18
AprOops Concepts in Python With Examples (Full Tutorial)
What Is the Python Object-Oriented Programming Concept?
Object-oriented programming is a programming paradigm in which everything is represented as an object. OOPs, implement real-world entities in the form of objects. We know that Python is an object-oriented programming language like C++ and Java. OOP in Python helps developers to develop reusable, scalable, modular, and efficient code.
In this Python tutorial, we'll delve deep into the OOP concepts in Python with illustrations. If you want to make use of Python's OOP features, you need first to understand what are the OOP concepts used in Python. To help you out, let us now begin. Additionally, enrolling in a Python for Data Science and AI Training program can help you master OOP principles and their applications in data science and AI projects. To help you out, let us now begin.
| Read More: Top 50 Python Interview Questions and Answers |
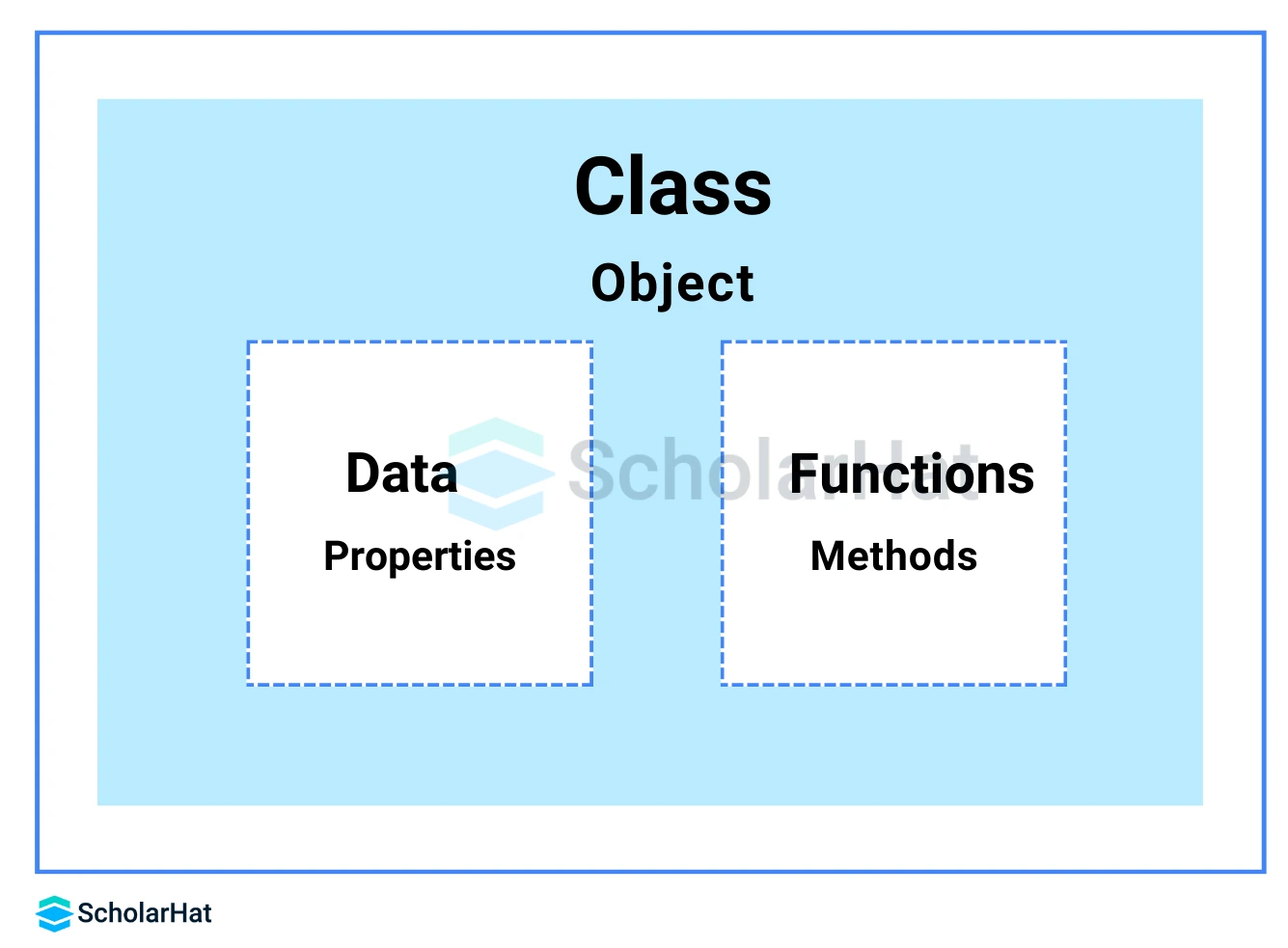
1. Class in Python
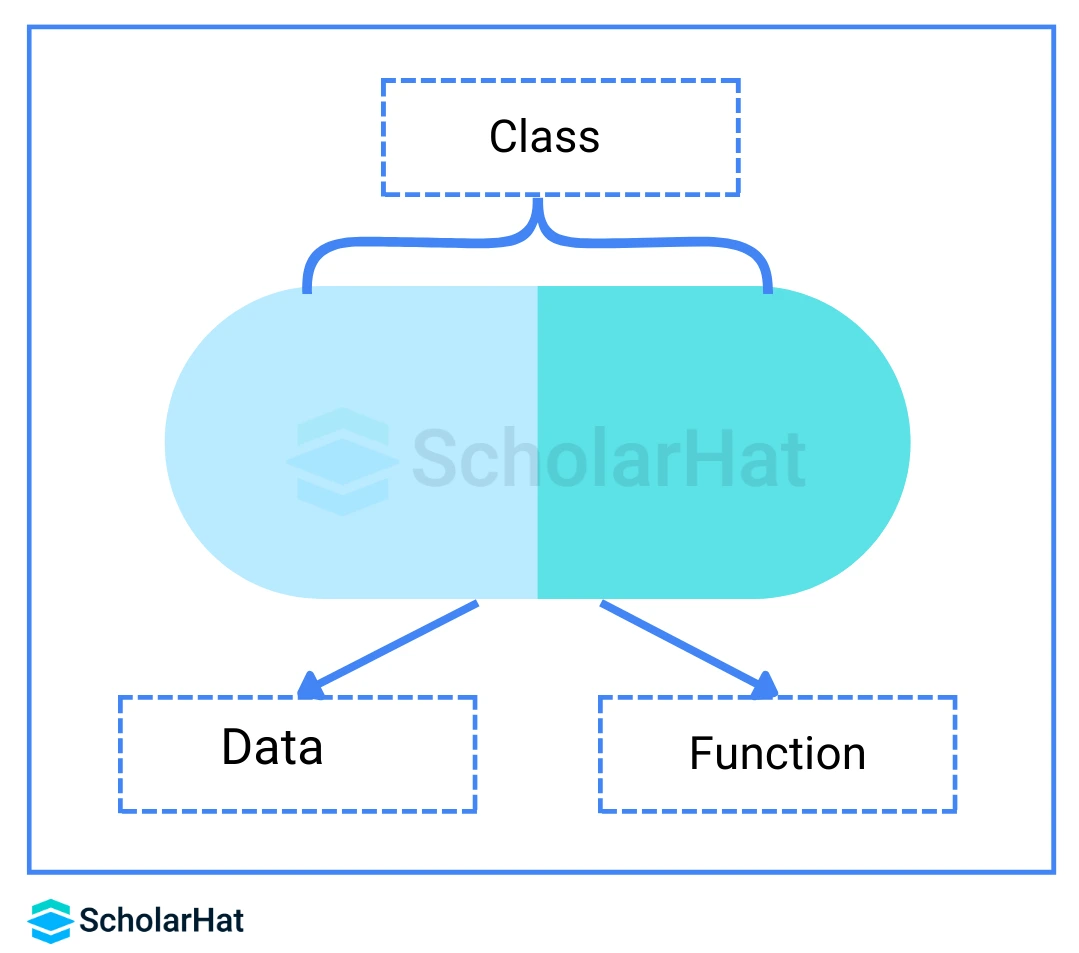
A class in Python is a collection of objects, like a blueprint for an object. In Python, a class is the foundational element of object-oriented programming. An instance of a class is created to access its data types and member functions.
