18
AprTop 50+ React Interview Question & Answers
Are you getting ready for a React interview but not sure what to study? Don’t worry; we are here to help! We have collected the most important ReactJS interview questions so you can prepare confidently. From essential topics like components and state to advanced React interview questions about hooks and performance, we make learning easy. Practicing React coding interview questions will help you solve problems faster and feel more confident.
In the Interview tutorial, you will find React interview questions and answers explained thoroughly. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, our guide covers ReactJS interview questions for professional developers, including app optimization and best coding practices. With the proper preparation, you can clear your ReactJS interview and get the job you want!
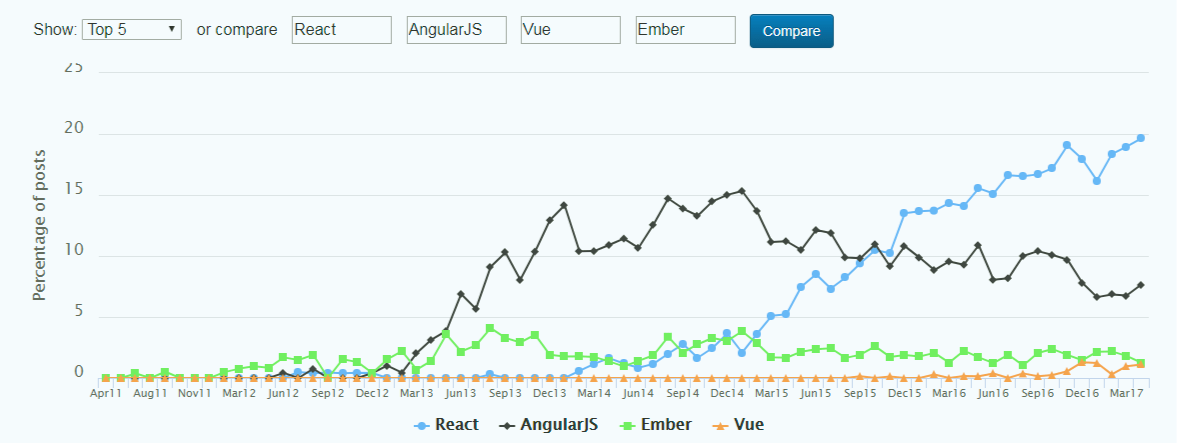
As of today, there are around 1,000 contributors on GitHub. Isn’t that impressive? One of the reasons React stands out is its unique features, like the Virtual DOM and reusable components, which grab the attention of front-end developers everywhere. Even though React is just a library for ‘View’ in the MVC (Model-View-Controller) model, it's still giving tough competition to full-blown frameworks like Angular, Meteor, and Vue. Curious to see how React compares to other JS frameworks? Check out the graph below to see the trend of the most popular JavaScript frameworks!
Scope of React
Choosing the right technology for your web or application development can be tricky, right? But React has emerged as one of the fastest-growing JavaScript frameworks today. It's no surprise that the demand for React certification is growing rapidly. Developers love React because it offers a quick learning curve, clean abstraction, and reusable components. It's a favorite for front-end development. And the best part? React keeps evolving, so there’s no stopping it anytime soon. So, are you ready to dive into React and boost your development skills?
Why are React.js Skills in Demand?
React.js is very popular because it helps developers build fast and interactive web applications. Many big companies use React, so there are lots of job opportunities for React developers.
- Easy to learn – React has a simple structure, making it easier for beginners to start coding.
- Fast Performance – It updates web pages quickly using a smart way called the virtual DOM.
- Strong Community Support – Many developers use React, so you can easily find help and resources.
- High Demand in Jobs – Many companies look for React developers because it’s used in big projects.
- Reusable Components – You can use the same code again, which saves time and makes development faster.
Basic React Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners
1. What is React?
Facebook created the front-end JavaScript library React in 2011. React uses a component-based methodology that allows you to create reusable user interface components. It’s primarily used for building dynamic and complex mobile and web user interfaces.
- Component-Based – React allows you to build reusable UI components, making development faster and more organized.
- Fast Performance – It uses the virtual DOM to update web pages quickly and efficiently.
- Huge Demand – Many companies use React, so learning it helps in cracking React interview questions and getting good job opportunities.
2. What characteristics does React have?
React's key characteristics include:
- It supports Server-side rendering.
- It uses aVirtual DOM instead of the real DOM to optimize performance.
- It follows a unidirectional data flow (data binding).
- It enables the construction of UI using reusable or composable components.
3. What are the most important benefits of utilizing React?
Several key benefits of React include:
- Learning React is easy and intuitive.
