jQuery Ajax Methods
In this article we are going to see about the ajax feature in jQuery, and how we can use it to get the data from the server and posting the data to the server.
What is Ajax?
Ajax stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML, it is a technique to update the web page without reloading the entire page. Behind the scene, it will send and receive the data from server.
Any event occur in web page will create an XMLHttpRequest object by JavaScript, this object will send a request to a server, the server process the request and send a response back to a web page, finally, the response is read by JavaScript.
jQuery and Ajax
jQuery provides several functions which allow us to make AJAX request from a web page.
$(selector).load() - load data from the server
$.get() & $.post() – get raw data from the server
$.getJSON() - get the JSON data
$.ajax() - Provides core functionality
Read More - jQuery Interview Questions for Freshers
jQuery AJAX Advantages
jQuery AJAX having the following advantages :
It allows us to take out entire page reload and give us the flexibility to load only a part of the page
Simple API
Cross-Browser Support
GET and POST supported
Load JSON, XML, HTML or even script and many more
jQuery load() function
$(selector).load(url,data,callback) allows HTML content to be loaded from the server. Based on overload of load(), we can pass URL , with data and callback function.
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#myButton").click(function(){
$("#myDiv").load('Sample.html')
})
});
The load() is above code is use to grab the html data from sample.html and append it to myDiv element
Example Code
<button id="btnServerData">Get Server Data</button> <div id="divHtml">
$(document).ready(function () {
$('#btnServerData').click(function () {
$("#divHtml").load('Sample.html'); // Load with Sample URL
})
});
Sample.Html<h2> Hi I'm sample </h2> <div id="sampleDiv"> </div>Result in Browser
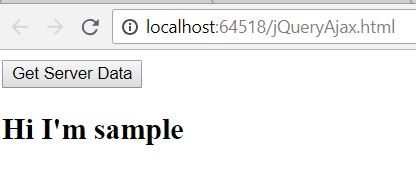
Figure 2.1 Got the sample HTML content by clicking the button
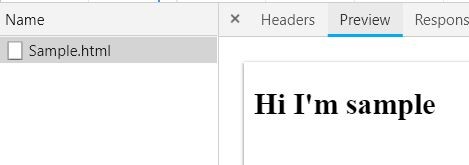
Figure 2.2 Service call traced in browser developer tool network section
Loading with selector
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#myButton").click(function(){
$("#myDiv").load('Sample.html #myElement')
})
});
The above code is used to filter the element from the URL sample.html using the selector. Basically it will download entire page and filter the element
$(document).ready(function () {
$('#btnServerData').click(function () {
$("#divHtml").load('Sample.html #divHtml'); // Load with Sample URL with selector
})
});
This will be useful when you cache the entire page and playing with multiple element of the page
load(url, data)
In the load() function sata can be passed thorugh the URL as given below.
$("#myDiv").load('GetCustomer.cshtml, {message:”Hello”})
$("#divHtml").load("/Home/SendReceivedValue", { inputString: "Hello" })
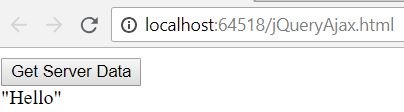
Figure 2.3 Ajax call with data using load()
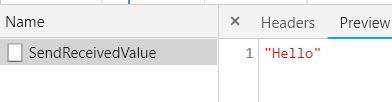
Figure2.4 Service call traced in inspect element
load() with callback function
$("#myDiv").load('GetCustomer.cshtml',function(response,status,xhr){
if(status == "success"){
}});
//status: gives the status of the call
//Xhr: XML Http Request
$("#divHtml").load("/Home/SendReceivedValue", { inputString: "Hello" }, function (response, status, xhr) {
if (status = "success") {
alert("Call Success : " + xhr.status);
}
});
})
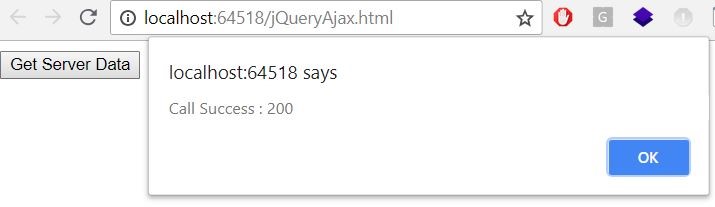
Figure 2.5 Call back function with alert box
jQuery Ajax GET Request
$.get() gives you more flexibility for making these GET request $.get(url,data,callback,data type) can retrieve data from a server
By comparing with load() the get() contains an extra overload called data type, where you can mention the data type of the data when you want to receive from server.
