08
JanWhat are Operators in Java - Types of Operators in Java ( With Examples )
Operators in Java: An Overview
The operators in Java programming act as potent instruments for data manipulation and control flow are its heart and soul. In this Java tutorial, we'll explore the different types of Java operators and give examples of how they can be used.
95% of Java newbies miss jobs without basic skills. Don’t lose out—Enroll now in our Java Free Course to start strong and land your dream role!
Read More: Best Java Developer Roadmap 2024
What are Java Operators?
Operators in Java, a Java toolkit, are being used as a symbol that performs various operations according to the code. Some Operators of JAVA are "+","-","*","/" etc. The idea of using Operators has been taken from other languages so that it behaves expectedly.
Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions For Freshers
Types of Operators in Java
There are various types of Operators in Java that are used for operating. These are,
- Arithmetic operators in Java
- Relational operators in Java
- Logical operators in Java
- Assignment operator in Java
- Unary operator in Java
- Bitwise operator in Java
- Comparison operator in Java
- Ternary operator in Java
Arithmetic Operators in Java
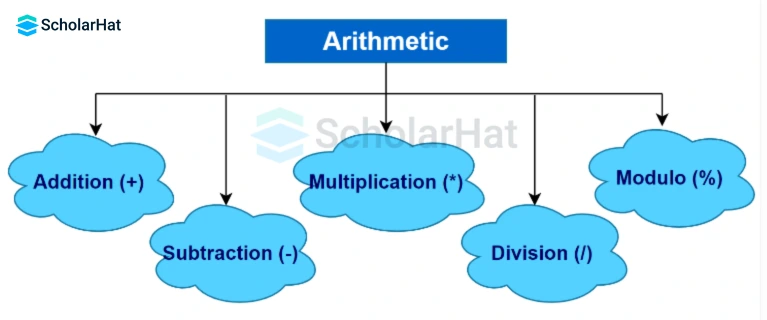
Arithmetic Operators in Java are particularly used for performing arithmetic operations on given data or variables. There are various types of operators in Java, such as
| Operators | Operations |
|---|---|
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| x | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| % | Modulus |
Arithmetic Operators in Java Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declare variables
int a = 15, b = 5;
// addition operator
System.out.println("a + b = " + (a + b));
// subtraction operator
System.out.println("a - b = " + (a - b));
// multiplication operator
System.out.println("a * b = " + (a * b));
// division operator
System.out.println("a / b = " + (a / b));
// modulo operator
System.out.println("a % b = " + (a % b));
}
}
Output
a + b = 20
a - b = 10
a * b = 75
a / b = 3
a % b = 0
Read More - Java Programmer Salary In India
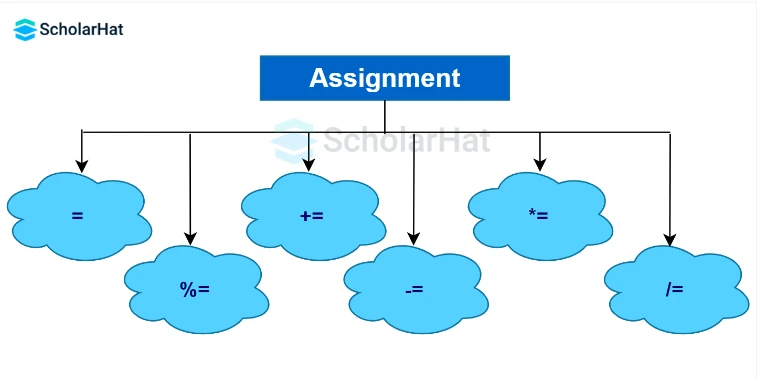
Assignment Operator in Java
Assignment Operators are mainly used to assign the values to the variable that is situated in Java programming. There are various assignment operators in Java, such as
| Operators | Examples | Equivalent to |
|---|---|---|
| = | X = Y; | X = Y; |
| += | X += Y; | X = X + Y; |
| -= | X -= Y; | X = X - Y; |
| *= | X *= Y; | X = X * Y; |
| /= | X /= Y; | X = X / Y; |
| %= | X %= Y; | X = X % Y; |
Assignment Operator in Java Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create variables
int a = 5;
int var;
// assign value using =
var = a;
System.out.println("var using =: " + var);
// assign value using =+
var += a;
System.out.println("var using +=: " + var);
// assign value using =*
var *= a;
System.out.println("var using *=: " + var);
}
}
Output
var using =: 5
var using +=: 10
var using *=: 50Relational Operators in Java
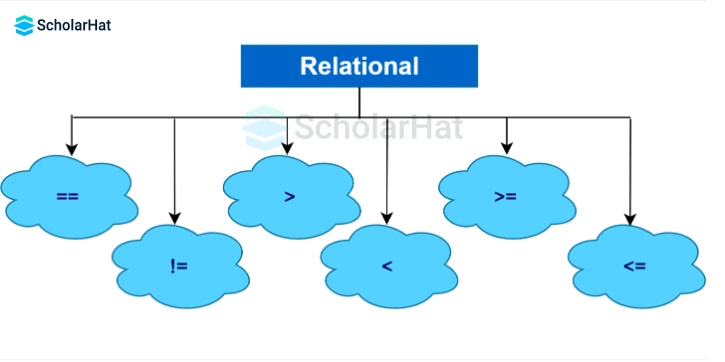
Java relational operators are assigned to check the relationships between two particular operators. There are various relational operators in Java, such as
