What is Multiple Inheritance in Java with Example
The Multiple Inheritance in Java
Let's understand multiple inheritance in Java, a topic that's frequently addressed yet can be hard. Unlike some other programming languages, such as C++, Java does not offer multiple inheritance through classes. That means a class cannot directly inherit from multiple classes. Why? Mainly to avoid complexity and ambiguity, such as when two parent classes have methods with the same signature. But don't worry Java has a solution for this: interfaces, which provide the benefits of multiple inheritance while being clean and straightforward!
But In this Java Tutorial, we are going to discuss specifically Multiple Inheritance in Java, which will include why multiple inheritance in Java is not supported and how to achieve multiple inheritances in Java, and more on. Learn Java basics to earn ₹10 LPA fast. Don’t wait, Enroll now in our Free Java Course with Certification to kickstart your tech career!
| > Top Java Interview Questions And Answers > Java Multithreading Interview Questions |
What is Multiple Inheritance?
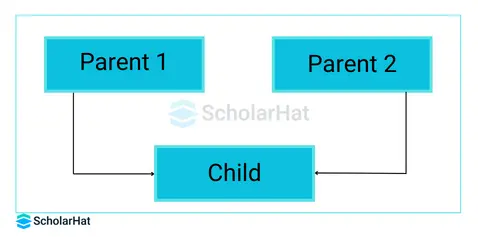
- Multipleinheritanceisthe capability of creating a single class with characteristics of multiple superclasses.
- In popular object-oriented programming languages such as C++, we can achieve multiple inheritance very easily
- But in the case of Java, It doesn’t provide support for multiple inheritances in classes.
- Java doesn’t support multiple inheritances because it can lead to a diamond problem
- We will talk about the diamond problem in multiple inheritancelaterinthis article.
- Before that, we will see how other types of inheritance support Java.
| Note: Java doesn’t support Multiple Inheritance |
Types of Inheritance in Java:
There are more 4 types of Inheritance in Java except Multiple inheritance
- Single inheritance in Java.
- Multi-level inheritance in Java.
- Hierarchical Inheritance in Java.
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java.
1. Single Inheritance in Java:
- As the heading shows, just one class is subject to this kind of inheritance.
- The parent shares its characteristics with just one child class.
- The attributes in this sort of inheritance are only shares from one parent class.
- In this inheritance Code, reusability and the implementation of new features are made easier.
- The following shows how single inheritance can be achieved:

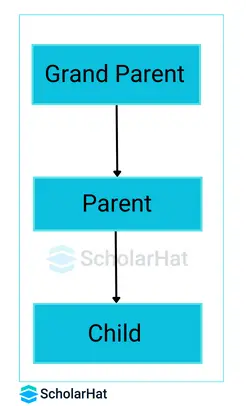
2. Multi-level inheritance In Java.
- In Multi-Level Inheritance, a class extends to another class that is already extended from another class.
- For example, if A daughter extends the feature of the mother and the mother extends from the grandmother, then this scenario is known to follow Multi-level Inheritance.
- As the name shows, numerous base classes are involved in multi-level inheritance.
- The newly derived class from the parent class becomes the base class for another newly derived class.
- The inherited features in multilevel inheritance in Java likewise come from several base classes.
- The following shows how single inheritance can be achieved:
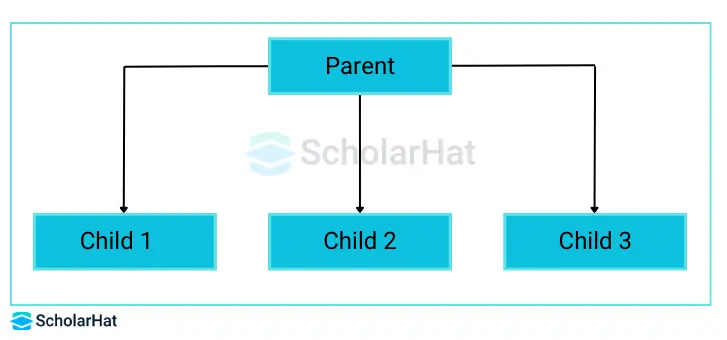
3. Hierarchical Inheritance in Java.
- Hierarchical inheritance in Java is the sort of inheritance when many subclasses derive from a single class.
- In short, It is a mixture of various inheritance types called hierarchical inheritance.
- Because so many classes are descended from a single superclass,
- Since It is different from multilevel inheritance.
- This process makes dynamic polymorphism.
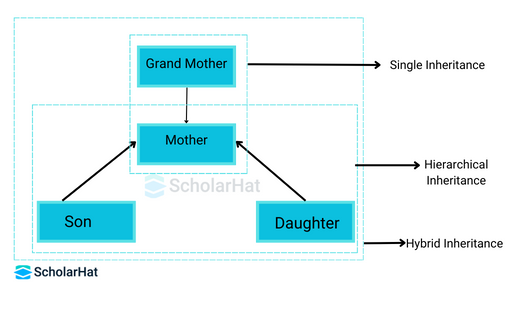
4. Hybrid Inheritance in Java.
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java is a combination of all inheritances.
- Single and hierarchical inheritances or multiple inheritance.
- For example, if we have class Son and class Daughter that extend class Mother and then there is another class Grand Mother that extends class Mother, then this type of Inheritance is known as Hybrid Inheritance.
