30
DecTop 50 MySQL Interview Questions and Answers
MySQL is one of the most widely used relational database management systems, known for its reliability, speed, and flexibility. It plays a vital role in handling and managing data for web applications, making it a must-know tool for developers and database administrators. Whether you are just starting or looking to sharpen your skills, understanding MySQL is a big step forward.
In this MySQL tutorial, I will walk you through some of the most common MySQL interview questions. Do not worry. We will keep it simple, clear, and easy to follow! By the end, you will feel more confident and ready to tackle any interview that comes your way. Ready to dive in and learn more? Let us get started!
MySQL Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
1. What is MySQL? How does it get differentiated from other relational databases?
MySQL is a multithreaded, multi-user, open-source relational database management system based on Structured Query Language(SQL). It can run on various platforms like Windows, Linux & UNIX. It is highly scalable and reliable, making it the most popular and widely used open-source database.
Factors that differentiate MySQL from other relational databases are:
- Free to use – MySQL is open-source, but databases like Oracle need a license.
- Faster performance – MySQL is quick for simple tasks, while PostgreSQL handles complex queries better.
- Easy to use – MySQL is simple to set up, but SQL Server needs more steps.
- Different storage engines – MySQL lets you choose, but PostgreSQL has only one main engine.
- Big community – MySQL has more free help, but Oracle mainly has paid support.
2. Differentiate MySQL from SQL.
The Difference Between SQL and MySQL is that SQL is a language used for managing and querying data in databases, while MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that uses SQL for data manipulation and management.
| SQL | MySQL |
| It is a structured query language that manages the relational database management system. | It is a relational database management system that uses SQL. |
| It is not an open-source language. | MySQL is an open-source platform. It allows access to anyone. |
| SQL supports XML and user-defined functions. | It doesn’t support XML and any user-defined functions |
| SQL can be implemented in various RDBMS such as PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server, and others. | MySQL is a specific implementation of an RDBMS that uses SQL for querying and managing databases. |
| SQL itself is not a product and doesn’t have a license. It’s a standard language. | MySQL is open-source and available under the GNU General Public License (GPL). |
3. What are SQL commands? Classify the SQL commands.
SQL commands are a set of instructions used to interact with databases like SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, etc. These commands are responsible for creating and manipulating the database, as well as providing access rights to specific users.
Classification of SQL Commands
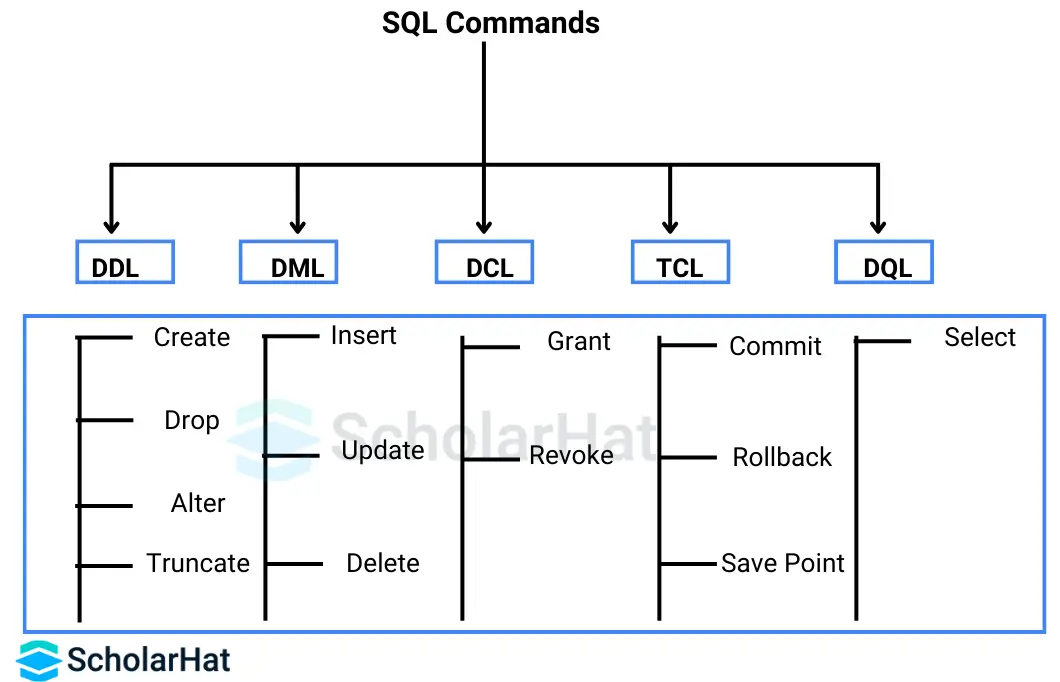
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
These SQL commands are used for creating, deleting, altering, and truncating tables. All DDL commands are auto-committed, meaning changes are permanently saved in the database. In this category, we have four commands:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- DROP
- TRUNCATE
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
These SQL commands modify data in the database. Unlike DDL, DML commands are not auto-committed, meaning changes can be rolled back. In this category, we have three commands:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
3. Data Query Language(DQL)
This SQL command is used to fetch/retrieve data from database tables. In this category, we have only the SELECT command.
4. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
These SQL commands are used to handle changes affecting the data in the database. They manage transaction states, allowing for rollback to a stable point if necessary. In this category, we have three commands:
- SAVEPOINT
- ROLLBACK
- COMMIT
5. Data Control Language (DCL)
These SQL commands manage database security, including user permissions and access to objects like tables, views, and stored procedures. In this category, we have two commands:
- GRANT
- REVOKE
Read More: Basics Of SQL Commands
3. Describe how you will create a database.
You can create a database in MySQL using the CREATE DATABASE command.
CREATE DATABASE my_database;4. Provide me with the differences between CHAR and VARCHAR data types.
Here are three simple differences between CHAR and VARCHAR in MySQL:
- Fixed vs. Flexible – CHAR always takes the same space, while VARCHAR only uses space for the actual text.
- Memory Usage – CHAR(10) always uses 10 spaces, but VARCHAR(10) uses only what is needed (e.g., "Hi" takes 2 spaces).
- Speed vs. Storage – CHAR is faster for same-size data, but VARCHAR saves space for different-length text.