data : It is used to pass data to the server.
data type : It is used to define the type of the data received from server it can be HTML, string, JSON or XML and many more
Important Note
The get() will automatically convert to ajax() behind the scene which we discuss later in this article
$(document).ready(function () {
$('#btnServerData').click(function () {
$.get("Sample.html", function (response) {
$("#divHtml").html(response)
});
})
});
Result in Browser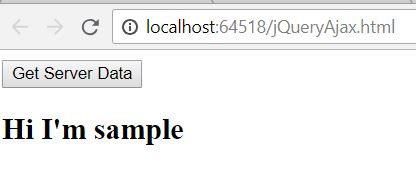
Figure 3.1 Fetching the HTML content from Sample.html
$.get() with Data
$('#btnServerData').click(function () {
$.get("/Home/GetEmployee", { empId: 1 }, function (response) {
$("#divHtml").html(JSON.stringify(response))
}); })
From the above code it is obvious the data Employee id passed to the action to filter the Employee List based on given Id.
C# Code public ActionResult GetEmployee(int empId)
{
List<Employee> employees = new List<Employee>();
employees.Add(new Employee { EmployeeId = 1, FirstName="Arun", LastName = "Kumar" });
employees.Add(new Employee { EmployeeId = 2, FirstName="Govind", LastName = "Raj" });
return Json(employees.Where(e => e.EmployeeId == empId),JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
$.getJSON(url,data,callback) will retrieve the JSON data from a server
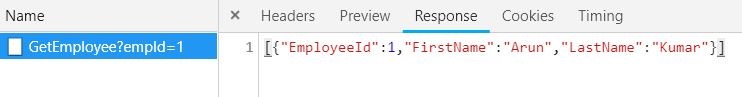
$.getJSON("/Home/GetEmployee", { empId: 1 }, function (response) {
alert(response[0].FirstName)
});
Result in Browser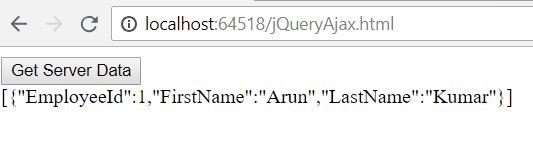
Figure 3.1 Fetching the JSON data from MVC action
Tracing Using Inspect Element
Important Note
The data will be passed as a Query string in Get Request, the amount of data pass to the server will be limited based on browser.
Figure 3.2 Http call trace in browser developer tool
jQuery Ajax Post Request
Post request will not be cached in the browser, we can post large amount to data, the api syntax is identical to get(). It is mainly used for data insertion and update in server Unlike get(), post() will pass the data to server through request body. $.post(url,data,callback,data type) can post data to a server and to retrieve the result.
Example Code
$.post("/Home/PostEmployee", { EmployeeId: 1, FirstName: "Arun", LastName: "Kumar" }, function (response) {
$("#divHtml").html("FirstName:" + response.FirstName)
});
C# Code public ActionResult PostEmployee(int EmployeeId, string FirstName, string LastName )
{
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.EmployeeId = EmployeeId;
employee.FirstName = FirstName;
employee.LastName = LastName;
return Json(employee);
}
Result in Browser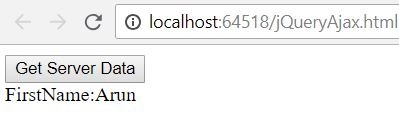
Figure 4.1 Posting the data and retrieving it using post()
Fiddler : Tracing Request and Response
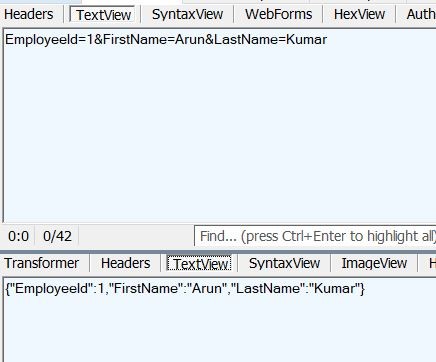
Figure 4.2 HTTP call trace in Fiddler
Fiddler is proxy to track the traffic between our browser and server, refer https://www.telerik.com/fiddler to learn more about fiddler
jQuery ajax() Method