Classes are defined with the class keyword.
Syntax
class ClassName:
# Statement-1
.
.
.
# Statement-N
Example
class ScholarHat:
pass The above class, ScholarHat is created.
2. Objects in Python
An object is a real-world entity having a particular behavior and a state. It can be physical or logical. Here state and behavior signify attributes and methods respectively. All functions have a built-in attribute __doc__, which returns the docstring defined in the function source code. An object is an instance of a class and memory is allocated only when an object of the class is created.
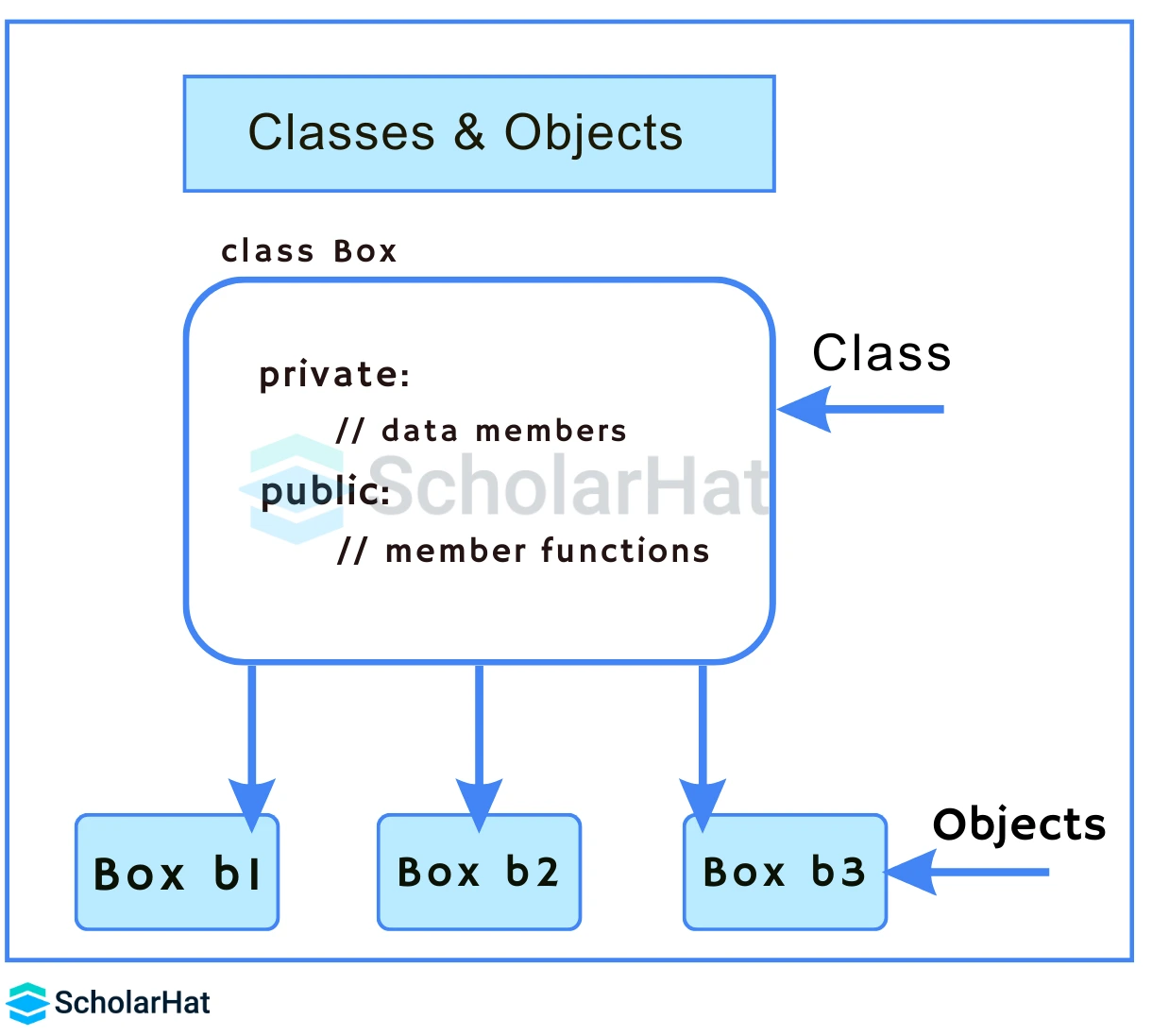
Example of Object Declaration in Python
#define a class
class ScholarHat:
pass
#define an object
obj = ScholarHat() This will create an object named obj of the ScholarHat class.
1. The Python __init__ Method
The __init__ method gets invoked as soon as the object is created. It is like the constructor of a class. The method initializes the data members of the class for an object.
| Read More: |
2. The Python self
self is the first parameter in the method definition of a class. We do not give a value for this parameter when we call the method, Python provides it It is a default argument for any method of the class. We have learned the "this" keyword in Java. The self-parameter works similarly.