| Operators | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| == | Is equal to | 3 == 5 returns false |
| != | Not equal to | 3 != 5 returns true |
| > | Greater than | 3 > 5 returns false |
| < | Less than | 3 < 5 returns true |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | 3 >= 5 returns false |
| <= | Less than or equal to | 3 <= 5 returns true |
Relational Operators in Java Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create variables
int a = 7, b = 11;
// value of a and b
System.out.println("a is " + a + " and b is " + b);
// == operator
System.out.println(a == b); // false
// != operator
System.out.println(a != b); // true
// > operator
System.out.println(a > b); // false
// < operator
System.out.println(a < b); // true
// >= operator
System.out.println(a >= b); // false
// <= operator
System.out.println(a <= b); // true
}
}
Output
a is 7 and b is 11
false
true
false
true
false
trueLogical Operators in Java
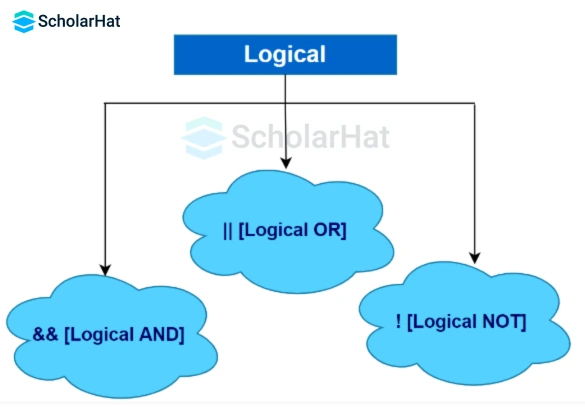
Logical Operators in Java check whether the expression is true or false. It is generally used for making any decisions in Java programming. Not only that but Jump statements in Java are also used for checking whether the expression is true or false. It is generally used for making any decisions in Java programming.| Operators | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| && [ logical AND ] | expression1 && expression2 | (true) only if both of the expressions are true |
| || [ logical OR ] | expression1 || expression2 | (true) if one of the expressions in true |
| ! [ logical NOT ] | !expression | (true) if the expression is false and vice-versa |
Logical Operators in Java Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// && operator
System.out.println((6 > 3) && (8 > 6)); // true
System.out.println((6 > 3) && (8 < 6)); // false
// || operator
System.out.println((6 < 3) || (8 > 6)); // true
System.out.println((6 > 3) || (8 < 6)); // true
System.out.println((6 < 3) || (8 < 6)); // false
// ! operator
System.out.println(!(6 == 3)); // true
System.out.println(!(6 > 3)); // false
}
}
Output
true
false
true
true
false
true
false
Unary Operator in Java
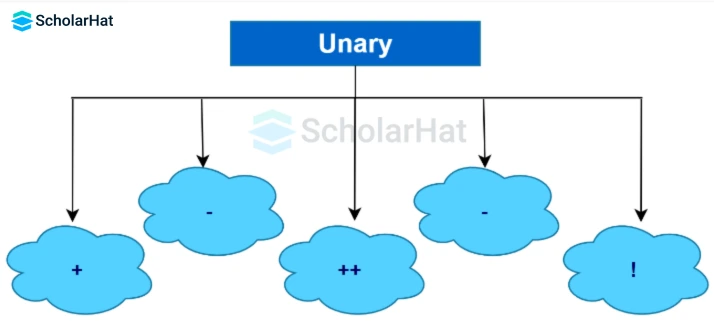
Unary Operators in Java are used in only one operand. There are various types of Unary Operators in Java, such as
| Operators | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Unary Plus |
| - | Unary Minus |
| ++ | Increment operator |
| -- | Decrement Operator |
| ! | Logical complement operator |
Unary Operator in Java Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declare variables
int a = 13, b = 13;
int result1, result2;
// original value
System.out.println("Value of a: " + a);
// increment operator
result1 = ++a;
System.out.println("After increment: " + result1);
System.out.println("Value of b: " + b);
// decrement operator
result2 = --b;
System.out.println("After decrement: " + result2);
}
}
Output
Value of a: 13
After increment: 14
Value of b: 13
After decrement: 12Bitwise Operators in Java
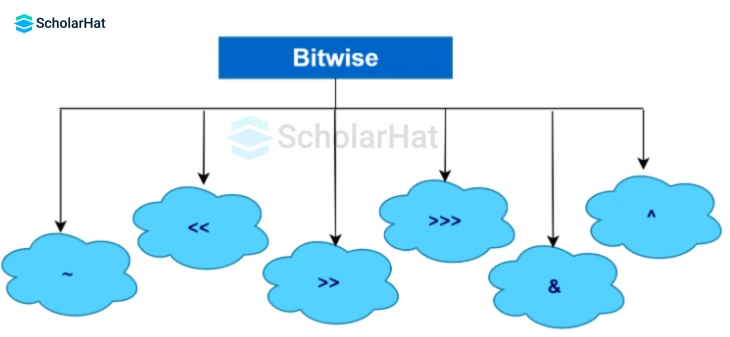
Bitwise Operators in Java are used to assist the performance of the operations on individual bits. There are various types of Bitwise Operators in Java, such as. We will see the working of the Bitwise Operators in the Java Online Compiler.