CREATE TABLE example (
fixed_text CHAR(10), -- Always stores 10 characters
flexible_text VARCHAR(10) -- Stores up to 10 characters, but only uses needed space
);5. What are the frequently used MySQL functions?
| Function Name | Functionality |
| ABS() | Returns the absolute value of a number. |
| ROUND() | Rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places. |
| CEIL() | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to a given number. |
| FLOOR() | Returns the largest integer less than or equal to a given number |
| EXP() | Calculates the exponential value of a number |
| LOG() | Calculates the natural logarithm of a number |
| NOWO | Returns the current date and time as a single value |
| CURRDATEO | Returns the current date and time |
| CONCAT (X, Y) | Concatenates two string values creating a single string output |
| DATEDIFF (X, Y) | Determines the difference between the two dates |
6. What is a query in MySQL? What are the types of SQL queries?
A Query in MySQL is a request for data or information from a database. It is a way to interact with the database to perform various operations like retrieving, inserting, updating, or deleting the data. Users can query a database for specific information, and MySQL returns the resultant record/records.
- A query consists of SQL commands, expressions, and operators that define criteria for how the database should search, filter, modify, or present the data.
Following are some common types of SQL queries:
1. Data Retrieval Queries
These queries retrieve data from one or more tables in the database. They use the SELECT statement and may include filtering, sorting, and grouping operations.
Example
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table WHERE condition; 2. Data Manipulation Queries
These queries modify data in the database tables. They include INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements.
Example
INSERT INTO table (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2); 3. Data Definition Queries
These queries define or alter the structure of database objects such as tables, indexes, or views. They include CREATE, ALTER, and DROP statements.
Example
CREATE TABLE table_name (column1 datatype, column2 datatype); 5. Data Control Queries
These queries manage access to the database objects by granting or revoking privileges to users or roles. They include GRANT and REVOKE statements.
Example
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON table TO user; 6. Transaction Control Queries
These queries manage transactions in the database, such as starting, committing, or rolling back transactions. They include BEGIN TRANSACTION, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK statements.
Example
BEGIN TRANSACTION; 7. Join Queries
These queries retrieve data from multiple tables by joining them based on specified conditions. They use JOIN clauses, including INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, and FULL JOIN.
Example
SELECT * FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column; 8. Subquery or Nested Queries
These queries include one query (subquery) nested inside another query (outer query). They can be used in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
Example
SELECT column1 FROM table1 WHERE column2 IN (SELECT column3 FROM table2 WHERE condition); 7. What is a subquery? What are the types of SQL subqueries?
An SQL subquery, also known as an inner query or nested query, is a query inside another query or an outer query. A subquery may occur in clauses such as SELECT, FROM, WHERE, UPDATE, etc. It's also possible to have a subquery inside another subquery, which is particularly useful for advanced SQL interview questions. The innermost subquery is run first, and its result is passed to the containing query (or subquery). This concept is fundamental for understanding MySQL query optimization and is often tested in technical interviews.
The following are types of SQL subqueries
- Single-row: It returns at most one row of results. It is generally used with comparison operators such as =, >, <, etc.
Example
SELECT column1 FROM table1 WHERE column2 = (SELECT column2 FROM table2 WHERE condition); - Multi-row: It returns at least two rows. It can be used with operators like IN, ANY, or ALL.
Example
SELECT column1 FROM table1 WHERE column2 IN (SELECT column2 FROM table2 WHERE condition); - Correlated Subquery: It is a subquery related to the information from the outer query.
Example
SELECT column1 FROM table1 t1 WHERE column2 > (SELECT AVG(column2) FROM table1 t2 WHERE t1.column3 = t2.column3); - Nested Subquery: It is a subquery inside another subquery.
Example
SELECT column1 FROM table1 WHERE column2 = (SELECT MAX(column2) FROM (SELECT * FROM table2) AS subquery); - Multi-column: It is also known as a multi-column correlated subquery that returns multiple columns of data and is correlated with the outer query.
Example
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table1 t1 WHERE (column1, column2) IN (SELECT column1, column2 FROM table2 t2 WHERE t1.column3 = t2.column3);
8. What are the different data types in MySQL?
The data types in MySQL can be categorized into mainly three categories:
- Numeric Data Types: The numeric data types are integer, fixed-point, floating-point, and bit values. They can be signed or unsigned, except BIT.
Type Name Description TINYINT Very Small Integer SMALLINT Small Integer MEDIUMINT Medium-sized Integer INT Standard Integer BIGINT Large Integer DECIMAL Fixed-point number FLOAT Single-precision floating-point number DOUBLE Double-precision floating-point number BIT Bit-field Example
CREATE TABLE example_numeric_types ( roll INT, salary DECIMAL(15,2), score DOUBLE(7,2) ); - String Data Types: They are used for storing text.
Type Name Description CHAR fixed-length nonbinary(character) string VARCHAR variable-length nonbinary string BINARY fixed-length binary string VARBINARY variable-length binary string TINYBLOB Very small BLOB(binary large object) BLOB Small BLOB MEDIUMBLOB Medium-sized BLOB LONGBLOB Large BLOB TINYTEXT A very small nonbinary string TEXT Small nonbinary string MEDIUMTEXT Medium-sized nonbinary string LONGTEXT Large nonbinary string ENUM An enumeration; each column value is assigned, and one enumeration member SET A set; each column value is assigned zero or more set members Example
CREATE TABLE example_string_types ( name VARCHAR(300), father_name CHAR(30), comments TEXT ); - Temporal Data Types: They are for date and time and a combination of date and time.
Type Name Meaning DATE A date value, in ' CCYY-MM-DD ' Format TIME A Time value, in ' hh : mm :ss ' format DATETIME Date and time value, in ' CCYY-MM-DD hh : mm :ss ' format TIMESTAMP A timestamp value, in ' CCYY-MM-DD hh : mm :ss ' format YEAR A year value, in CCYY or YY format Example
CREATE TABLE example_date_types ( birthday DATE, created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, event_time DATETIME ); - Spatial Data Types: These are used to store geometric data. Some of these types are:
Type Name Meaning GEOMETRY The base data type for all spatial data types. POINT A single location in space LINESTRING A sequence of points that form a line POLYGON A planar surface representing a multi-sided shape Example
CREATE TABLE example_spatial_types ( location POINT, path LINESTRING, area POLYGON );
9. What does a MySQL database contain?
A MySQL database contains one or more tables containing several records or rows. Within these rows, data is contained in various columns or fields.