Example illustrating Classes and Object creation in Python
class Company:
# class attribute
role = "employee"
# Instance attribute
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
# Object instantiation
Sakshi = Company("Sakshi")
Sourav = Company("Sourav")
# Accessing class attributes
print("Sakshi is an {}".format(Sakshi.__class__.role))
print("Sourav is also an {}".format(Sourav.__class__.role))
# Accessing instance attributes
print("My name is {}".format(Sakshi.name))
print("My name is {}".format(Sourav.name))
Output
Sakshi is an employee
Sourav is also an employee
My name is Sakshi
My name is Sourav | Read More: Python Classes and Objects with Examples |
OOP Concepts in Python with Examples

| Read More: Top 50 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers |
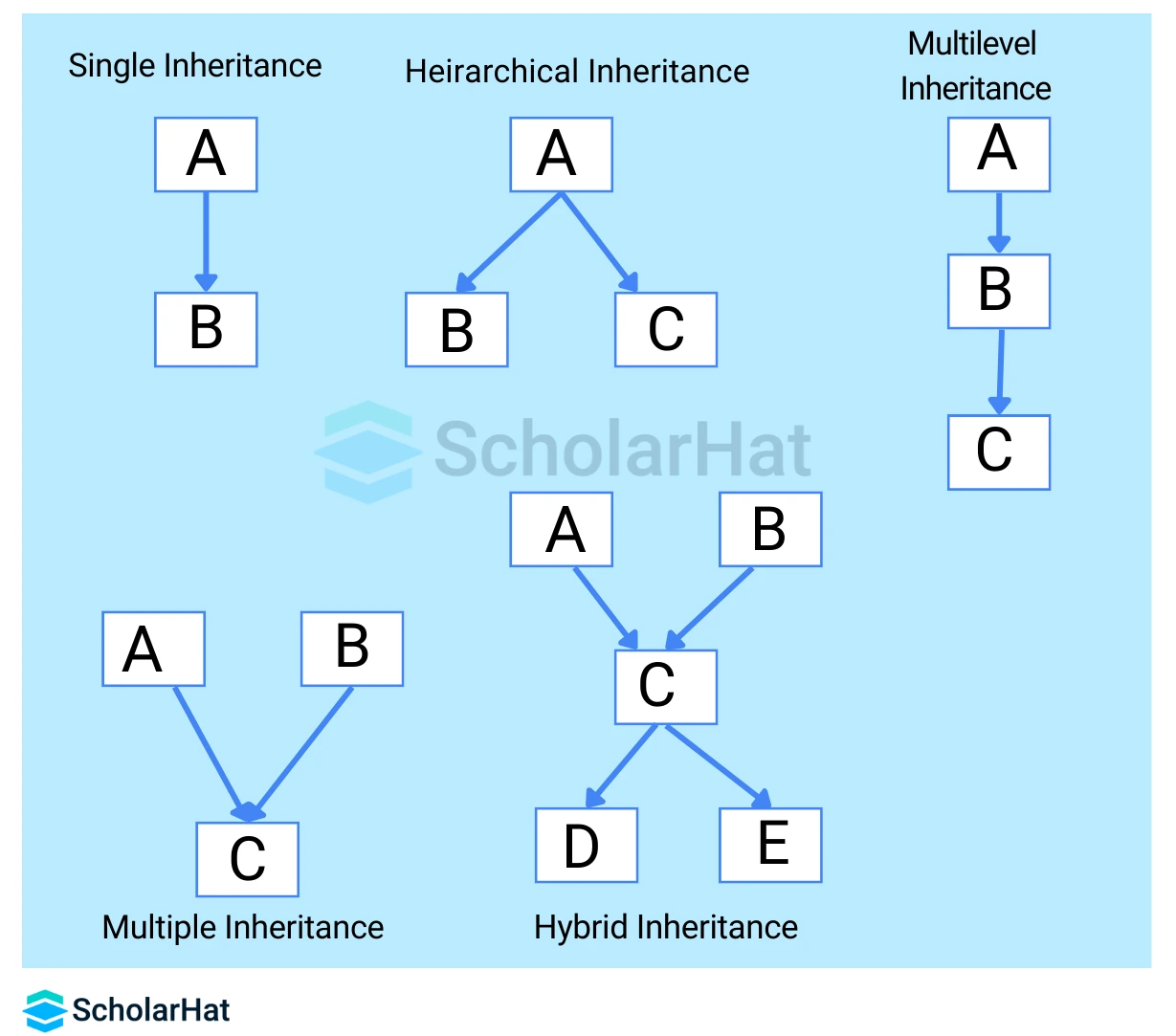
1. Python Inheritance
It is the phenomenon when a class derives its characteristics from another class. In other words, when an object of a class derives all its properties from the parent object. The class that inherits the properties is known as the child class/derived class and the main class is called the parent class/base class.
class Person(object):
def __init__(self, name, idnumber):
self.name = name
self.idnumber = idnumber
def display(self):
print(self.name)
print(self.idnumber)
def details(self):
print("My name is {}".format(self.name))
print("IdNumber: {}".format(self.idnumber))
# child class
class Employee(Person):
def __init__(self, name, idnumber, salary, post):
self.salary = salary
self.post = post
# invoking the __init__ of the parent class
Person.__init__(self, name, idnumber)
def details(self):
print("My name is {}".format(self.name))
print("IdNumber: {}".format(self.idnumber))
print("Post: {}".format(self.post))
# creation of an object variable or an instance
emp = Employee('Sourav', 234, 50000, "SEO")
emp.display()
emp.details()
In the above code, we have created two classes i.e. Person (parent class) and Employee (Child Class). The Employee class inherits from the Person class.
Output
Sourav
234
My name is Sourav
IdNumber: 234
Post: SEO 2. Python Polymorphism
Polymorphism means the ability to take more than one form in Python programming language. With this feature, you can use the same function to perform different tasks thus increasing code reusability.
