK contains tools for developing, monitoring, and debugging Java codes. | JRE contains class libraries and other supporting files required by JVM for executing Java programs. | JVM does not include any software development tools. |
| It is platform-dependent, i.e. different platforms require different JDK. | It is also platform-dependent as JDK. | It is platform-independent. |
| It is primarily used for creating Java programs that JRE and JVM can execute. | It is mainly responsible for creating an environment for the execution of Java programs. | JVM specifies all the implementations and is responsible for providing them to JRE. |
| JDK = JRE + Development tools | JRE = JVM + Class libraries | JVM = provides a runtime environment. |
Summary
Java Development Kit (JDK), Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and Java Virtual Machine (JVM) are all important components of the Java platform. In summary, JDK enables developers to compile programs, JRE is essential for running those programs on multiple platforms, and the JVM takes charge of executing them. This article also contains the difference between JVM, JRE, and JDK. Master core Java concepts like JVM, JRE, and JDK. Take the next step with our Java Microservices Course.
Top coders use full-stack skills to run projects. Don’t stay small, Enroll now in our Java Full Stack Course to stand tall.
FAQs
- Java programs are developed using the JDK (Java Development Kit). It comes with coding, debugging, and compilation tools.
- The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is used to run Java programs. The JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and essential libraries are included.
- Code written in Java is executed by the JVM. It executes Java programs and is a part of the JRE.
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.