18
AprSuper Keyword in Java Explained
Understanding the super Keyword in Java
The super keyword is one of the most important features of Java. However, Java is an object-oriented programming language with strong inheritance management and the utilization of features. The super keyword is an essential feature of Java inheritance since it allows a subclass to communicate with its superclass.
In this Java tutorial, we will learn all about the super keyword in Java including the usage of the super keyword in Java, and the advantages of the super keyword in Java. So remove all your distractions, and let's focus on What is the super Keyword?
Fast-track your full-stack development journey by enrolling in our Java Full Stack Developer Certification Course now!
What is the super Keyword in Java?
- In Java, the super keyword enables referencing a subclass's parent or superclass.
- It is frequently used to gain access to superclass members (fields or methods) that the subclass has overridden.
- Super.methodName() allows you to invoke the superclass's method from within a subclass.
- In order to initialize inherited members, super() is also used to invoke the superclass constructor from the subclass constructor.
- To put it briefly, this super keyword is essential for programmers who wish to preserve inheritance hierarchies and allow code reuse in object-oriented programming.
| Related Article: - What Is this Keyword in Java? |
Usage of Java Super Keyword
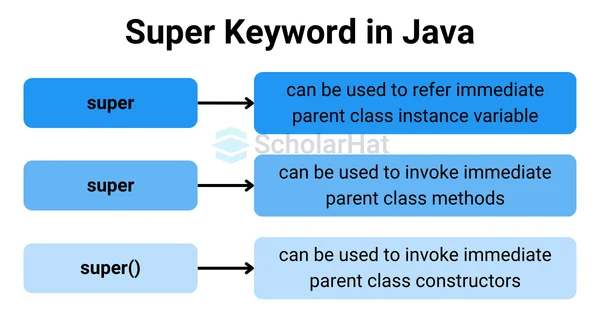
It is mostly used in the following three ways :
- Use of super with Variables(Access the variables and methods of the superclass)
- Use of super with Methods(Address naming problems between members of the superclass and subclass)
- Use of super with Constructors(Invoke the constructor of the superclass)
1. Use of super keyword with Variables
The super keyword can be used to access the variable in the superclass if the subclass has a variable with the same name as the superclass's variable.
class Animal {
String name = "Animal";
}
class Dog extends Animal {
String name = "Dog";
void display() {
System.out.println("Name in superclass: " + super.name);
System.out.println("Name in subclass: " + name);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.display();
}
} Output
Name in superclass: Animal
Name in subclass: Dog
2. Use of Super keyword with Methods
class Animal {
void display() {
System.out.println("I am an animal lover");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void display() {
System.out.println("I have a dog");
}
void printMessage() {
super.display(); // Calls the display() method of Animal class
display(); // Calls the display() method of Dog class
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.printMessage();
}
} Output
I am an animal lover
I have a dog
3. Use of super keyword with Constructors
class Animal {
Animal(String name) {
System.out.println("Animal constructor called: " + name);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
Dog(String name) {
super(name); // Calls the constructor of Animal class
System.out.println("Dog constructor called");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog("Buddy");
}
} Output
Animal constructor called: Buddy
Dog constructor called
Features of Super Keyword in Java
- A subclass's constructor needs to call the parent class's constructor when it is created, which is why super is used to call a superclass constructor. Using the super() keyword, which invokes the parent class' constructor, this is achieved.
- To invoke a superclass method, use super: The super keyword allows a subclass to invoke a method specified in its parent class. This comes in handy when the subclass wishes to call the method's implementation from the parent class in addition to its own.
- To access a superclass field, use super: The super keyword allows a subclass to access a field declared in its parent class.
- A constructor's super statement needs to come first: The super() declaration needs to come first in the subclass constructor when calling a superclass constructor.
- The use of super in a static situation is prohibited: In a static context, like a static method or a static variable initializer, the super keyword is not permitted.
- It is possible to call a parent class method using the super keyword, although it is not required. If a method is called without the super keyword, if it isn't overridden in the subclass, it will call the implementation of the parent class.
A real-world example of super keyword in Java
// Superclass Company
class Company {
String companyName;
int companySize;
Company(String companyName, int companySize) {
this.companyName = companyName;
this.companySize = companySize;
}
void displayCompanyInfo() {
System.out.println("Company Name: " + companyName);
System.out.println("Company Size: " + companySize + " employees");
}
}
// Subclass Employee extending Company
class Employee extends Company {
String employeeName;
int employeeId;
Employee(String companyName, int companySize, String employeeName, int employeeId) {
super(companyName, companySize); // invoking superclass constructor
this.employeeName = employeeName;
this.employeeId = employeeId;
}
void displayEmployeeInfo() {
super.displayCompanyInfo(); // invoking superclass method
System.out.println("Employee Name: " + employeeName);
System.out.println("Employee ID: " + employeeId);
}
}
// Main class to demonstrate
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee emp = new Employee("DotNetTricks Innovation.", 500, "Sourav Kumar", 1001);
emp.displayEmployeeInfo();
}
}
Output
Company Name: DotNetTricks Innovation.
Company Size: 500 employees
Employee Name: Sourav Kumar
Employee ID: 1001
Explanation
Advantages of Using Super Keyword
1. Access to Superclass Members
- This feature helps resolve naming disputes and guarantees that the right version is used by granting access to superclass variables and functions, even when they are overridden in a subclass.
2. Constructor Chaining
- By calling the superclass constructor via super(), the object is guaranteed to be in a consistent state and allows for the correct initialization of inherited elements prior to subclass-specific initialization.
| Read More: Constructor Chaining in Java |
3. Maintaining Inheritance
- By preserving and improving the behavior of parent classes, it promotes code reuse and preserves the "is-a" relationship in inheritance.