- It adheres to the MVC design pattern.
- React improves efficiency with Virtual DOM.
- It allows you to createdynamic web applications easily.
- It’s great for SEO optimization.
- It supports reusable components.
- Comes with practical tools.
- Has a large and active community.
- React supports a variety of code-testing methods.
4. Can web browsers interpret JSX directly?
No, web browsers cannot understand JSX directly. It needs to be converted into regular JavaScript using tools like Babel before browsers can read it.
5. What are the main drawbacks of React?
Here are the key drawbacks of React:
- React is just a library, not a full-fledged framework.
- Its extensive library can take time to understand fully.
- Beginner developers might find it challenging to grasp and write React code.
- It uses JSX and inline templating, which may be confusing for some and complicates coding.
6. Describe JSX.
JSX stands for JavaScript XML. It is an extension of JavaScript that allows you to write HTML-like syntax within your JavaScript code. JSX enhances React’s functionality by allowing developers to create UI components that are easier to understand and maintain. Preprocessors, like Babel, convert JSX expressions into standard JavaScript code.
7. Why is JSX unreadable by browsers?
Browsers can only read JavaScript objects, but JSX is not a standard JavaScript object. To make JSX understandable to browsers, we must use JSX transformers (like Babel) to convert it into JavaScript code, which browsers can then execute.
8. Why do we use JSX?
- Performance: JSX allows for faster execution as it gets converted to JavaScript.
- React uses components that combine both markup and logic, which simplifies code structure.