10. What are the different tables present in MySQL?
Many tables are present in MySQL by default. But, MyISAM is the default database engine used in MySQL. Five types of tables are present:
- MyISAM
- Heap
- Merge
- INNO DB
- ISAM
11. What are SQL dialects?
SQL dialects are different versions of SQL used by various database systems. Even though SQL is a standard language, different databases have their own variations. These variations are called SQL dialects.
Examples of SQL Dialects
- MySQL: Uses LIMIT to limit rows in a query.
- SQL Server: Uses TOP instead of LIMIT.
- PostgreSQL: Uses RETURNING to get inserted data.
- Oracle SQL: Uses ROWNUM for row limits.
Each database follows the core SQL rules but adds its own features and syntax.
MySQL Interview Questions for 2 Years Experience
12. What is an index? What are the various ways to create an index?
An index is a special data structure related to a database table and used for storing its important parts, enabling faster data search and retrieval. Indexes are particularly efficient for large databases, significantly enhancing query performance.
There are the following ways to create an index:
- Using T-SQL statements to create an index.
- Using SQL Server Management Studio to browse to the table, right-click on the Indexes node, and select the "New Index" option.
- Specifying the PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE constraint in the CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE statement.
13. Differentiate between Clustered and Non-Clustered Index.
Here are the differences between Clustered and Non-Clustered Index.
| Clustered Index | Non-Clustered Index |
| A clustered index is faster. | A non-clustered index is slower. |
| Requires less memory for operations. | Requires more memory for operations. |
| Represents the main data. | Is a copy of the data. |
| A table can have only one clustered index. | A table can have multiple non-clustered indexes. |
| Leaf nodes are actual data. | Leaf nodes are not actual data but contain included columns. |
| Defines the physical order of data within a table. | Defines the logical order of data within the index. |
| Primary keys are clustered indexes by default. | Composite keys with unique constraints act as non-clustered indexes. |
14. What is a schema?
A schema is a collection of database structural elements such as tables, indexes, stored procedures, functions, and triggers. It represents the overall database architecture, defines object relationships, and specifies access permissions.
15. What is an SQL comment?
An SQL comment is a human-readable clarification added to SQL code for better understanding. It can be single-line (using --) or multi-line (using /* comment */). Comments are ignored by the SQL engine during execution.
16. What makes MySQL a popular and widely used RDBMS?
- Data Security: Provides a secure and reliable database system.
- Flexibility: Compatible with all operating systems and supports enterprise-level features.
- High Performance: Maintains speed and efficiency for demanding applications.
- Scalability: Supports on-demand scalability and customization.
- Advanced SQL Features: Offers enterprise-level tools and features.
- Full-Text Indexing: Includes full-text indexing and search capabilities.
- Query Caching: Enhances performance with memory caching.
- Replication: Allows duplication of one server on another for reliability.
17. How many index columns can be created in a table?
You can create up to 16 indexed columns in a table.
18. What is a constraint? What are the different types of constraints in MySQL?
Constraints are rules that enforce data integrity in a database table. They restrict the type of data that can be inserted into a table.
Types of Constraints:
- Primary Key: Ensures unique and non-null values for a column.
- Unique Key: Allows only unique values, with one null value permitted.
- Foreign Key: References a primary key in another table.
- Not Null: Ensures no null values are allowed.
- Default: Sets a default value for a column.
19. What is an SQL operator? What are the types of SQL operators?
An SQL operator is a reserved character, keyword, or combination of both used to perform operations in SQL queries, often within the WHERE clause.
Types of SQL Operators:
- Arithmetic Operators: Used for mathematical operations (+, -, *, /, %).
- Comparison Operators: Compare values (=, !=, <>, >, <, >=, <=).
- Logical Operators: Combine multiple conditions (AND, OR, NOT).
- Compound Operators: Combine assignment and operations (+=, -=, *=).
20. What is a join in MySQL? Explain the types of joins.
A join in MySQL is a way to combine records from two or more tables in a database based on a related column. Joins allow you to retrieve data from multiple tables in a single query.
Types of Joins
- Inner Join: Retrieves records that have matching values in both tables.
- Left Join (Left Outer Join): Retrieves all records from the left table and matching records from the right table, with NULL values for unmatched rows in the right table.
- Right Join (Right Outer Join): Retrieves all records from the right table and matching records from the left table, with NULL values for unmatched rows in the left table.
- Full Join (Full Outer Join): Retrieves all records when there is a match in either the left or right table. Unmatched rows will have NULL values.
- CROSS Join: Returns the Cartesian product of two tables, i.e., all combinations of rows from both tables.
MySQL Interview Questions for 3 years of experience
Get ready for MySQL interview questions for 3 years of experience, focusing on key topics like query tuning, indexes, and improving database performance to crack your next interview.
21. What is the CASE() function?
The CASE() function is a way to implement the if-then-else logic in SQL. This function sequentially checks the provided conditions in the WHEN clauses and returns the value from the corresponding THEN clause when the first condition is satisfied. If none of the conditions is satisfied, the function returns the value from the ELSE clause in case it's provided. Otherwise, it returns NULL.
Syntax
CASE
WHEN condition_1 THEN value_1
WHEN condition_2 THEN value_2
WHEN condition_3 THEN value_3
...
ELSE value
END;
22. What are MySQL Triggers? How many Triggers are there in MySQL?
A trigger in MySQL is a procedural code in a database. Triggers are automatically triggered when specific events occur on a particular table. Specifically, this event involves inserting, modifying, or deleting table data, and the task can occur either before or immediately following any such event. During column updating, triggers are invoked automatically.
