11
JulDependency Injection in ASP.NET MVC using Unity IoC Container
In the previous articles, I have explained about the Understanding IoC, DI and Service Locator Pattern and IoC or DI Containers. Before proceeding with this article, please go through my last articles. In this article, you will learn how to use inUnity DI Container your Dependency Injection in ASP.NET MVC application to make the service layer and Presentation layer loosely coupled.
Step 1 - Create a new ASP.NET MVC Application
The first step is to create a new ASP.NET MVC Application using Visual Studio 2012 or higher as shown below:
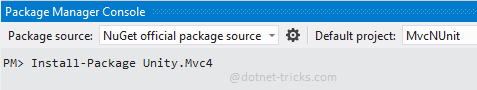
Step 2- Install Unity Container
Now install Unity container using Unity.Mvc4 (for MVC4) or Unity.Mvc5 (for MVC5) nuget package as per your ASP.NET MVC versions, using the NuGet Package Manager console tool as shown below:
Note
Make sure you are connected with internet.
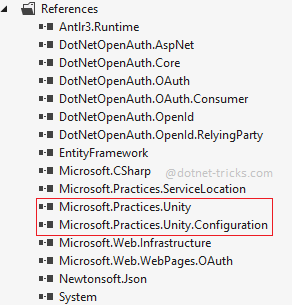
When it will be installed successfully, you will find the following two references add to your project and a Bootstrapper.cs class file in MVC4 and UnityConfig.cs file in MVC5 at a project level, as shown below:
//mvc4
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Practices.Unity;
using Unity.Mvc4;
namespace MvcNUnit
{
public static class Bootstrapper
{
public static IUnityContainer Initialise()
{
var container = BuildUnityContainer();
DependencyResolver.SetResolver(new UnityDependencyResolver(container));
return container;
}
private static IUnityContainer BuildUnityContainer()
{
var container = new UnityContainer();
// register all your components with the container here
// it is NOT necessary to register your controllers
// e.g. container.RegisterType<ITestService, TestService>();
RegisterTypes(container);
return container;
}
public static void RegisterTypes(IUnityContainer container)
{
}
}
}
//mvc5
using BAL;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Unity;
using Unity.Mvc5;
namespace UI
{
public static class UnityConfig
{
public static void RegisterComponents()
{
var container = new UnityContainer();
// register all your components with the container here
// it is NOT necessary to register your controllers
// e.g. container.RegisterType<ITestService, TestService>();
DependencyResolver.SetResolver(new UnityDependencyResolver(container));
}
}
}
Step 3- Add a New Service Layer
Add a new Folder in the project of the name Repository and add the following interface and a class in this folder:
//Product.cs
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
//IProductRepository.cs
public interface IProductRepository
{
IEnumerable<Product> GetAll();
Product Get(int id);
Product Add(Product item);
bool Update(Product item);
bool Delete(int id);
}
//ProductRepository.cs
public class ProductRepository : IProductRepository
{
private List<Product> products = new List<Product>();
private int _nextId = 1;
public ProductRepository()
{
// Add products for the Demonstration
Add(new Product { Name = "Computer", Category = "Electronics", Price = 23.54M });
Add(new Product { Name = "Laptop", Category = "Electronics", Price = 33.75M });
Add(new Product { Name = "iPhone4", Category = "Phone", Price = 16.99M });
}
public IEnumerable GetAll()
{
// TO DO : Code to get the list of all the records in database
return products;
}
public Product Get(int id)
{
// TO DO : Code to find a record in database
return products.Find(p => p.Id == id);
}
public Product Add(Product item)
{
if (item == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("item");
}
// TO DO : Code to save record into database
item.Id = _nextId++;
products.Add(item);
return item;
}
public bool Update(Product item)
{
if (item == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("item");
}
// TO DO : Code to update record into database
int index = products.FindIndex(p => p.Id == item.Id);
if (index == -1)
{
return false;
}
products.RemoveAt(index);
products.Add(item);
return true;
}
public bool Delete(int id)
{
// TO DO : Code to remove the records from database
products.RemoveAll(p => p.Id == id);
return true;
}
}
The above repository acts as a new layer and will be used to decouple the model layer from the controller layer.
Step 4- Register the Dependency in Bootstrapper.cs or UnityConfig.cs file
Replace BuildUnityContainer method's content with the following code that registers the ProductRepository Service. You can also register the Product Controller in which we will inject the dependency, but it is optional.
private static IUnityContainer BuildUnityContainer()
{
var container = new UnityContainer();
// register all your components with the container here
// it is NOT necessary to register your
// e.g. container.RegisterType<ITestService, TestService>();
//registered dependency here
container.RegisterType<IProductRepository, ProductRepository>();
RegisterTypes(container);
return container;
}
//mvc5
using BAL;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Unity;
using Unity.Mvc5;
namespace UI
{
public static class UnityConfig
{
public static void RegisterComponents()
{
var container = new UnityContainer();
// register all your components with the container here
// it is NOT necessary to register your controllers
// e.g. container.RegisterType<ITestService, TestService>();
//registered dependency here
container.RegisterType<IUnitOfWork, UnitOfWork>();
DependencyResolver.SetResolver(new UnityDependencyResolver(container));
}
}
}
Step 5- Inject Service to Controller
Now inject the dependency for the IProductRepository interface using the Product Controller's constructor as shown below:
public class ProductController : Controller
{
readonly IProductRepository repository;
//inject dependency
public ProductController(IProductRepository repository)
{
this.repository = repository;
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
var data = repository.GetAll();
return View(data);
}
//Other Code
}
Step 6 – Setup Dependency Injection with Unity in Global.asax.cs
Now, setup the Bootstrapper or UnityConfig class with in the Application_Start method so that it can initialize all dependencies. This will be done by calling Initialise() method of the Bootstrapper class or RegisterComponents() methods of UnityConfig.cs class as shown below:
//mvc4
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
WebApiConfig.Register(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration);
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
AuthConfig.RegisterAuth();
//Setup DI
Bootstrapper.Initialise();
}
//mvc5
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
// Setup DI
UnityConfig.RegisterComponents();
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
}
Step 7- Run the Application and see how it works
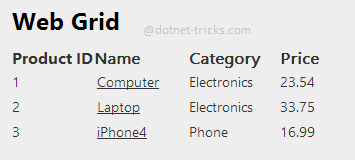
What do you think?
I hope you will enjoy the tips while programming with ASP.NET MVC. I would like to have feedback from my blog readers. Your valuable feedback, question, or comments about this article are always welcome.