- It offerstype safetyand catches most problems duringcompilation.
- JSX simplifies the creation of templates within React applications.
9. What is the difference between functional components and class components in React?
The difference between functional components and class components in React:
| Factors | functional components | class components |
| Definition | Simple JavaScript functions | Uses ES6 class syntax |
| State Management | Uses useState hook | Uses this.state |
| Lifecycle Method | Uses hooks like useEffect | Uses lifecycle methods like componentDidMount |
| Performance | Faster and lightweight | Slightly slower due to more boilerplate code |
| Code Complexity | Short and easy to read | More complex and longer |
| Use cases | Preferred for simple UI components | Useful when complex logic and lifecycle methods are needed |
| React Version | Recommended in modern React | Mostly used in older React versions |
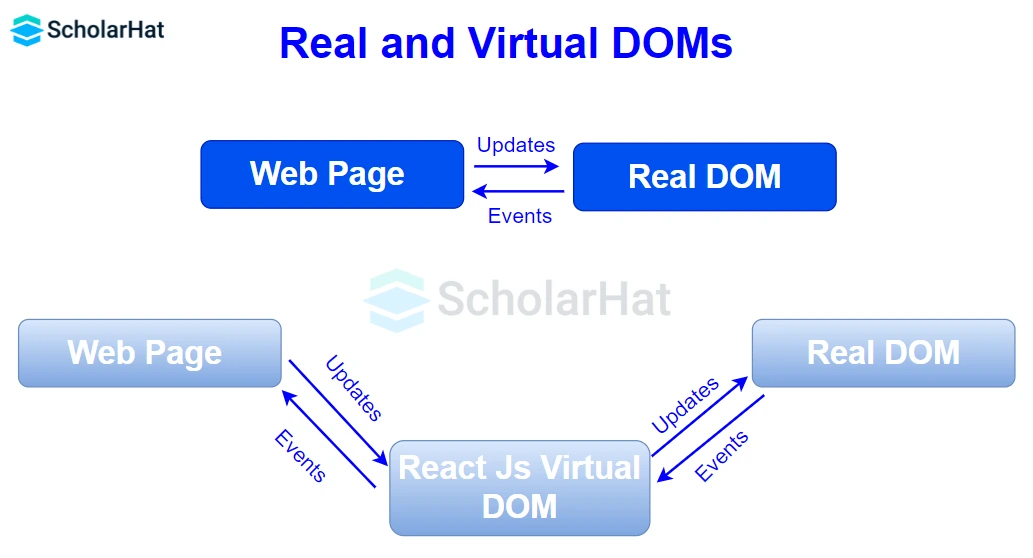
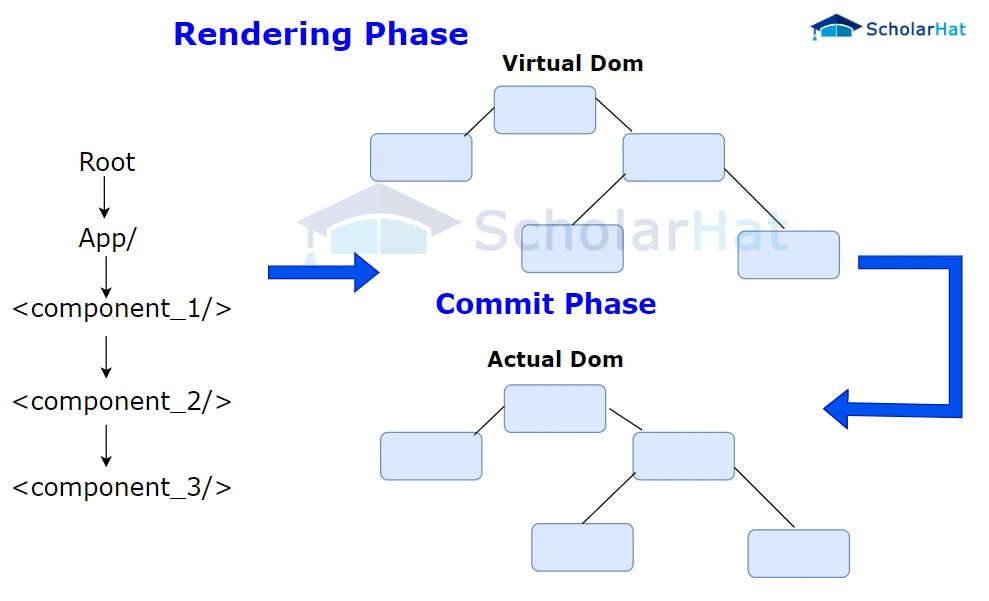
10. What does Virtual DOM mean to you?
The Virtual DOM is essentially a lightweight copy of the actual DOM. It is used by React to improve performance. React’s render function builds a virtual DOM tree representing the elements, attributes, and content as JavaScript objects. When there is a change in the data model, React updates this virtual tree and then applies necessary changes to the real DOM efficiently.
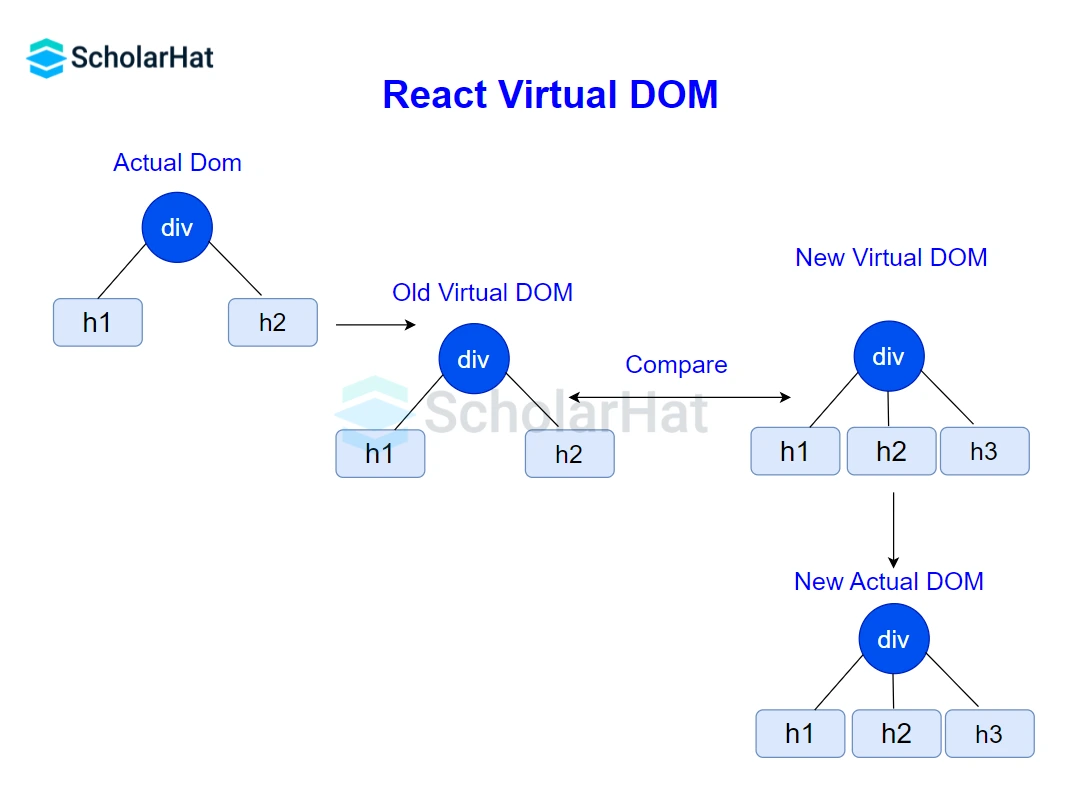
11. Describe how the Virtual DOM operates.
The Virtual DOM operates in three stages:
- When any data in the React application changes, the Virtual DOM representation of the user interface is re-rendered.