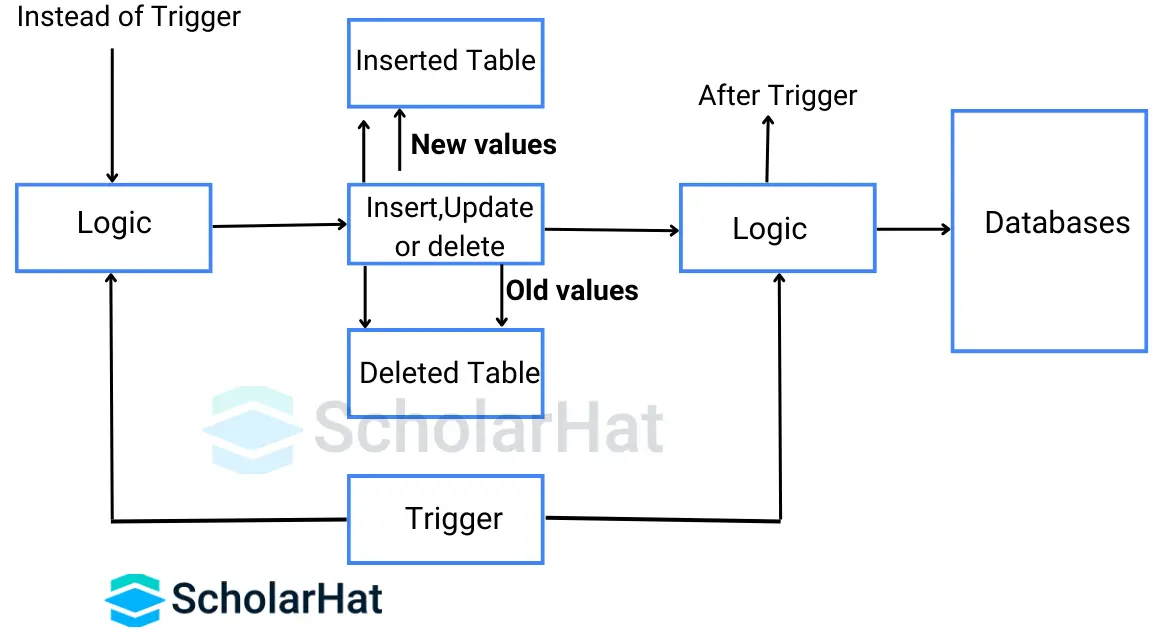
There are various reasons for using triggers:
- Audit Trails
- Validation
- Referential integrity enforcement
There are six triggers available in the MySQL database:
- BEFORE INSERT
- AFTER INSERT
- BEFORE UPDATE
- AFTER UPDATE
- BEFORE DELETE
- AFTER DELETE
Example to illustrate the working of triggers in MySQL
Let's suppose there's a table named Employees with the following schema:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
salary DECIMAL(10, 2),
is_active BOOLEAN
);
We want to create a trigger that automatically updates the is_active column to true for employees whose salary is greater than $5000.
DELIMITER //
CREATE TRIGGER update_active_status
AFTER INSERT ON employees
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.salary > 5000 THEN
UPDATE employees
SET is_active = true
WHERE id = NEW.id;
END IF;
END//
DELIMITER ;
In this trigger:
- AFTER INSERT ON employees specify that the trigger should activate after an insert operation on the employees table.
- FOR EACH ROW indicates that the trigger will be executed for each row affected by the insert operation.
- NEW.salary refers to the salary value of the newly inserted row.
- If the salary of the newly inserted employee is greater than $5000, the trigger updates the is_active column to true for that employee.
Now, let's insert a record into the employees table:
INSERT INTO employees (name, salary) VALUES ('John Doe', 6000);
After this insert operation, the is_active column for the employee with a salary of $6000 will be automatically set to true by the trigger.
23. What are views in MySQL? How do you create and execute views in MySQL?
In MySQL, a view is a virtual table based on the result set of an SQL statement. A view contains rows and columns, just like a real table. The fields in a view are fields from one or more real tables in the database. It is created by combining one or more tables. The difference between a view and a table is that views are definitions that build on other tables.
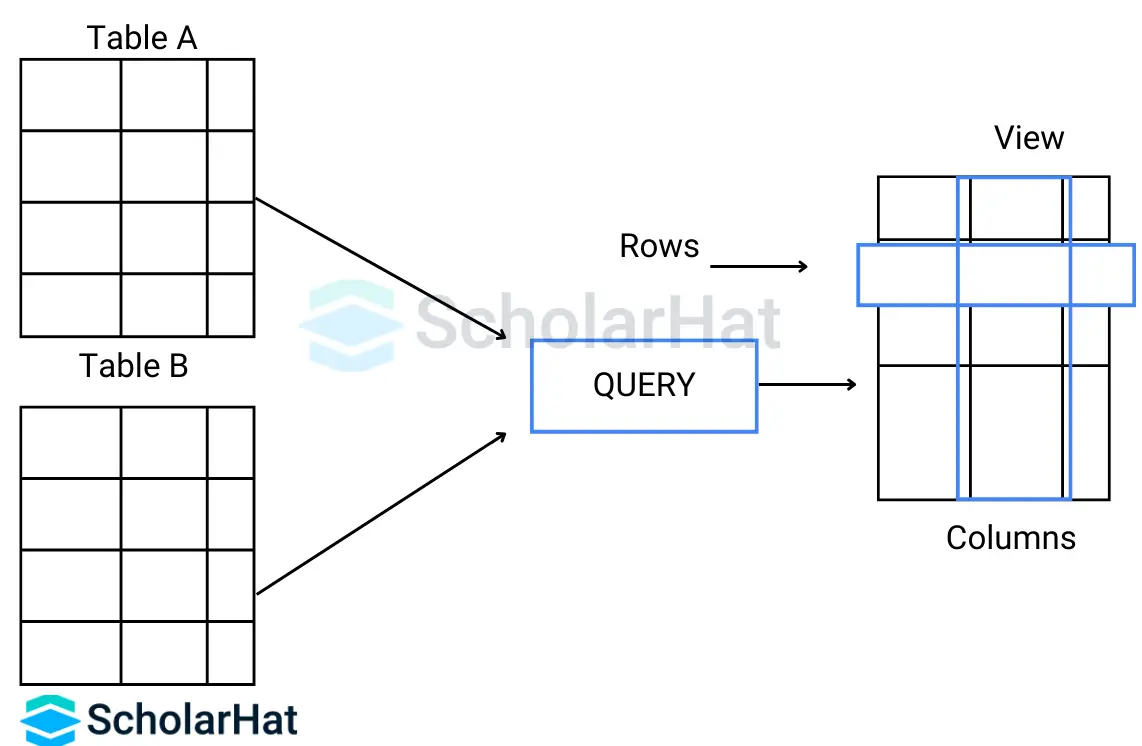
Views take very little space, simplify complex queries, limit access to the data for security reasons, enable data independence, and summarize data from multiple tables. Views do not store any data of their own but display data stored in other tables. A view is created with the CREATE VIEW statement.
