18
AprHow To Reverse A String In Java: Explained
Reverse A String In Java
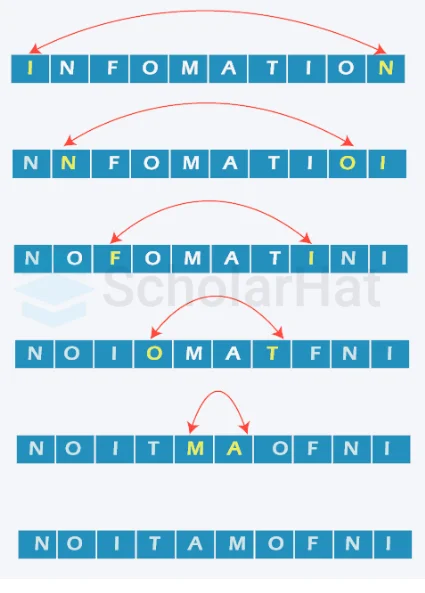
To reverse a string in Java word by word, you can split the string into an array of words using the split() method, reverse the order of the words in the array, and then join them back into a single string using StringBuilder or String. join(). This process allows you to maintain the original words' order while reversing their sequence in the string.
In this Java tutorial, We are gonna see how to reverse a string in Java word by word, so bring yourself to the present and understand this article carefully.
Gain the skills needed for top developer roles by joining our Free Java Certification CourseTraining program.
Understanding Strings in Java
- Strings are objects in Java that represent character sequences.
- They cannot have their content changed once they are created since they are immutable.
- Java has two mutable options, StringBuilder and StringBuffer, for effective string manipulation.
- For understanding strings there are two main points to be considered first they are as follows.
1. Strings' immutability
Because Java allows strings to be immutable, once a string object is created, its contents cannot be changed. A new string object is actually created by any operation that seems to modify an existing string.2. Overview of StringBuffer and StringBuilder
In Java, String has mutable counterparts called StringBuilder and StringBuffer. They are effective for operations like concatenation and reverse because they offer ways to change strings without generating new objects.
Methods to Reverse a String in Java
In Java programming, reversing a string is a frequently used action that can be accomplished in various ways.
Here are several Java methods for reversing a string, along with corresponding code samples with output.
- Using the StringBuilder Class and Its Description
- Using Recursion
- Using Iterative Approach
- Using Stack
- Using Collections Framework
1 Using the StringBuilder Class
Java's StringBuilder class is a flexible tool for constructing changeable strings. It offers a number of ways to work with string content, one of which is an inbuilt method named reverse() that allows you to reverse a string.
How To for Reversing a String Making Use of StringBuilder
- Initialize a StringBuilder object with the original string after creating it.
- Make use of the StringBuilder object's reverse() method.
- Return the StringBuilder object to its original string form.
Example
public class ReverseStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String original = "Welcome to Scholarhat";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(original);
String reversed = sb.reverse().toString();
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed);
}
}
Output
Reversed String: tahralohcS ot emocleW
2. Using Recursion
How to Reversing a String Making Use of Recursion-Based String Reversal
- Define a recursive function that accepts the string as an input along with its length.
- Return the string if its length is one or less.
- If not, concatenate the first character at the end and run the procedure recursively with the substring.
| Read More: Recursion in Data Structures |
Example
public class ReverseStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String original = "Welcome to Scholarhat";
String reversed = reverseString(original);
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed);
}
public static String reverseString(String str) {
if (str.isEmpty()) {
return str;
}
return reverseString(str.substring(1)) + str.charAt(0);
}
}
Output
Reversed String: tahralohcS ot emocleW
3. Using Iterative Approach
- Set up a blank string or StringBuilder object from scratch.
- Reverse the order of the original string's loops.
- To the newly created string or StringBuilder object, append each character.
Example
public class ReverseStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String original = "Welcome to Scholarhat";
String reversed = "";
for (int i = original.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
reversed += original.charAt(i);
}
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed);
}
}
Output
Reversed String: tahralohcS ot emocleW
4. Using Stack
- Place each character in the string into the corresponding stack.
- Add each character to a new string or StringBuilder object by popping it off the stack.
Example
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReverseStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String original = "Welcome to Scholarhat";
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for (char c : original.toCharArray()) {
stack.push(c);
}
StringBuilder reversed = new StringBuilder();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
reversed.append(stack.pop());
}
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed.toString());
}
}
Output
Reversed String: tahralohcS ot emocleW
5. Using Collections Framework
- Convert the string to a list of characters.
- Use Collections.reverse() to reverse the list.
- Convert the list back to a string.
| Read More: Collection Framework in Java |
Example
import java.util.*;
public class ReverseStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String original = "Welcome to Scholarhat";
List charList = new ArrayList<>();
for (char c : original.toCharArray()) {
charList.add(c);
}
Collections.reverse(charList);
StringBuilder reversed = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : charList) {
reversed.append(c);
}
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed.toString());
}
}
output
Reversed String: tahralohcS ot emocleW
3. Comparing the Effectiveness of Various Techniques
Analysis of Space Complexity
- StringBuilder: The reversed string has an O(n) space complexity.
- Recursion: Because of the recursion stack, space complexity is O(n).
- Iterative Approach: For the inverted string, the space complexity is O(n).
- Stack: For both the stack and the inverted string, the space complexity is O(n).
- Framework for Collections: For both the list and the inverted string, the space complexity is O(n).
Top Applications for Every Method
- StringBuilder: Perfect for the majority of ordinary situations where simplicity and efficiency are needed.
- Recursion: Ideally used in instructional settings or where the nature of the problem calls for a recursive solution.
- Iterative Approach: Practical when you want a simple implementation and memory overhead is an issue.
- Stack: Appropriate for handling issues or ideas pertaining to stacks.
- Collections Framework: Useful in scenarios when you wish to make use of pre-existing tools and are already working with lists.
| Read More: String in Java Interview Questions with Answers |