- It then compares the new Virtual DOM with the previous one, finding the differences.
- Only the modified items are updated in the real DOM, resulting in efficient rendering.
12. What does React's render() method achieve?
Every React component must have a render() method. This method returns the HTML that should be displayed by the component. It's important to note that all elements to be rendered must be wrapped in a single parent element like a <div> or <form>.
Read More - React Roadmap
13. How may multiple components be integrated into one?
There are various methods in React that allow you to integrate multiple components into one, helping build complex user interfaces. These methods include:
- JSX Composition: Combining multiple components using JSX.
- Passing Components as Props: You can pass components as props to child components to combine them into one.
- Conditional Rendering: Dynamically render components based on certain conditions.
- Higher-Order Components (HOCs): These are functions that take a component and return a new component with additional functionality.
- Render Props: A technique for sharing code between React components using a function prop.
14. What Do React Props Mean?
Props (short for properties) are an essential feature in React. They allow data to flow from parent components to child components. Similar to HTML attributes, props store values passed to a component. They are immutable, meaning you cannot modify props within a component. You can think of props as arguments to a function, allowing you to pass data between components in a reusable way.
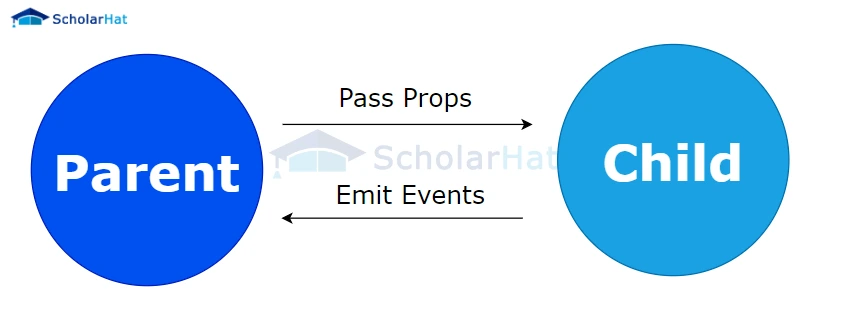
15. In React, what is a State?
State is a fundamental concept in React that allows components to create dynamic, interactive user interfaces. Unlike props, which are immutable, the state can be updated within a component to reflect changes. States are objects that manage the data of a component, and they control how the component is rendered. You can access and modify the state using this.state().
For more information on React states, check out this guide.
16. What are the types of side effects in React?
In React, side effects are anything that happens outside the component, like fetching data or updating the DOM. Understanding side effects is important for answering React interview questions and handling state properly.
Here are the main types of side effects:
- Data Fetching – Getting data from an API, which is a common topic in ReactJS interview questions.
- DOM Updates – Changing the web page manually, like updating the title or handling animations.
- Timers and Intervals – Using setTimeout or setInterval, often asked in React coding interview questions.
In ReactJS interview questions for experienced developers, you may also be asked how to manage side effects using the useEffect hook in functional components.
17. What is an Effect with Cleanup and an Effect without Cleanup?
In React, effects are side tasks like fetching data or updating the DOM, usually handled inside the useEffect hook. Understanding these is important for React interview questions and real-world projects.
Effect Without Cleanup
- Runs a task that doesn’t need cleanup after the component updates or unmounts.
- Example: Fetching data, logging messages, or updating the document title.
- This is a common ReactJS interview question for beginners.
Effect with Cleanup
- Runs a task that needs to be cleaned up to prevent memory leaks or unwanted behavior.
- Example: Removing event listeners, clearing timers (setTimeout, setInterval), or unsubscribing from APIs.
- Frequently asked in ReactJS interview questions for experienced developers to test proper resource management.
In React coding interview questions, you may be asked how to use the return function inside useEffect for cleanup.
18. What is pop drilling in React?
Prop drilling happens when you pass data (props) from a parent component to a deeply nested child component. This makes the code harder to manage, especially in large applications. Understanding prop drilling is important for React interview questions and handling state efficiently.
19. Describe the error boundaries.
Error boundaries are special React components that catch JavaScript errors in their child components and prevent the entire app from crashing. They help in handling errors gracefully, making the UI more stable.
- They are React class components that use the componentDidCatch and getDerivedStateFromError methods.
- They only catch errors in child components, not in event handlers or asynchronous code.