Syntax to Create a View
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Example of a View
CREATE VIEW [Indian Customers] AS
SELECT CustomerName, ContactName
FROM Customers
WHERE Country = 'India';
Execution of a View
SELECT * FROM [Indian Customers];
24. Describe the relationships in MySQL.
The relationship in MySQL is classified into three types:
- One-to-One: Each record in one table corresponds to only one record in another table and vice versa. This relationship is established using foreign key constraints.
Example Illustrating a one-to-one relationship between two tables: users and profiles
CREATE TABLE users ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR(50) UNIQUE, email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE ); CREATE TABLE profiles ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, user_id INT UNIQUE, full_name VARCHAR(100), FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id) );The user_id column in the profiles table establishes the one-to-one relationship with the id column in the users table. This column acts as a foreign key referencing the id column in the users table.
- One-to-Many: Each record in one table corresponds to several records in another table. This relationship between two tables can be established using foreign keys.
Example Illustrating a one-to-many relationship between two tables: orders and order_items
CREATE TABLE orders ( order_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, customer_id INT, order_date DATE, total_amount DECIMAL(10, 2), FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers(customer_id) ); CREATE TABLE order_items ( item_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, order_id INT, product_name VARCHAR(100), quantity INT, price DECIMAL(10, 2), FOREIGN KEY (order_id) REFERENCES orders(order_id) );Here, each order in the orders table can have multiple corresponding items in the order_items table, identified by the order_id foreign key.
- Many-to-many: Each record in both tables corresponds to several records in another table. To create this relationship, add a third table containing the same key column from each of the other tables.
Let's suppose there are two entities: students and courses. Each student can enroll in multiple courses, and each course can have multiple students enrolled.
Here, we'll create three tables:
- students: Stores information about students.
- courses: Stores information about courses.
- student_course: Acts as a junction table linking students to courses.
Example Illustrating a many-to-many relationship between two tables: students and courses
CREATE TABLE students ( student_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, student_name VARCHAR(100) ); CREATE TABLE courses ( course_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, course_name VARCHAR(100) ); CREATE TABLE student_course ( student_id INT, course_id INT, PRIMARY KEY (student_id, course_id), FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(student_id), FOREIGN KEY (course_id) REFERENCES courses(course_id) );To insert data into these tables:
-- Inserting students INSERT INTO students (student_name) VALUES ('John'); INSERT INTO students (student_name) VALUES ('Alice'); -- Inserting courses INSERT INTO courses (course_name) VALUES ('Mathematics'); INSERT INTO courses (course_name) VALUES ('Physics'); -- Enrolling students in courses INSERT INTO student_course (student_id, course_id) VALUES (1, 1); -- John enrolled in Mathematics INSERT INTO student_course (student_id, course_id) VALUES (1, 2); -- John enrolled in Physics INSERT INTO student_course (student_id, course_id) VALUES (2, 1); -- Alice enrolled in Mathematics
25. What is a heap table in MySQL?
A heap table is usually used for temporary and fast temporary storage.
- BOLB or TEXT fields are not permitted in the heap table.
- comparison operators like =, <,>, = >,=< can be used only.
- The heap table didn’t support the AUTO_INCREMENT command.
- Indexes should be NOT NULL in the heap table.
26. What are the differences between Nested Query and Correlated Query?
| Parameters | Nested Query | Correlated Query |
| Definition | A query is written inside another query and the result of the inner query is used in the execution of the outer query. | A query is nested inside another query and an inner query uses values from the outer query. |
| Approach | Bottom-up approach i.e. Inner query runs first, and only once. The outer query is executed with the result from the Inner query. | Top to Down Approach i.e. Outer query executes first and for every Outer query row Inner query is executed. |
| Dependency | Inner query execution is not dependent on Outer query. | The inner query is dependent on the Outer query. |
| Performance | Performs better than Correlated Query but is slower than Join Operation. | Performs slower than both Nested Query and Join operations as for every outer query inner query is executed. |
27. Which storage engines are used in MySQL?
Storage engines are also called table types. MySQL supports multiple storage engines, each with its characteristics and features. Some of them are:
- InnoDB: It is the default storage engine in MySQL. It provides ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions, foreign key support, and row-level locking.
- MyISAM: It is a popular storage engine that doesn't support transactions or foreign keys, but offers full-text search capabilities and is suitable for read-heavy workloads, such as data warehousing and logging applications.
- MEMORY (HEAP): This engine stores data in memory that is useful for temporary tables, session data, and caching.
- Archive: Optimized for storing large volumes of data with minimal storage space. It supports compression and is suitable for archiving purposes or storing historical data.
- CSV: Stores data in comma-separated values (CSV) format and is suitable for exchanging data between different systems.
- NDB (MySQL Cluster): A distributed storage engine designed for clustering and scalability. It provides features like data distribution, automatic sharding, and partitioning for large-scale applications.
28. How do you find duplicate rows in the MySQL table?
We found the duplicate rows in MySQL Table by the following command:
SELECT column1, column2, ..., COUNT(*)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column1, column2, ...
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
29. What is the difference between renaming a column and giving an alias to it?
Renaming a column means permanently changing its actual name in the original table using the ALTER TABLE statement. This affects the structure of the table itself.
Syntax to Rename a Column
ALTER TABLE table_name
CHANGE old_column_name new_column_name column_definition;
Example to Rename a Column
ALTER TABLE my_table
CHANGE old_column_name new_column_name VARCHAR(50);
This statement will rename the column old_column_name to new_column_name in the table my_table and change its data type to VARCHAR(50).
Giving an alias to a column means giving it a temporary name using the AS keyword while executing an SQL query. It does not affect the original column name in the table schema. Aliases are used for readability or to resolve naming conflicts in query results.
Syntax to Give an Alias to a Column
SELECT column_name AS alias_name
FROM table_name;
Example of Give an Alias to a Column
SELECT first_name AS fname, last_name AS lname
FROM employees;
The result set will have columns named fname and lname instead of first_name and last_name, respectively.
30. What is a primary key?
A primary key is a set of one or more fields/columns of a table that uniquely identifies a record in a database table. It can not accept null, or duplicate values. It is either an existing table column or a column that is specifically generated by the database according to a defined sequence.
