18
AprAn Easy Way To Understanding Python Slicing
Slicing in Python
Slicing in Python is a technique for taking out certain parts of strings, lists, or tuples from sequences. By specifying a range of indices, you may quickly retrieve sub-sections of this sequence. It offers a straightforward and accessible approach to executing actions that might otherwise need loops or complicated indexing.
In the Python tutorial, we will study what is slicing in Python?, including why is it important for developers?, slicing syntax, default parameter in slicing, advance slicing techniques in Python, practical applications of slicing, real-world examples of slicing in Python, and many more.
What is Slicing in Python?
Slicing in Python is a method that involves slicing a string from beginning to finish in order to obtain a substring. To put it another way, if you have a string and you want a certain section of it, you may slice off the undesirable portion to achieve the desired result.
Why is Slicing Important for Python Developers?
Slicing in Python is very useful for the developers to enhance their productivity by:
- Allows developers to quickly and easily access and modify specific parts of sequences like lists, strings, and tuples.
- Provides a concise and readable way to perform operations that would otherwise require loops or complex indexing.
- Create views of data without copying the entire sequence, which is particularly useful when working with large datasets.
- Supports negative indexing and step values, giving developers the option of working with sequences in both forward and backward orientations.
| Read More: |
| Python Career Guide: Is it worth learning in 2025? |
| 10 Python Developer Skills You Must Know in 2025 |
| Python Developer Roadmap: How to Become a Python Developer? |
What is an Index?
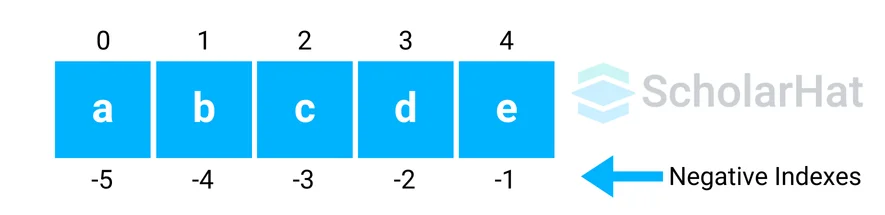
Syntax of Slicing in Python
slice(start, stop, step)
The start, stop, and step arguments are the standard ones for Python slicing:
- start: Describe the slice's beginning index.
- stop: Determine the slice's last component.
- step: Define the interval between each element in the slice.
Example
my_String = 'BANARAS'
# Using slice constructor
s1 = slice(3)
s2 = slice(1, 5, 2)
s3 = slice(-1, -12, -2)
print("String slicing")
print(my_String[s1])
print(my_String[s2])
print(my_String[s3])
Output
String slicing
BAN
AA
SRNB
Advanced Slicing Techniques in Python
1. Using Negative Indexing in Slicing
Example
#Python program to print the number
#using Negatve index
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
sliced_list = my_list[-4:-1]
print(sliced_list);
Output
20
30
402. Slicing with Steps for More Control
Slicing with steps in Python allows you to have more control over how you extract elements from a sequence. The step option allows you to skip entries, change the order, or choose elements at precise intervals.
Example
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
# Example 1: Skipping Elements
sliced_list = my_list[1:8:3]
print(sliced_list)
Output
20
50
803. Reversing Sequences Using Slicing
Reversing sequences in Python with slicing is a simple and efficient approach to obtaining the components of a sequence in reverse order. This method works with additional sequence types such as tuples, lists, and strings.
Example
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
reversed_list = my_list[::-1]
print("Reversed List:", reversed_list)
Output
Reversed List: [50, 40, 30, 20, 10]4. Slicing Multidimensional Sequences
In Python, you may slice multidimensional sequences to extract sub-arrays or sub-sections from lists or arrays by providing ranges of indices for each dimension.