- Commonly asked in React coding interview questions related to debugging and error handling.
- Used to display a fallback UI instead of breaking the entire application.
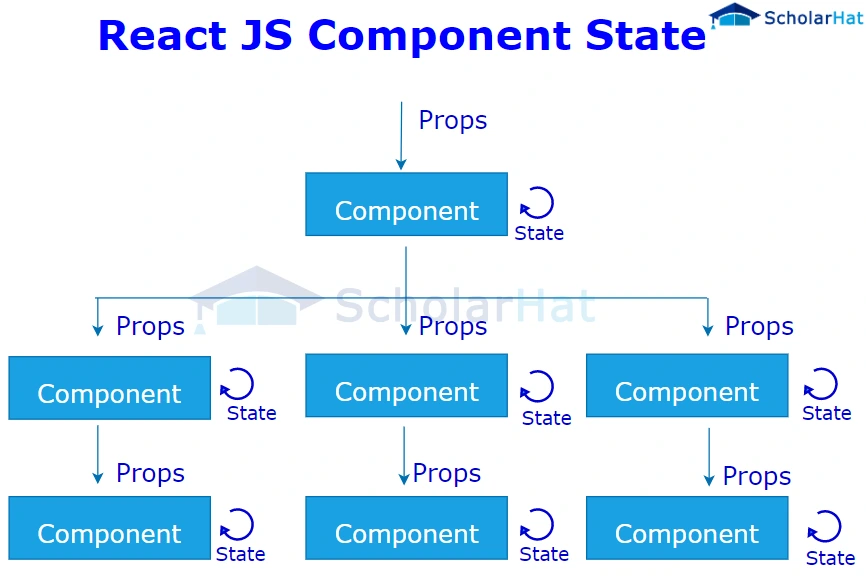
20. Distinguish in React between States and Props.
Here are the key differences between State and Props in React:
| SN | Props | State |
| 1. | Props are read-only and cannot be modified. | A state can be modified asynchronously. |
| 2. | Props are immutable. | State is mutable and can change over time. |
| 3. | Props are used to pass data between components. | State holds information specific to a component. |
| 4. | Child components can access props. | The state is not directly accessible by child components. |
| 5. | Components communicate with each other using props. | The state is used to trigger dynamic changes within a component. |
| 6. | Props can be used in stateless components. | State is incompatible with stateless components. |
| 7. | Props make components reusable. | State is specific to the component and cannot be reused. |
| 8. | The parent component manages external props. | The component itself manages its internal state. |
21. In React, how can the State of a component be updated?
To update the state of a component in React, you use the this.setState() method. This method ensures that the component re-renders with the updated state. It's important to note that state updates are asynchronous, so the state might not be immediately updated after calling setState().
Example:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Counter extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0,
};
}
incrementCount = () => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Counter</h1>
<p>Count: {this.state.count}</p>
<button onClick={this.incrementCount}>Increment</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Counter; React Interview Questions and Answers for Intermediate
22. Define the differences between React's stateless and stateful components.
| SN | Stateless Components | Stateful Components |
| 1. | There is no state held or managed by the stateless components. | The state can be held or managed by the stateful components. |
| 2. | Knowledge of past, present, and potential future state changes is absent from it. | It may include information about past, present, and potential future state changes. |
| 3. | Another name for it is a functional component. | Another name for it is a class component. |
| 4. | It is clear and easy to comprehend. | Compared to the stateless component, it is more complex. |
| 5. | It is incompatible with all React lifecycle methods. | It is compatible with any React lifecycle method. |
| 6. | Reusing the stateless components is not possible. | Reusing the stateful components is possible. |