Example of Primary Key
Employee Table
| Emp_Id | Emp_Name | Address | Mobile_No | |
| 1 | Sakshi | Delhi | 123456789 | abc@xyz.com |
| 2 | Sourav | Hazaribagh | 223365796 | jkl@gmail.com |
| 3 | Pragati | Nanded | 175468965 | ghi@yahoo.com |
In the above table, Emp_Id is the primary key. Each employee has a unique ID assigned to them, ensuring that no two employees share the same ID.
MySQL interview questions for 5 years Experience Candidates
31. What is a Unique Key? Elaborate with an example.
A unique key is a unique value amongst other values that are used to protect duplication of the values in a column of the table. The primary use of a unique key in a table is to prevent duplicate values. But, when it comes to the unique values, the primary key also includes them. So, there is one big difference that makes a unique key different, and it is that the unique key may have a NULL as a value but the primary key does not allow NULL as a value.
Example of Unique Key
Employee Table
| Emp_Id | Emp_Name | Address | Mobile_No | |
| 1 | Sakshi | Delhi | 123456789 | abc@xyz.com |
| 2 | Sourav | Hazaribagh | 223365796 | jkl@gmail.com |
| 3 | Pragati | Nanded | 175468965 | ghi@yahoo.com |
In the Employee relation, a Unique Key could be applied to the email column, allowing null values to be present while maintaining the uniqueness requirement for non-null entries.
32. Describe the foreign key in MySQL.
A foreign key is an attribute that is a Primary key in its parent table but is included as an attribute in another host table. It is a column (or columns) that references a column (most often the primary key) of another table.
Example of Foreign Key
Employee Table
| Emp_Id | Emp_Name | Address | Mobile_No | |
| 1 | Sakshi | Delhi | 123456789 | abc@xyz.com |
| 2 | Sourav | Hazaribagh | 223365796 | jkl@gmail.com |
| 3 | Pragati | Nanded | 175468965 | ghi@yahoo.com |
Department Table
| Dept_Id | Dept_Name | Designation |
| 101 | Video | Video_Maker |
| 201 | Search_Engine | SEO |
| 301 | Content | Writer |
To establish a relationship between these tables, we can introduce a foreign key in the "Employee" table that references the primary key of the "Department" table. Let's add a column called "Dept_ID" as a foreign key in the "Employee" table.
Employee Table
| Emp_Id | Emp_Name | Address | Mobile_No | Dept_Id | |
| 1 | Sakshi | Delhi | 123456789 | abc@xyz.com | 101 |
| 2 | Sourav | Hazaribagh | 223365796 | jkl@gmail.com | 201 |
| 3 | Pragati | Nanded | 175468965 | ghi@yahoo.com | 301 |
Read More: Different Types of SQL Keys
33. Differentiate Primary Key and Foreign Key
| Comparison Basis | Primary Key | Foreign Key |
| Definition | A primary key is a unique identifier for each record in a table. | A foreign key establishes a relationship between tables by referencing the primary key of another table. |
| Basic | Ensures uniqueness and data integrity within a single table. | Establishes relationships and maintains referential integrity between tables. |
| NULL | The primary key column value can never be NULL. | The foreign key column can accept a NULL value |
| Count | A table can have only one primary key. | A table can have more than one foreign key. |
| Duplication | No duplicate primary key values are allowed within the table. | Can contain duplicate foreign key values, reflecting multiple records associated with the same reference. |
| Indexing | Primary keys are automatically indexed to enhance data retrieval speed. | Foreign keys can be indexed but are not automatically indexed. |
| Deletion | The primary key value can't be removed from the table. If you want to delete it, then make sure the referencing foreign key does not contain its value. | The foreign key value can be removed from the table without bothering that it refers to the primary key of another table. |
| Insertion | Each new record must have a unique primary key value assigned. | The foreign key can reference an existing primary key value or be NULL if the relationship is optional. |
| Temporary table | Primary keys can be applied to temporary tables. | Foreign keys can also be applied to temporary tables to establish relationships. |
| Relationship | Primary keys define the basis for establishing relationships with other tables. | Foreign keys establish relationships and connect data between related tables. |
Read More: Differences between Primary Key and Foreign Key
34. What is a transaction? What are the different types of transactions in SQL Server?
We use transactions when we try to modify more than one table or view that is related to each other. Transactions affect SQL Server performance greatly. Since when a transaction is initiated then, it locks all the tables’ data that are used in the transaction. Hence during the transaction life cycle, no one can modify these tables’ data that are used by the transaction. The reason behind the locking of the data is to maintain Data Integrity.
There are the following types of transactions in SQL Server as given below:
- Implicit Transaction
- Explicit Transaction
35. How to drop the primary key in MySQL?
In the following way, we can do this:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP PRIMARY KEY;
Example
ALTER TABLE Employees DROP PRIMARY KEY;
36. How to prevent duplicate records when making a query?
We can do this using the DISTINCT statement in combination with SELECT or creating a unique key for that table.
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2 FROM table_name;ALTER TABLE table_name ADD CONSTRAINT constraint_name UNIQUE (column1, column2);
MySQL Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
37. What is a join in MySQL?
In MySQL, joins are used to query data from two or more tables. A join condition is a relationship among some columns in the data tables that take part in SQL join. Database tables are related to each other with SQL keys. We use this key relationship in SQL Joins.
Types of SQL Joins
- Inner Join
The inner join in SQL selects all rows or columns that match in both tables or as long as the SQL condition is valid.
- Left Outer Join / Left Join
The LEFT JOIN retrieves all data from the left table (table1) and the rows or columns that match from the right table (table2). If neither table contains any matched rows or columns, it returns NULL.
- RIGHT JOIN / RIGHT Outer JOIN
The RIGHT JOIN retrieves all data from the right table (table 2) as well as the matching rows or columns from the left table (table 1). If neither table contains any matched rows or columns, it returns NULL.
- Full Outer Join
It is a result set that combines both LEFT JOIN & RIGHT JOIN. The connected tables return all records from both tables and place NULL if no matches are found in the table. It is also known as a FULL OUTER JOIN.
- CROSS JOIN
CARTESIAN JOIN, which returns the Cartesian product of two or more connected tables, is another name for it. The CROSS JOIN creates a table that merges each row from the first table with each row from the second table. There is no need to provide any conditions in CROSS JOIN.