| Operators | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| ~ | Bitwise Complement |
| << | Left shift |
| >> | Right shift |
| >>> | Unsigned Right shift |
| & | Bitwise AND |
| ^ | Bitwise exclusive OR |
Bitwise Operators in Java Example
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "ScholarHat";
boolean result;
// checks if str is an instance of
// the String class
result = str instanceof String;
System.out.println("Is str an object of String? " + result);
}
}
Output
Is str an object of String? trueComparison Operators in Java
To compare two values (or variables), comparison operators are used. This is crucial to programming since it facilitates decision-making and the search for solutions. A comparison's return value is either true or false. These are referred to as "Boolean values."
| Operators | Operations |
|---|---|
| == | Equal to |
| != | Not equal |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
Example
public class ComparisonOperatorsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 20;
// Equal to (==) operator
boolean isEqual = (num1 == num2);
System.out.println("num1 is equal to num2: " + isEqual);
// Not equal to (!=) operator
boolean isNotEqual = (num1 != num2);
System.out.println("num1 is not equal to num2: " + isNotEqual);
// Greater than (>) operator
boolean isGreaterThan = (num1 > num2);
System.out.println("num1 is greater than num2: " + isGreaterThan);
// Less than (<) operator
boolean isLessThan = (num1 < num2);
System.out.println("num1 is less than num2: " + isLessThan);
// Greater than or equal to (>=) operator
boolean isGreaterThanOrEqual = (num1 >= num2);
System.out.println("num1 is greater than or equal to num2: " + isGreaterThanOrEqual);
// Less than or equal to (<=) operator