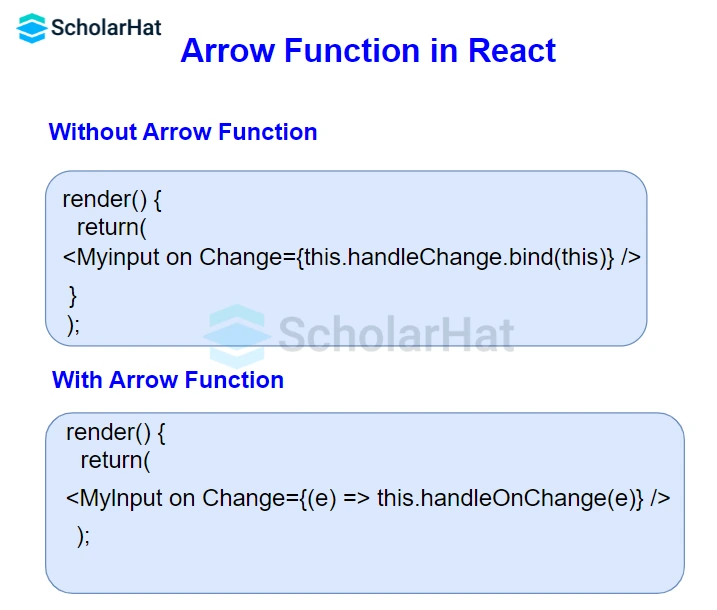
23. What is the purpose of an arrow function in React?
Arrow functions are essentially a condensed form of function expression writing syntax. The functions are also referred to as "fat arrows" (=>). Due to ES6's default lack of auto-binding, these functions enable the components' contexts in React to be bound correctly. Most of the time, arrow functions come in handy when interacting with higher-level functions.
24. What does React define as an event?
Events in React are the responses that are set off by particular actions, such as key presses, mouse clicks, and mouse hovers. Managing these events is comparable to managing DOM element events. However, there are some syntactical variations, such as the following:
- Events are named in camel case rather than only lowercase.
- Functions are passed in place of strings when passing events.
25. How may an event be created in React?
You may create a React event by carrying out the following example:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class MyComponent extends Component {
// Event handler function
handleClick = () => {
alert('Button clicked!');
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>React Event Example</h1>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default MyComponent; 26. What do React's synthetic events mean?
- The objects that serve as a cross-browser wrapper for the native event of the browser are known as synthetic events.
- They create a single API that combines several browsers' behaviors.
- This is done to ensure that the properties displayed by the events are consistent across various browsers.
27. Describe the differences between controlled and uncontrolled components in React.
Let's understand the differences between controlled and uncontrolled components in React
| SN | Controlled | Uncontrolled |
| 1. | It doesn't hold onto its internal state. | It keeps its internal state. |
| 2. | In this case, the parent component controls the data. | In this case, the DOM itself controls the data. |
| 3. | As a prop, it accepts its current value. | To get their current values, it uses a ref. |
| 4. | Control over validation is possible. | Control over validation is not permitted. |
| 5. | It has more control over the data and form elements. | Its power over the data and form elements is restricted. |
28. Describe Lists in React.
- Data can be shown in an ordered way using lists. Lists in React can be formed similarly to how they are in JavaScript.
- With the help of the map() method, we may go through the list's elements.
29. What use do keys provide in React?
- The UI is driven by data that corresponds to distinct Virtual DOM Elements, which are identified by keys.
- By reusing every element already present in the DOM, they assist React in rendering as efficiently as possible.
- These keys have to be distinct strings or numbers, or else React simply rearranges the elements rather than re-rendering them.
- The performance of the application increases as a result.
30. How are React forms created?
- HTML forms and React forms are comparable.
- However, with React, the state is updated exclusively through setState() and is stored in the component's state property.
- As a result, a JavaScript function manages the elements' submissions and prevents them from immediately updating their state.
- The information that a user enters into a form is fully accessible to this function.