SELF JOIN- It is a SELF JOIN that was used to build a table by combining two tables. It names at least one table temporarily in an SQL statement.
Read More: Different Types of SQL Joins
38. Describe the architecture of MySQL.
MySQL follows the client-server architecture. The client communicates with the server over the network using MySQL protocol.
- The top layer contains the services most network-based client/server tools or servers need such as connection handling, authentication, security, and so forth.
- The second layer contains much of MySQL’s brains. This has the code for query parsing, analysis, optimization, caching, and all the built-in functions.
- The third layer contains the storage engines that are responsible for storing and retrieving the data stored in MySQL.
39. Write a query to select random rows from a table.
For this, we will use the RAND() function in combination with ORDER BY and LIMIT. In some SQL flavors, such as PostgreSQL, it's called RANDOM().
Example
The below query will return five random rows from a table in MySQL
SELECT * FROM table_name
ORDER BY RAND()
LIMIT 5;
40. What is an access control list?
To provide secure access to some crucial data specific to its business, organizations create a sequence of permissions linked to various data objects. These lists are known as the access control list (ACL).
ACL serves as the basis for the server’s security that helps troubleshoot the connection problems for users. These are also known as grant tables cached by MySQL. MySQL verifies a user for authentication and grants permissions in a sequence when the user executes a command.
MySQL interview questions for 10 years of Experience Candidates
41. Explain the LIKE clause in MySQL.
The LIKE clause in MySQL is used to search for patterns in strings. It allows the use of wildcard characters such as '%' (matches zero or more characters) and '_' (matches any single character) to perform flexible pattern matching.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE columnN LIKE pattern;
Example
SELECT * FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeName LIKE 'a%';
The above query selects all employees with EmployeeName starting with "a".
SELECT * FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeName LIKE '%a';
The above query selects all employees with EmployeeName starting with "a".
SELECT * FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeName LIKE '_r%';
The above query selects all employees with EmployeeName having "r" in the second position.
SELECT * FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeName LIKE 'a%o';
The above query selects all employees with EmployeeName that starts with "a" and ends with "o".
42. What is normalization? What are the different normal forms?
Normalization or data normalization is a process of organizing the data into a tabular format (database tables) keeping four goals in mind.
- Reduce data redundancy
- Reduce data dependency
- Reduce data duplication
- Reduce data inconsistency
This leads to enhanced data integrity, more tables within the database, more efficient data access and security control, and greater query flexibility.

43. Discuss Equi Join.
Equi join is a special type of join, also known as simple join, in which we use only an equality operator("="). Hence, when you make a query for join using the equality operator, such a join query comes under Equi join.
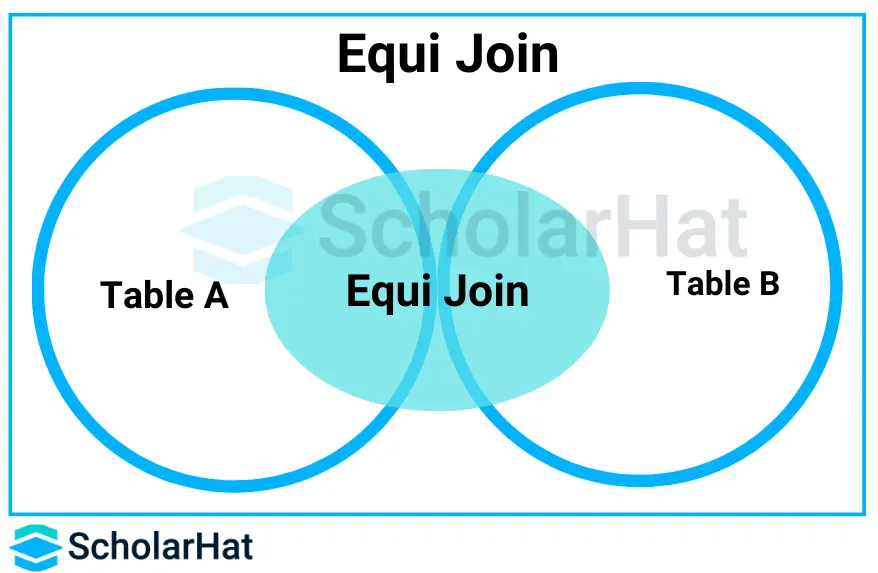
The equi join creates a JOIN for equality or matching of the single or multiple column values of the relative tables. Apart from that, the equi join also creates the JOIN by using JOIN along with the ON clause and then providing the names of the columns with their relative tables to check equality using the equal operator.
Equijoin is a classified type of inner join that returns output by performing joining operations from two tables based on the common column that exists in them. The resultant result can have repeated column names.
Syntax of Inner Join
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Inner Join Example
Below is a simple example showing the use of joins where the tables "tblDept" and "tblEmp" are being joined based on the DeptId column.
SELECT * FROM tblEmp JOIN tblDept
ON tblEmp.DeptID = tblDept.DeptID;
Inner Join Output
In the join condition, you can also use other operators like <,>,<>.
44. What is Scaling in MySQL?
In MySQL, scaling capacity is the ability to handle the load, and it’s useful to think of the load from several different angles, such as:
- Quantity of data
- Number of users
- User Activity
- Size of related datasets
45. Can you define all the keys in a database table?
In a database table, you can have only three types of keys: primary key, unique key, and foreign key. Other types of keys are only concepts of RDBMS that you need to know.
46. What is MySQL Workbench?
MySQL Workbench is a unified visual database designing or GUI tool used for working on MySQL databases. It is developed and maintained by Oracle which provides SQL development, data migration, and comprehensive administration tools for server configuration, user administration, backup, etc. We can use this Server Administration to create new physical data models, E-R diagrams, and SQL development. It is available for all major operating systems.
