06
FebIf Else Statement In Python
Python If Else Statements: Conditional Statements
If-else statements or conditional statements are fundamental Python structures for making decisions based on a given condition. These statements are frequently used in organizations to develop sophisticated decision-making systems. They allow you to regulate he flow of your program, increasing its versatility and interactivity.
In this Python tutorial, we'll look at the if-else statement, covering what it is, how it works, and when to use it. We'll also look at the if-else statement in Python with examples. Only 10% of learners become Python experts. Be one with our Free Python Online Course—start your journey now!
What is an if-else statement?
- Python's decision-making depends mainly on if-else expressions.
- They define a structure for executing distinct code blocks based on whether a given condition is true or false.
- Consider your program as a road with forks; if-else statements serve as those forks, directing the program's progress based on the conditions encountered.
For example, if you're developing a weather app, you could use an if-else expression to decide whether to suggest an umbrella. The requirement would be: "Is it raining?" If true, the code recommends bringing an umbrella; if false, it may suggest sunglasses.
Types of Control Flow in Python
- Python If Statement
- Python If Else Statement
- Python Nested If Statement
- Python Elif
- Ternary Statement | Short Hand If Else Statement
Python If Statement
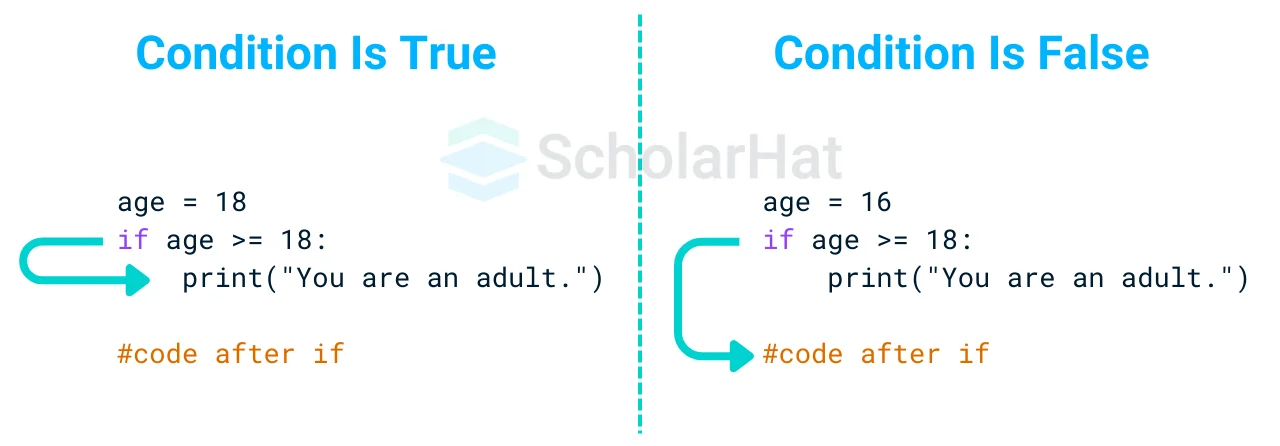
The if statement is a basic decision-making expression. It determines whether a specific statement or block of statements will be executed.
Flowchart
Syntax
if condition:
# code block to execute if condition is True
Example
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult.")
Output
You are an adult.
Explanation
Python If Else Statement
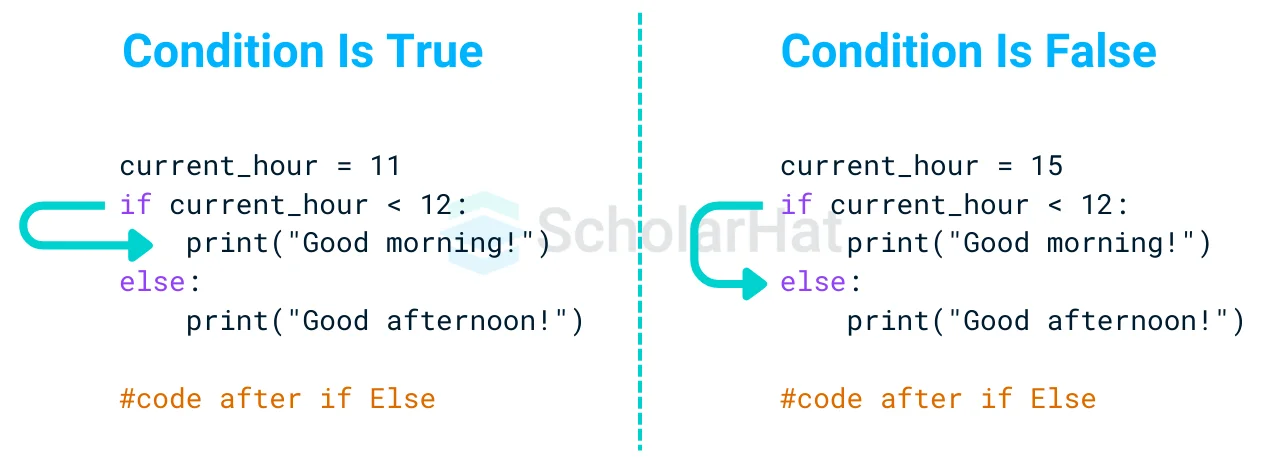
- The if statement itself indicates that if a condition is true, a block of statements will be executed.