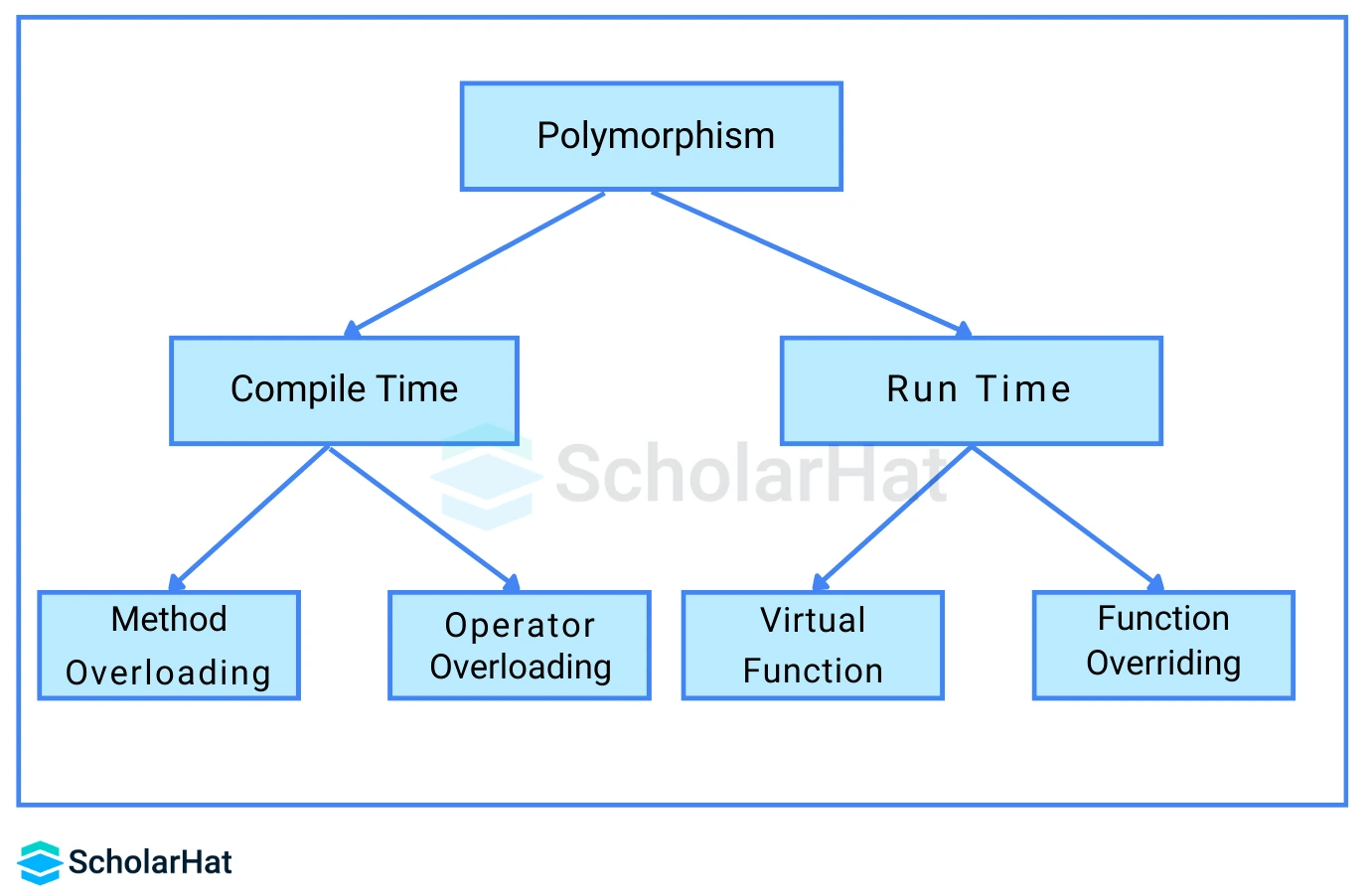
Example illustrating Polymorphism
class MangoTree:
def respire(self):
print("The mango trees do respiration at night.")
class NeemTree(MangoTree):
def respire(self):
print("Respiration in neem trees occurs mainly through stomata.")
def main():
my_mango_tree = MangoTree()
my_neem_tree = NeemTree()
my_mango_tree.respire()
my_neem_tree.respire()
Output
The mango trees do respiration at night.