It is mainly available in three editions, which are given below:
- Community Edition (Open Source, GPL)
- Standard Edition (Commercial)
- Enterprise Edition (Commercial)
47. What are character manipulation functions? Give some examples.
Character manipulation functions represent a subset of character functions, and they're used to modify the text data.
| Function Name | Description |
| CONCAT() | joins two or more string values appending the second string to the end of the first one |
| SUBSTR() | returns a part of a string satisfying the provided start and end points |
| LENGTH() | returns the length of a string, including the blank spaces |
| REPLACE() | replaces all occurrences of a defined substring in a provided string with another substring |
| INSTR() | returns the numeric position of a defined substring in a provided string |
| LPAD() and RPAD() | return the padding of the left-side/right-side character for right-justified/left-justified value |
| TRIM() | removes all the defined characters' white spaces, from the left, right, or both ends of a provided string |
48. How do you find the nth highest value in a column of a table?
To find the nth highest value in a column of a table in MySQL, we can use the ORDER BY clause along with LIMIT to specify the desired row.
Syntax
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column_name DESC
LIMIT n-1, 1;
Example
The below query finds the 3rd highest value in the salary column of a table named employees.
SELECT salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 2, 1;
49. How to create a new user in MySQL?
A USER in MySQL is a record in the USER-TABLE. It contains the login information, account privileges, and host information for MySQL account to access and manage the databases. We can create a new user account in the database server using the MySQL Create User statement. It provides authentication, SSL/TLS, resource-limit, role, and password management properties for the new accounts.
Syntax
CREATE USER [IF NOT EXISTS] account_name IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
In the above syntax, the account_name has two parts one is the username, and another is the hostname, which is separated by @ symbol. Here, the username is the name of the user, and the hostname is the name of the host from which the user can connect with the database server.
50. How can you optimize a MySQL query?
MySQL query optimization involves various techniques such as indexing, using appropriate data types, minimizing the number of queries, optimizing table structure, avoiding unnecessary calculations, and utilizing query caching.
MySQL Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
51. What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE commands in MySQL?
| DELETE | TRUNCATE |
| Used to remove specific rows based on a condition. | Removes all rows from a table without using a condition. |
| It can be rolled back if used within a transaction. | Cannot be rolled back. |
| Triggers are fired. | Triggers are not fired. |
| Slower as it processes rows individually. | Faster because it removes data in bulk. |
| Does not reset the auto-increment counter. | Resets the auto-increment counter to zero. |
52. How does MySQL handle NULL values in a query?
In MySQL, NULL represents missing or undefined values. NULL values cannot be compared using standard operators like =. To handle NULL values:
- Use the
IS NULLorIS NOT NULLoperators. - Use functions like
IFNULL(),COALESCE(), orNULLIF()for handling NULL values in expressions.
Example:
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary IS NULL;
53. What is a cursor in MySQL?
A cursor in MySQL is a database object used to iterate through a result set row by row. Cursors are typically used in stored procedures when you need to process individual rows in a query result.
Example:
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE cursor_example()
BEGIN
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT FALSE;
DECLARE emp_name VARCHAR(255);
DECLARE cur CURSOR FOR SELECT name FROM employees;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = TRUE;
OPEN cur;
read_loop: LOOP
FETCH cur INTO emp_name;
IF done THEN
LEAVE read_loop;
END IF;
SELECT emp_name;
END LOOP;
CLOSE cur;
END;
//
DELIMITER ;
54. How can you improve the performance of a MySQL database?
- Use appropriate indexes on frequently queried columns.
- Optimize queries by avoiding
SELECT *and using specific column names. - Use EXPLAIN to analyze query execution plans.
- Partition large tables for efficient data access.
- Enable query caching for faster retrieval of repetitive queries.
- Regularly monitor and tune MySQL configuration parameters.
55. What is the difference between MyISAM and InnoDB storage engines?
| MyISAM | InnoDB |
| Does not support transactions. | Supports transactions. |
| Faster for read-heavy operations. | Better for write-heavy and mixed operations. |
| Does not support foreign keys. | Supports foreign keys. |
| Table-level locking. | Row-level locking. |
| Suitable for simple applications. | Ideal for complex, high-performance applications. |
56. How do you back up and restore a MySQL database?
Backup: Use the mysqldump utility:
mysqldump -u username -p database_name > backup.sql
Restore: Use the mysql command:
mysql -u username -p database_name < backup.sql
57. What are temporary tables in MySQL?
Temporary tables are used to store intermediate results during query processing. These tables exist only for the duration of the session and are automatically dropped when the session ends.
Example
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_table AS
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary > 50000;
58. What is the use of the GROUP BY clause in MySQL?
The GROUP BY clause is used to aggregate data based on one or more columns. It is often used with aggregate functions like SUM(), AVG(), and COUNT().
Example
SELECT department, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY department;
59. How do you handle errors in MySQL stored procedures?
You can handle errors in MySQL stored procedures using the DECLARE ... HANDLER statement. This allows you to specify actions to take when specific errors occur.
Example
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE error_handling_example()
BEGIN
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR SQLEXCEPTION
BEGIN
ROLLBACK;
SELECT 'An error occurred!';
END;
START TRANSACTION;
INSERT INTO employees (name, salary) VALUES ('John', 100000);
COMMIT;
END;
//
DELIMITER ;
60. What are the differences between UNION and UNION ALL in MySQL?
| UNION | UNION ALL |
| Removes duplicate rows from the result set. | Includes duplicate rows in the result set. |
| Performs slightly slower due to duplicate elimination. | Faster as it does not check for duplicates. |
| Default behavior when combining query results. | Explicitly specified to include all results. |
Summary
In this article, we’ve covered everything from basic to advanced MySQL interview questions. Whether you’re just starting out or already have experience, these questions can help you prepare effectively. If you’re aiming for a successful career in database development, take the time to go through these questions carefully. Want to learn MySQL from scratch? Enroll in our SQL Server Course and start your journey today!
Test your Skills by following MCQs
Test your skills with the following MySQL interview MCQs covering query optimization, indexing techniques, joins, stored procedures, and database normalization!
Q 1: Which storage engine is the default in MySQL?
| Download this PDF Now - MySQL Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat |
FAQs
- SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language used for managing relational databases.
- MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL to store, retrieve, and manipulate data.
- Atomicity – A transaction is all or nothing.
- Consistency – Data remains in a valid state before and after a transaction.
- Isolation – Transactions do not interfere with each other.
- Durability – Once committed, a transaction remains even after system failure.
- PRIMARY KEY – Uniquely identifies a row and cannot be NULL (only one per table).
- UNIQUE KEY – Ensures uniqueness but allows NULL values (multiple per table).
Take our Mysql skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