- Why? Because we observe that there are two kinds of inheritance here- Hierarchical and Single Inheritance.
- In short, A hybrid inheritance combines more than two inheritance types, such as multiple and single.
Why is Multiple Inheritance Not Supported in Java?
- Java doesn’t support multiple inheritances in classes because it can create a diamond problem.
- To understand the diamond problem easily, let’s assume that multiple inheritances can be supported in Java.
- In that case, we will imagine a class hierarchy like the below image.
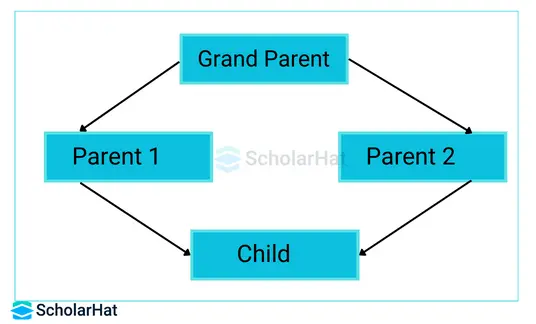
Suppose we have two classes Mother and Uncle which have the same method feature(). If multiple inheritance is possible then the Grandchild class can inherit data members (properties) and methods (behavior) of both Mother and Uncle classes. Now, the Grandchild class has two feature() methods inherited from Mother and Uncle. The problem occurs in a method call, when the feature() method is called with the Grandchild class object which method will be called, will it be of Mother or Uncle? This is an ambiguty problem because of which multiple inheritance is not supported in Java.
Example -1
Example:
import java.util.*;
class Mother{
public void feature(){
System.out.println("Feature method inside Mother.");
}
}
class Uncle{
public void feature(){
System.out.println("Feature method inside Uncle.");
}
}
//let multiple inheritance be possible.
public class GrandChild extends Mother, Uncle{
public static void main(String args[]){
GrandChild obj = new GrandChild();
//Ambiguity problem in method call which class display() method will be called.
obj.feature();
}
}
Output:
Mother.java:15: error: '{' expected
public class GrandChild extends Mother, Uncle{
^
1 error
error: compilation failed
Now the question is what is the solution to this diamond problem? And how to achieve multiple inheritance in Java. Yes, we can achieve multiple inheritance in Java by using Interfaces. Now let's see how the interface works in multiple inheritance with demonstration in the Java Compiler.
Multiple Inheritance in Java Using Interface
- Multiple Inheritance is a feature of object-oriented programming
- Where a child class can inherit properties of more than one parent class.
- The problem occurs when methods with the same signature or feature exist in both the parent classes.
- On calling the method, the compiler cannot determine which parent class method to call and even on calling which class method gets the priority.
- In that case, we use the interface in multiple inheritances.
interface Parent1 {
void mother();
}
interface Parent2 {
void father();
}
class Family implements Parent1, Parent2 {
public void mother() {
System.out.println("Mothers Feature");
}
public void father() {
System.out.println("Fathers Feature");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Family a = new Family();
a.mother();
a.father();
}
}
Output:
Mothers Feature
Fathers Feature
Example 2
// Java Program to Illustrate Unsupportance of
// Multiple Inheritance
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// First Parent class
class Parent1 {
// Method inside first parent class
void Enjoy() {
// Print statement if this method is called
System.out.println("Parent1");
}
}
// Class 2
// Second Parent Class
class Parent2 {
// Method inside first parent class
void Enjoy() {
// Print statement if this method is called
System.out.println("Parent2");
}
}
// Class 3
// Trying to be child of both the classes
class Test extends Parent1, Parent2 {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating object of class in main() method
Test t = new Test();
// Trying to call above functions of class where
// Error is thrown as this class is inheriting
// multiple classes
t.Enjoy();
}
}
Output
A compilation error is thrown. As shown from the code above, on calling the method Enjoy() using Test object will cause complications such as whether to call Parent1’s Enjoy() or Parent2’s Enjoy() method. Now we can achieve the result by using the interfaceMultiple Inheritance in Java Using Interface
// Interface 1
interface Parent1 {
void fun();
}
// Interface 2
interface Parent2 {
void fun();
}
// Class implementing both interfaces
class Test implements Parent1, Parent2 {
// Overriding fun() method from both interfaces
public void fun() {
System.out.println("Child Class");
}
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test t = new Test();
t.fun();
}
}
Output
Child ClassSyntax of implementing Multiple interfaces:
Syntax:
Class Grand_Parent
{
---
----
}
class Parent Extends Grand_Parent
{
----
----
}
class Child Extend Parent
{
-----
-----
}
An Alternative to Multiple Inheritance in Java
- The alternative to multiple inheritance is known as an interface.
- Java does not support multiple inheritance of classes, meaning a class cannot inherit from more than one class.
- So instead, Java uses interfaces to achieve a similar effect.
- An interface in Java is a collection of abstract methods, which are implemented by classes that implement the interface.
- Likewise, abstract classes and interfaces cannot be used to create objects
- Interface methods do not have a body, Because the body is provided by the "implement" class.
- On implementation of an interface, we must override all of its methods
- Interface methods are by default stays abstract and public
- Interface attributes are by default public, static, and final
- An interface cannot contain a constructor that's why it cannot be used to create objects.
Conclusion
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.