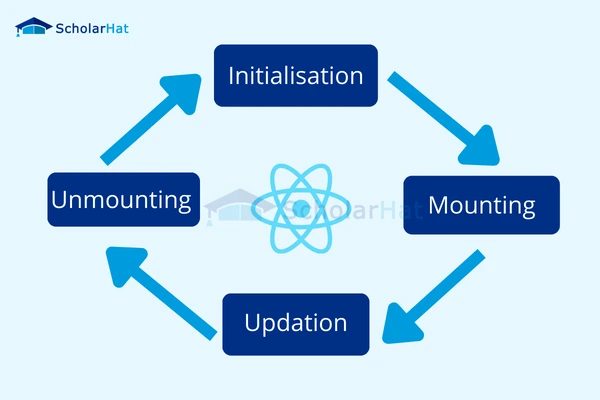
31. What stages does the lifecycle of a React component go through?
The life cycle of a React component has the following phases:
- Initial Phase
- Mounting Phase
- Updating Phase
- Unmounting Phase
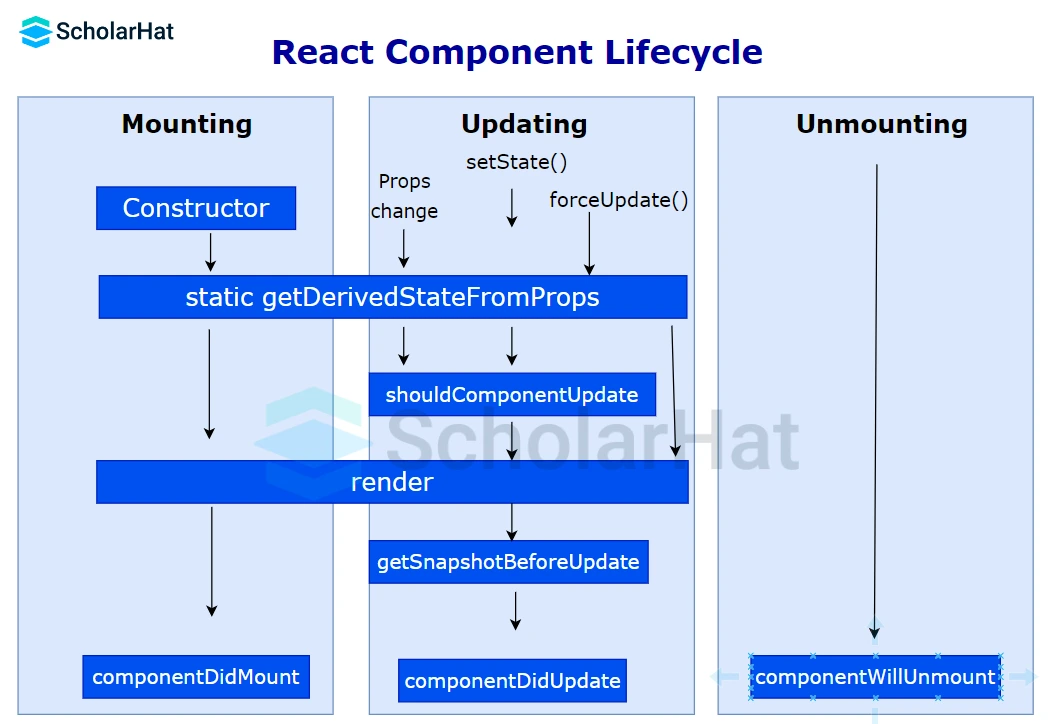
32. Define the lifecycle methods of React components.
The important React lifecycle methods are:
- getInitialState()
- componentWillMount()
- componentDidMount()
- componentWillReceiveProps()
- shouldComponentUpdate()
- componentWillUpdate()
- componentDidUpdate()
- componentWillUnmount()
33. What do React's Pure Components mean?
The simplest and fastest components that can be written are called pure components. Any component with merely a render() can be swapped out. These elements improve the application's functionality and code simplicity.
34. What are React's Higher Order Components (HOC)?
- React's higher-order components are a sophisticated React method for reusing component logic.
- This function accepts a component as input and outputs a new one. Stated otherwise, this function takes another function as an input.
- The official website states that it is a pattern that results from React's compositional structure rather than a feature or part of the React API.
35. How does React's HOC work?
HOC can be used for a wide range of tasks, some of which are listed below:
- Code Reusability
- Props manipulation
- State manipulation
- Render hijacking
36. What distinguishes a React component from an element?
Elements and components in React differ mostly in the following ways:
| SN | Element | Component |
| 1. | An element is a simple JavaScript object that specifies the desired characteristics of the DOM node and component state. | The fundamental building block of a React application is a component. This class or function takes an input and outputs a React element in return. |
| 2. | It simply contains data about the kind of component, its attributes, and any child components that are contained within. | It has access to the React lifecycle functions and is capable of holding states and props. |
| 3. | It is unchangeable. | It is changeable. |
| 4. | On elements, we are unable to use any methods. | We are able to use techniques on parts. |
React Interview Questions for Experienced Developers
37. What is the React commenting process?
We can write comments in React just like we would in JavaScript. Two possible methods are:
- Comments in a single line
- Multiple-line comments
38. Why does React need component names to begin with a capital letter?
The component names in React must begin with a capital letter. The component name will throw an error as an unrecognized tag if we start it in lowercase. The reason behind this is that JSX treats tag names in lowercase HTML tags.
39. In React, what are fragments?
React components that return multiple elements employ fragments. It lets you group a list of several offspring without expanding the DOM with another node.
40. Why do fragments work better in React than container divs?
- Because fragments do not generate additional DOM nodes, they operate more quickly and use less memory.
- Maintaining the intended layout might be challenging with certain CSS styling, such as CSS Grid and Flexbox, which introduce <div> tags in the middle and have unique parent- child relationships.
- There is less clutter in the DOM Inspector.
42. How can I use React validation on props?
- props validation is a tool that aids developers in preventing faults and issues in the future.
- It improves the readability of your code.
- PropTypes is a unique property used by React components that helps you find errors by verifying the data types of values supplied through props.
- You do not have to define components with propTypes in order to use them.