Respiration in neem trees occurs mainly through stomata.
3. Python Encapsulation
Encapsulation helps to wrap up the functions and data together in a single unit. By privatizing the scope of the data members it can be achieved. This particular feature makes the program inaccessible to the outside world.
Example illustrating Encapsulation
class Base:
def __init__(self):
self.a = "ScholarHat"
self.__c = "DotNetTricks"
# Creating a derived class
class Derived(Base):
def __init__(self):
# Calling constructor of Base class
Base.__init__(self)
print("Calling private member of base class: ")
print(self.__c)
obj1 = Base()
print(obj1.a)
The Derived class inherits from Base and attempts to access __c, which results in an AttributeError because private attributes are not accessible from derived classes.
Output
ScholarHat
4. Python Abstraction
Abstraction in Python programming language helps in the process of data hiding. It assists the program in showing the essential features without showing the functionality or the details of the program to its users. It generally avoids unwanted information or irrelevant details but shows the important part of the program.
Example illustrating Abstraction
class TestAbstraction:
def __init__(self):
self.x = ""
self.y = ""
def set(self, a, b):
self.x = a
self.y = b
def print_values(self):
print("x =", self.x)
print("y =", self.y)
t1 = TestAbstraction()
t1.set("ScholarHat", "DotNetTricks")
t1.print_values()
The above Python program defines a TestAbstraction class with a constructor that initializes two attributes, x, and y, to empty strings. The set method allows setting these attributes to given values, while the print_values method prints their current values. An instance of TestAbstraction, t1, is created, and the set method is used to assign the values "ScholarHat" to x and "DotNetTricks" to y. Finally, the print_values method is called to print these values.
Output
x = ScholarHat
y = DotNetTricks
Object-oriented vs. Procedure-oriented Programming languages
| Object-oriented Programming | Procedural Programming |
| Object-oriented programming is built on objects having a state and behavior. | It is a step-by-step programming approach consisting of a list of instructions. |
| It follows a bottom-to-top approach. | It follows a Top-to-Down approach. |
| Modifying and updating the code is easier. | Modifying the code is difficult as compared to OOPs. |
| Enhances data security by regulating the flow of information exclusively to authorized entities, ensuring controlled access to sensitive data. | There are no constraints on data flow; it's accessible to anyone. |
| Examples of object-oriented programming languages are C++, Java, .Net, Python, C#, etc. | Examples of procedural languages are C, Fortran, Pascal, VB etc. |
Object-Oriented Design Principles in Python
Have you heard of SOLID principles? It is an acronym that groups five core principles for object-oriented design.
1. Single Responsibility
2. Open-Closed Principle (OCP)
3. Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
4. Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
5. Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
Advantages of OOP in Python Development
- Modularity: Classes allow you to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable pieces.
- Reusability: Code can be reused through inheritance and polymorphism, reducing redundancy.
- Encapsulation: Data hiding and abstraction help protect object integrity by restricting access to certain components.
- Maintainability: Well-structured code is easier to manage, debug, and update.
- Flexibility: Polymorphism and dynamic binding provide the ability to extend and modify code behavior without altering existing code.
- Improved Productivity: Reusability and modularity lead to faster development and iteration cycles.
- Real-world Modeling: Objects allow for natural modeling of real-world entities and relationships, making the code more intuitive.
| Read More: |
Summary
This article has made you familiar with OOP in Python Programming. Understanding how to work with objects and classes is essential for any programmer, and that’s why exploring this tutorial would be beneficial for those who want to be able to master this powerful language. Thanks for reading! We hope you have a better understanding of OOP concepts and object classes in Python now.
FAQs
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Encapsulation
- Abstraction