13
Mar.NET8 Developer Roadmap for 2025
The .NET Developer Roadmap is a learning guide that helps individuals become proficient in developing applications using Microsoft's .NET platform. It covers all the important topics like learning C#, using databases, building web apps, and working with new tools like Blazor and cloud services.
In this .NET tutorial, we’ll explore the .NET 8 roadmap designed for aspiring .NET and C# developers.

What Is .NET?
.NET is a free, open-source, cross-platform development platform created by Microsoft that enables developers to build and run a wide range of applications from web, desktop, mobile, to cloud, IoT, and games using multiple programming languages like C# and Visual Basic.
Why Become a .NET Developer?
1. High Demand in the Job Market
- Widely used in enterprise applications (banking, insurance, healthcare, government)
- Consistently ranks among top development platforms globally
- Job openings for .NET full stack, backend, API, and cloud developers are plentiful
2. Lucrative Salary Potential
- .NET developers earn competitive salaries in India, the US, and Europe.
- Higher earning potential with skills in Azure, Microservices, and Blazor
3. Cross-Platform Development
- One codebase for Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Create mobile apps with .NET MAUI/Xamarin
- Build responsive frontend UIs with Blazor WebAssembly
4. Robust Ecosystem & Community
- Backed by Microsoft’s regular updates
- Massive developer community, support forums, and GitHub projects
5. Security & Stability
- Enterprise-level security and scalability
- Used by governments and Fortune 500 companies for mission-critical systems
6. Career Growth
- .NET Full Stack Developer
- Azure Cloud Developer
- Software Architect
- Tech Lead / Engineering Manager
Step-by-Step Guide for becoming a .NET Developer
In a world driven by fast, scalable, and secure applications, .NET stands tall as one of the most powerful and in-demand frameworks. Whether you're dreaming of building enterprise-grade web apps, crafting sleek mobile interfaces, or designing high-performance APIs, the .NET ecosystem has everything you need.
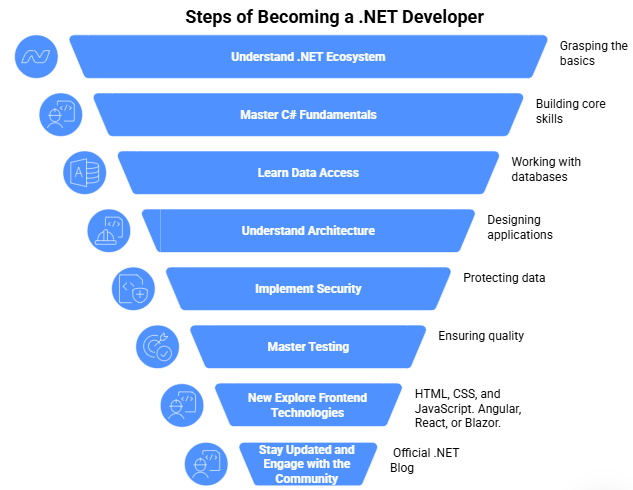
1.Understanding .NET and its Ecosystem
Before getting into the specifics, it’s crucial to have a deep understanding of the .NET ecosystem and its various components. Let's explore the key aspects of .NET and its related technologies.
.NET8 Framework
.NET 8 is a free, cross-platform, and open-source programming framework that enables the development of various web, mobile, and cloud computing applications. It's not only a framework version but much more than that. It redefines how software applications are built and deployed, enabling developers to meet the evolving demands of modern computing.
It offers enhanced performance, improved diagnostic and observability, expanded cross-platform support, advanced tooling and integration, long-term support (LTS), and much more. The .NET Framework supports a variety of programming languages, including C#, VB.NET, and F#.
.NET Core8
It is a modular, lightweight, and high-performance version of the .NET Framework, designed to support modern application development scenarios such as microservices, containerization, and cloud-based deployment. .NET Core is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
ASP.NET8 and ASP.NET Core8
ASP.NET is a web development platform, which provides a programming model, a comprehensive software infrastructure, and various services required to build up robust web applications for PC and mobile devices. It works on top of the HTTP protocol and uses the HTTP commands and policies to set a browser-to-server bilateral communication and cooperation.
ASP.NET Core is a web framework for building modern Web Applications and APIs. Its major characteristics include MVC (Model-View-Controller), Razor Pages, SignalR (real-time communication), and middleware for request processing. ASP.NET Core Open-Source and cross-platform version of ASP.NET, designed to run on top of the .NET Core Platform. It offers improved performance, modularity, and modern web development practices support.
You need to understand the ASP.NET Core request pipeline, middleware, and filters, dependency injection using built-in Service Container methods, exception handling and error logging, etc.
Read More - Dot Net Interview Questions
2. Mastering C# and .NET Fundamentals
C# is a modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft. It was first introduced in 2002 as part of Microsoft’s .NET framework. It is a simple, powerful, and type-safe programming language used to build desktop, web, game, and mobile applications. It supports both static and dynamic typing. It is a very versatile programming language that is continuously evolving. Therefore, a .NET or a C# developer must remain up to date with the changes.
C# Language Features
- Variables, data types, and operators
- Control flow (conditionals, loops)
- Object-oriented programming (classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism)
- Exception handling
- Delegates and events
- Generics
- LINQ (Language Integrated Query)
- Async and await for asynchronous programming
NET Libraries and APIs
.NET provides a rich set of libraries and APIs for various tasks, such as:
- Collections and data structures
- File I/O and serialization
- Networking and web requests
- Threading and task parallelism
- Security and cryptography
Getting a hold of these libraries and APIs will enable you to write efficient and maintainable code in your .NET applications.
3. Data Access with Entity Framework and Entity Framework Core
Data access is a critical aspect of application development, and Entity Framework (EF) simplifies this process for .NET developers. Let's look at how to work with databases using EF and EF Core.