The load(), get() and post() are relay on ajax() behind the scene. ajax() has lot of different property, some of the key property are :
contentType – What is the type of data going to the server
data – data passing to the server
datatype – type od data coming back from server
error – call back can hook up if there is erroring request
success – call back can hook up after success response from the server
type – we need mention whether the request is GET or POST, by default the type will be GET
$.ajax({
url : ‘/Home/PostEmployee ’
data : data,
type:’POST’,
dataType: ‘json’,
success : function(data,status,xhr){},
error:function(data,status,xhr){}
})
<label> First Name: </label> <input type="text" id="txtFirstName" /> <label> Last Name: </label> <input type="text" id="txtLastName" /> <br /> <br /> <button id="btnServerData">Submit</button> <br /> <br /> <hr /> <div id="divHtml" style="color:blueviolet"> </div>
$('#btnServerData').click(function () {
var employeeData = { EmployeeId: 1, FirstName: "Gowtham", LastName: "K" }
$.ajax({
url: "/Home/PostEmployee",
data: employeeData,
dataType: 'json',
type:'POST'
success: function (data, status, xhr) {
debugger;
$("#divHtml").html("Inserted Value:" + data.FirstName + " " + data.LastName);
},
error: function (data, status, xhr) {
}
})
});
The above code will get a data from the first name and last name text box then post to server using $.ajax() API when the user click on submit button
C# Code public ActionResult PostEmployee(int EmployeeId, string FirstName, string LastName )
{
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.EmployeeId = EmployeeId;
employee.FirstName = FirstName;
employee.LastName = LastName;
return Json(employee);
}
Result in Browser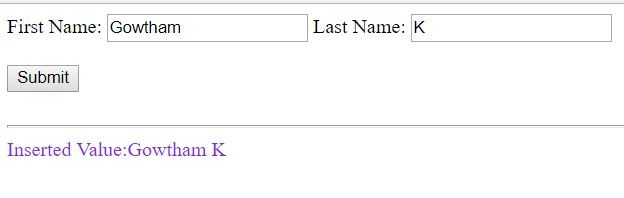
Figure 5.1 Post the data using Ajax()
GET Type in ajax()
<button id="btnServerData">Get Employee List</button> <br /> <br /> <hr /> <table id="results"></table>
$.ajax({
url: "/Home/GetEmployeeList",
// data: employeeData,
dataType: 'json',
type:'GET',
success: function (data, status, xhr) {
var len = data.length;
var firstRow = '<tr><th>Employee Id</th><th>First Name</th><th>Last Name</th></tr>';
$('#results').append(firstRow);
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
var row = '<tr>'+'<td>' + data[i].EmployeeId + '</td>' +'<td>' + data[i].FirstName + '</td>' + '<td>' + data[i].LastName + '</td>'+ '</tr>';
$('#results').append(row);
}
},
error: function (data, status, xhr) {
//console error here
},
});
Result in Browser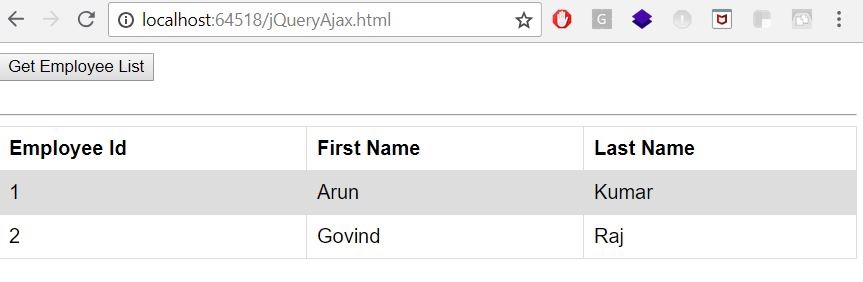
Figure 5.2: Get data and populating in table using ajax()
While clicking on button the Get request is send to server and server respond back with list of employee data then in success call back function we created a dynamic table to load the content.
Important Note
'GET' is default type of ajax()
Summary
In above article, we have learned about how to work with jQuery Ajax and how we can use it's various functions like load(), get(), getJSON(), post(), ajax() which support the different kind of datatypes like JSON, XML and HTML.