boolean isLessThanOrEqual = (num1 <= num2);
System.out.println("num1 is less than or equal to num2: " + isLessThanOrEqual);
}
}
Output
num1 is equal to num2: false
num1 is not equal to num2: true
num1 is greater than num2: false
num1 is less than num2: true
num1 is greater than or equal to num2: false
num1 is less than or equal to num2: true
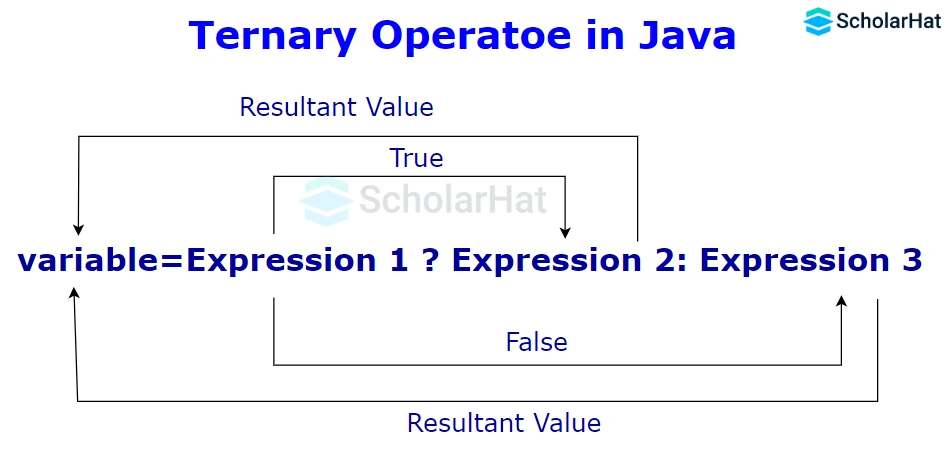
Ternary Operators in Java
The only conditional operator that accepts three operands is the ternary operator in Java. Java programmers frequently use it as a one-line alternative to the if-then-else expression. The ternary operator can be used in place of if-else statements, and it can even be used to create switch statements with nested ternary operators. The conditional operator uses less space and aids in writing if-else statements as quickly as possible even if it adheres to the same algorithm as an if-else statement
Example
public class TernaryOperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 20;
// Using the ternary operator to find the maximum of two numbers
int max = (num1 > num2) ? num1 : num2;
System.out.println("The maximum number is: " + max);
}
}
Output
The maximum number is: 20Operator Precedence in Java
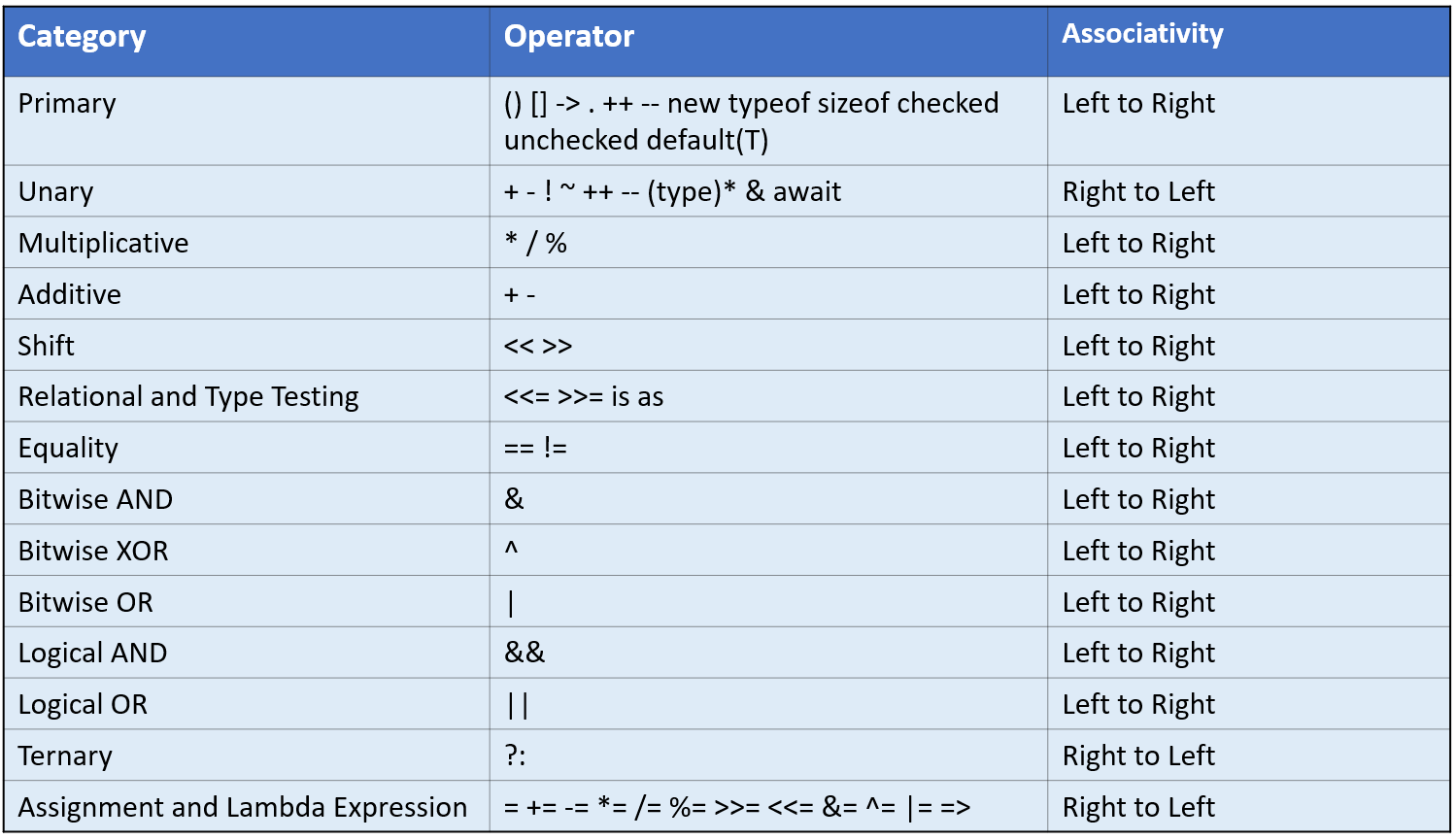
Summary
Operators are the building blocks of Java expressions, enabling developers to perform arithmetic, comparison, logical, and bitwise operations efficiently. Understanding different types of operators: arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, and more, is essential for writing clear and correct code.
Full-stack Java jobs pay ₹15–30 LPA in just 2 years. Don’t wait, Enroll now in our Java Full Stack Training to grow fast.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.