- However, if the condition is false, they will not. However, if we want to do anything else if the condition is false, we can use the else statement together with the if statement in Python to execute a block of code.
Flowchart
Syntax
if condition:
# code block to execute if condition is True
else:
# code block to execute if condition is False
Example
current_hour = 15
if current_hour < 12:
print("Good morning!")
else:
print("Good afternoon!")
Output
Good afternoon!Explanation
Python Nested If Statement
Syntax
if condition1:
if condition2:
# code block to execute if both condition1 and condition2 are True
else:
# code block to execute if condition1 is True but condition2 is False
else:
# code block to execute if condition1 is False
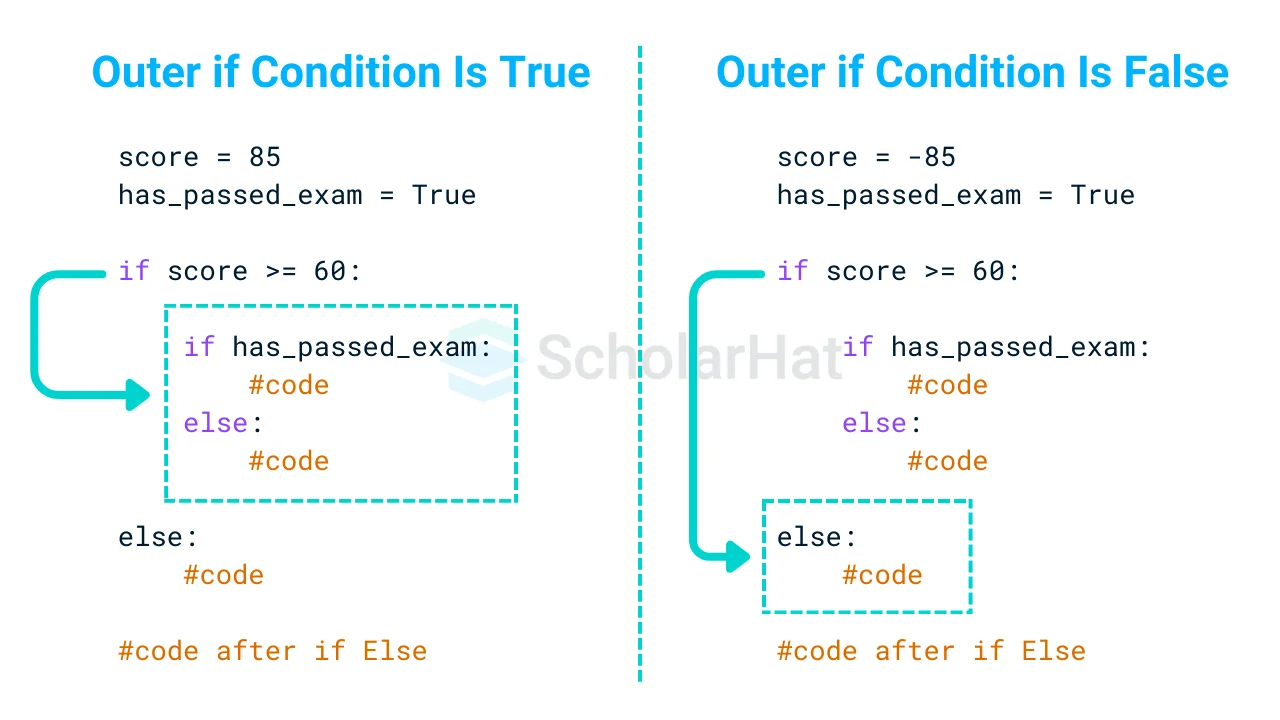
Example
score = 85
has_passed_exam = True
if score >= 60:
if has_passed_exam:
print("Congratulations! You passed with a score of", score)
else:
print("You scored well but did not pass the exam.")
else:
print("You did not pass. Try again.")
Output
Congratulations! You passed with a score of 85Explanation
The code checks whether the score is 60 or greater. If true, it also checks if has_passed_exam is true. Because both conditions are met (score = 85 and has_passed_exam = True), it displays "Congratulations!" You passed with an 85. If the score was lower or has_passed_exam was False, a different message would be displayed.Python Elif / if-else ladder
- In this conditional statement in Python, a user can select from a variety of options.The if statements are examined progressively, from top to bottom.
- When a condition evaluates to True, the related block is executed, while the remaining conditions are skipped.
- If none of the conditions hold, the last else block will be executed.
- It's also called an if-else ladder.