Database Fundamentals
You must have a fundamental clearance of the concepts related to databases like the various operations performed on them.
- SQL and relational database concepts (tables, columns, rows, keys, indexes, and relationships)
- CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
- Joins, transactions, and stored procedures
Working with Entity Framework
Entity Framework (EF) simplifies data access in .NET applications by allowing developers to work with databases using objects and LINQ queries. Key concepts to learn when working with EF include:
- DbContext and DbSet for managing database connections and querying data
- Code-First and Database-First approaches for defining data models
- Migrations for managing database schema changes
- Querying data using LINQ and raw SQL
- Tracking changes and saving data
Entity Framework Core
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is the lightweight, high-performance version of EF designed for .NET Core applications. While there are many similarities between EF Core and EF, there are also some differences and new features like:
- Improved performance and reduced memory usage
- Support for new database providers and platforms
- Simplified configuration and dependency injection
- Global query filters and query types for advanced querying scenarios
4. Application Architecture and Design Patterns
SOLID Principles
SOLID is an acronym representing five key design principles for writing maintainable and scalable code:
- Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
- Open/Closed Principle (OCP)
- Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
- Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
- Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
Other Design Principles and Patterns
In addition to SOLID, other important design principles and patterns one must know are:
- GOF 23 Design Pattern
- DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself)
- KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid)
- MVC (Model-View-Controller)
- Repository pattern
- Unit of Work pattern
Microservices Architecture
Microservices Architecture is a method of software development, where we break down an application into small, independent, and loosely coupled services. These services are developed, deployed, and maintained by a small team of developers. These services have a separate codebase that is managed by a small team of developers. Major concepts of architecture are:
- Cloud providers (Azure, AWS, etc.)
- Docker and containerization
- Kubernetes for container orchestration
- Message buses and event-driven architecture
- API gateways and service discovery
5. Security and Cryptography
Let's explore various security concepts and techniques relevant to .NET developers.
Authentication and Authorization
Authentication
It is the process of verifying the identity of a user, application, or system. In the context of a web application, it often involves confirming the identity of a user by checking their credentials (like username and password) against a data source (like a database). The following tools are provided by the .NET Ecosystem
- Forms Authentication
- Windows Authentication
- OAuth & OpenID Connect
- Identity Server
- ASP.NET Core Identity
Authorization
Key concepts and tools in the .NET ecosystem include:
- Role-Based Authorization
- Claims-Based Authorization
- Policy-Based Authorization
- Resource-Based Authorization
Cryptography and Data Protection
Cryptography and data protection techniques are essential to secure sensitive data in your applications. For this, some tools in the .NET ecosystem are:
- Symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms
- Hashing and digital signatures
- Secure random number generation
- .NET Core Data Protection APIs
6. Testing and Continuous Integration
Let's look at the various testing techniques and tools for .NET applications.
Unit Testing
Unit testing involves testing individual units of code in isolation. Key concepts and tools for unit testing in .NET include:
- Test frameworks (xUnit, NUnit, MSTest)
- Test runners and test explorers
- Asserts and test attributes
- Mocking libraries (Moq, NSubstitute, etc.)
Integration Testing and End-to-End Testing
Integration testing focuses on testing interactions between components, while end-to-end testing validates the entire application from the user’s perspective. In the .NET ecosystem, some tools and frameworks for these testing types are:
- ASP.NET Core TestHost and TestServer for integration testing
- Selenium and Playwright for browser-based end-to-end testing
- SpecFlow for Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
CI/CD is the practice of automating the process of building, testing, and deploying applications. Key concepts and tools for CI/CD in the .NET ecosystem include:
- Build and deployment tools (MSBuild, dotnet CLI)
- Version control systems (Git, Azure DevOps)
- CI/CD platforms (GitHub Actions, Azure Pipelines, Jenkins, TeamCity)
7. Frontend Frameworks/Libraries
- Have an in-depth understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Get a grip on front-end technologies like Angular, React, or Blazor.
8. Staying Up-to-Date with .NET and the Developer Community
It's very important to stay up-to-date with the latest trends, best practices, and technologies in the .NET ecosystem as we know that this technology is constantly evolving. For that:
- Follow the official .NET Blog
- Attending conferences, meetups, and webinars
- Participating in online forums and communities (Stack Overflow, Reddit, GitHub)
- Following industry leaders and influencers on social media
- Regularly reading books, articles, and tutorials on .NET topics
Conclusion
In conclusion, The .NET Developer Roadmap 2025 gives you a clear path to follow, whether you’re just starting out or looking to upgrade your skills. By learning step by step, from C# basics to advanced topics like APIs, Blazor, and cloud integration, you’ll be ready to build real-world applications with confidence. Stay consistent, keep learning, and you’ll grow into a strong and future-ready .NET developer.
This was all about the detailed procedure towards starting your journey in the direction of becoming a .NET Developer in 2025. For practicing the learned concepts, consider our .NET Training, ASP.NET Core Certification Training, .NET Microservices Certification Training, and Blazor Certification Training.
FAQs
- Forms Authentication
- Windows Authentication
- OAuth & OpenID Connect
- Identity Server
- ASP.NET Core Identity
- Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
- Open/Closed Principle (OCP)
- Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
- Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
- Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
- Variables, data types, and operators
- Control flow (conditionals, loops)
- Object-oriented programming (classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism)
- Exception handling
- Delegates and events
- Generics
- LINQ (Language Integrated Query)
- Async and await for asynchronous programming
- DbContext and DbSet for managing database connections and querying data
- Code-First and Database-First approaches for defining data models
- Migrations for managing database schema changes
- Querying data using LINQ and raw SQL
- Tracking changes and saving data
Take our Net skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.