Example
# 2D list (list of lists)
matrix = [
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16]
]
# Slicing to get a sub-matrix
sub_matrix = [row[1:3] for row in matrix[1:3]]
print("Sub-matrix:", sub_matrix)
output
Sub-matrix: [[6, 7], [10, 11]]Practical Applications of Slicing in Python
1. Slicing Lists in Python
Example
names = ['Aarav', 'Vivaan', 'Reyansh', 'Aadhya', 'Isha', 'Mira', 'Anaya']
# Slicing to get the first 3 names
first_three_names = names[:3]
print("First 3 names:", first_three_names)
Output
First 3 names: ['Aarav', 'Vivaan', 'Reyansh']2. Slicing Strings for Substring Extraction
Example
text = "Slicing strings is fun!"
# Slicing to get every second character
skipped_chars = text[::2]
print("Every second character:", skipped_chars)
Output
Every second character: Siigsrnsi u!3. Slicing Tuples in Python
Example
numbers = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
# Slicing to get a subtuple from index 2 to 5
sub_tuple = numbers[2:6]
print("Subtuple:", sub_tuple)
Output
Subtuple: (3, 4, 5, 6)Limitations of Slicing Tuples
- Slicing does not allow you to change a tuple's contents.
- Truncations are created when operations appear to alter a tuple.
- Slicing does not allow you to change the size of a tuple or add or remove components. New tuples with the specified size are the only ones you can make.
- Changes made in-place are not supported by tuples. It is not possible to modify already-existing tuples using operations like slicing. Only new ones may be created.
4. Slicing in NumPy Arrays
Example
# Create a 2D NumPy array
array_2d = np.array([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16]
])
# Slicing to get elements from rows 1 to 2 and columns 2 to 3
slice_2d = array_2d[1:3, 2:4]
print("2D Slice:\n", slice_2d)Best Practices for Slicing in Python
Various best practices for slicing in Python are widely used in lists, tuples, strings, and arrays:
1. Writing Readable and Maintainable Code
- Use descriptive variable names for slices to indicate their purpose and improve readability clearly.
- To make the code easier to read and maintain, add comments to complicated slices that explain the reasoning behind the slicing and its purpose.
2. Performance Considerations with Slicing
- Slicing in Python frequently generates views rather than copies, which can conserve memory and increase efficiency when working with huge datasets.
- Python's slicing procedures are designed for speed, allowing for the quick and efficient extraction of sub-sequences or sub-arrays.
3. Avoiding Common Errors in Slicing
- Ensure that slicing indices are within the bounds of the sequence to avoid errors or unexpected empty slices.
- When using the step parameter, verify that it’s set correctly to avoid skipping too many or too few elements.
Real-World Examples of Slicing in Python
1. Slicing in Data Analysis
- Operating Python slicing to extract specific rows, columns, or subsets from datasets. This allows for targeted analysis and visualization of relevant information.
- Using slicing to quickly handle and transform large datasets, improving efficiency in data cleaning and analysis tasks.
2. Slicing for Image Processing
- Using the slice technique to extract specific portions from an image, such as focusing on a certain object or area, can help with tasks like object recognition and feature extraction.
- Implement slicing to alter picture dimensions by choosing and resizing areas of the image, allowing for effective scaling and modification in a variety of applications.
3. Web Scraping with Slicing
- Use Python slicing to target and extract relevant portions of web page content, such as tables, lists, or specific HTML elements, for efficient data collection.
- Apply slicing to refine and preprocess scraped data, removing unwanted characters or formatting it into a structured format, which aids in subsequent analysis and processing.
4. Slicing in Machine Learning
- Adapting slicing to extract and select specific features or subsets of data from large datasets, aiding in feature engineering and improving model performance.
- Employ slicing to create variations of training data, such as cropping or rotating images, to enhance model robustness and generalization.
| Read More: |
| Python Developer Salary |
| Best 50+ Python Interview Questions and Answers |
| Python Attributes: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners |
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have examined Slicing in Python. Slicing in Python is an important concept followed by developers; it provides a strong and efficient way to shape sequences such as lists, strings, tuples, and arrays. Learning slicing helps developers to efficiently extract, modify, and analyze specific portions of data, which is crucial for tasks ranging from data preprocessing and feature selection to image processing and web scraping. If you want to learn Python thoroughly, ScholorHat provides a Free Python Programming Course for Beginners to help you better understand other Python concepts.