Syntax
if condition1:
# code block to execute if condition1 is True
elif condition2:
# code block to execute if condition1 is False and condition2 is True
elif condition3:
# code block to execute if condition1 and condition2 are False and condition3 is True
else:
# code block to execute if none of the above conditions are True
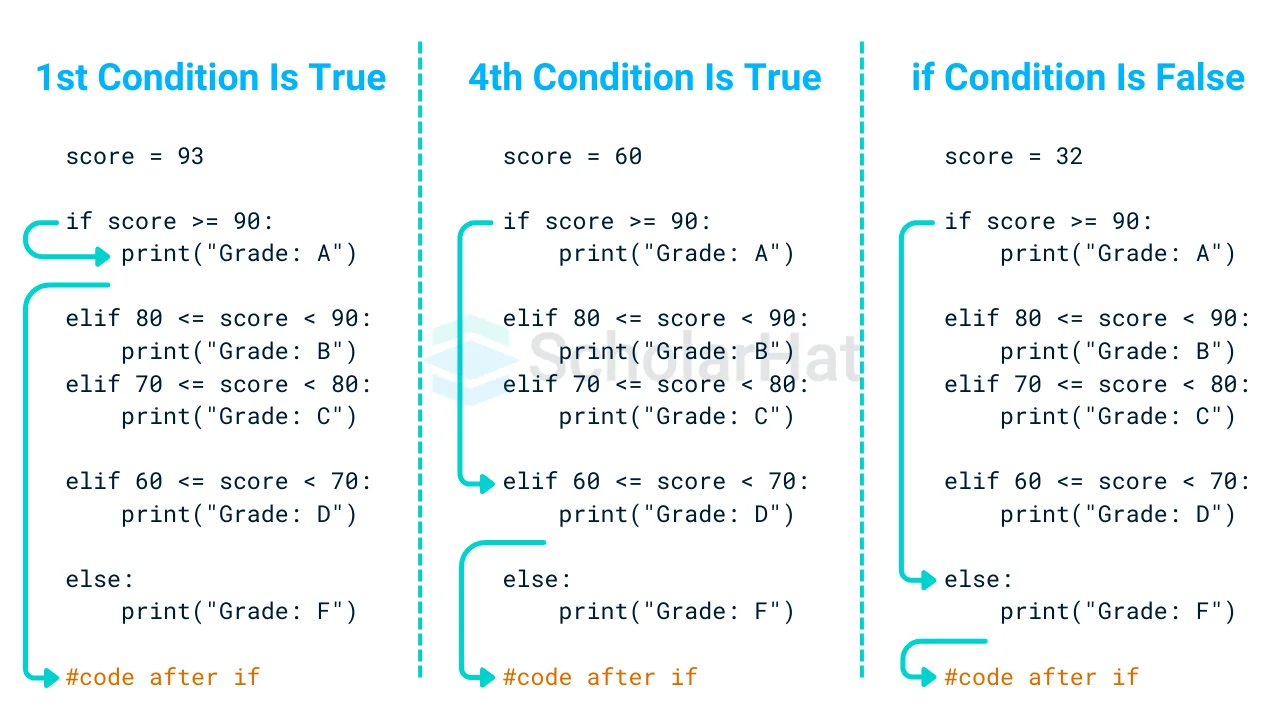
Example
score = 78
if score >= 90:
print("Grade: A")
elif 80 <= score < 90:
print("Grade: B")
elif 70 <= score < 80:
print("Grade: C")
elif 60 <= score < 70:
print("Grade: D")
else:
print("Grade: F")
Output
Grade: C
Explanation
The code evaluates the score and assigns a grade based on predefined ranges. The score of 78 falls within the range of 70 <= score < 80, meeting the criterion for grade C. "Grade: C" is printed. The remaining prerequisites are bypassed because one has already been met.Example
# Example performance rating
rating = 4.5
# Determine the appraisal feedback using an elif ladder
if rating >= 4.5:
feedback = "Outstanding performance! Expect a significant raise and bonus."
elif rating >= 3.5:
feedback = "Great job! You're doing well and can look forward to a good raise."
elif rating >= 2.5:
feedback = "Satisfactory performance. There’s room for improvement, but you’re on the right track."
elif rating >= 1.5:
feedback = "Needs improvement. Focus on developing your skills and meeting your goals."
else:
feedback = "Unsatisfactory performance. Immediate improvement is required."
print(f"Your appraisal feedback: {feedback}")
Output
Your appraisal feedback: Outstanding performance! Expect a significant raise and bonus.
Explanation
Ternary Statement | Short Hand If Else Statement
A ternary statement, often known as shorthand if-else, is a compact way to express an if-else condition on a single line. It uses the syntax value_if_true if condition, else value_if_false. This statement checks the condition and returns one value if it is True and another if it is False.Syntax
value_if_true if condition else value_if_false
Example
age = 16
status = "Adult" if age >= 18 else "Minor"
print(status)
Output
Minor
Explanation
In this example, the ternary statement determines whether the age is 18 or older. Because the age is 16, which is less than 18, the criterion is False, and the status is changed to "Minor". The print statement returns "Minor".Summary
This Python tutorial provides an in-depth look into conditional statements, focusing on how if-else structures enable code decision-making by evaluating conditions and executing related blocks. It covers a variety of control flow forms, such as simple if statements, if-else for handling alternative outcomes, nested ifs for several layers of checks, and elif ladders for multiple conditions.FAQs
Take our Python skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.