- We may use App.propTypes in the React component to apply validation on props.
- The JavaScript console will display warnings if any properties are supplied with an invalid type.
- You must set the App.defaultProps after defining the validation rules.
43. Describe create-react-app.
Facebook announced the Create React App tool to help developers create React applications. You can use it to construct React apps that are one page in length. You can avoid time-consuming setup and configuration tasks like Webpack or Babel by using the preset create-react app.
44. In React, how do you make a component?
In React, there are two ways to construct a component:
- Function Components: The easiest method for creating a component in React is this one. These are the only JavaScript functions that return React elements and take an object called props as their first parameter.
- Class Components: You can define a component using the ES6 class, and the class components function makes it easier.
45. What are theReact hooks?
React state and lifecycle aspects can be "hooked into" from a functional component using hooks, which are functions. Class components are not compatible with React Hooks. They permitted us to compose parts without a class. Common hooks include useState, useEffect, and useContext.
46. Why do we need to use React Hooks?
React Hooks make it easy to manage state and side effects in functional components. They help write cleaner and simpler code without using class components.
- Simplifies Code – Hooks remove the need for complex class components.
- Manages State Easily – useState helps handle data inside functional components.
- Handles Side Effects – useEffect manages tasks like fetching data and updating the DOM.
Read More: Most Asked React Hooks Interview Questions in 2025
47. What are the three important rules for React Hooks?
React Hooks have strict rules to ensure they work correctly inside functional components. Following these rules is important for writing clean and error-free code.
- Only Call Hooks at the Top Level – Hooks should not be inside loops, conditions, or nested functions.
- Only Use Hooks Inside React Components – Hooks must be used inside functional components or custom hooks, not in regular JavaScript functions.
- Follow the Rules of Hooks – Use the React Hooks ESLint plugin to check for mistakes and ensure correct usage.
48. Which guidelines should you adhere to when using React's hooks?
When using Hooks in your code, you have to abide by two rules:
- React Hooks can only be invoked at the highest level. Calling them from within loops, conditions, or nested functions is prohibited.
- Calling Hooks is only permitted from React Function Components.
49. How do forms work in React?
- Forms are used by React to facilitate user interaction with web applications.
- Users can interact with the program and enter the necessary data whenever needed by using forms.
- Certain elements are present in forms, including radio buttons, checkboxes, buttons, and text fields.
- Numerous functions, including user identification, searching, filtering, indexing, and more, are accomplished by using forms.
50. How do you interpret the term "props" in React?
Props are inputs to components in React. They have naming conventions similar to HTML tag attributes and can be single values or objects holding a set of values supplied to components upon creation. They are information that a parent component transmits to a child component. The following component functionality is the primary function of props in React:
- Give your component access to custom data.
- The status of the trigger changes.
- Use via this.props.reactProp within component's render() method.
51. How do refs work in React?
- The abbreviation for References in React is Refs.
- This attribute serves to keep a reference to a specific React element or component that the render configuration function of the component will return.
- It is employed to provide pointers to specific elements or components that render() has returned.
- They are useful when we need to add methods to the components or when we need to measure the DOM.
52. What are React's Forward Refs, and when are they used?
- One feature that is utilized to send a reference from one component to one of its child components is called ref forwarding.
- The React.forwardRef() function can be used to carry it out.
- It works very well with higher-order components and is utilized specifically in libraries of reusable components.
53. In React, which is the better choice—callback references or findDOMNode()?
- Callback references are a better solution than the findDOMNode() API.
- Because findDOMNode() precludes some future enhancements in React, and callback refs provide better control when the refs are set and unset.
54. What is React Router and how does React require it?
- Developed on top of React, React Router is a robust routing library that facilitates the addition of new screens and processes to the application.
- By doing this, the URL and the data that is shown on the webpage are kept up to date.
- It is used to create single-page web apps and has a consistent structure and behavior.
- It's easy to use React Router's API.
55. Describe React Router's benefits.
The following list includes React Router's key benefits:
- It is not required to manually set the browser history in this case.
- Link is used to navigate the application's internal links. It is comparable to the anchor element.
- For rendering, the Switch function is used.
- There is only one Child element required by the router.
- All of the components are listed in <Route> in this.
- The three packages that make up the packages are Web, Native, and Core. It supports the React application's small size.
56. What distinguishes Conventional Routing from React Routing?
React routing and conventional routing differ in the following ways:
| SN | Conventional Routing | React Routing |
| 1. | Every view in conventional routing has a new file in it. | There is just one HTML page involved in React Routing. |
| 2. | A server receives the HTTP request in order to deliver the associated HTML page. | The only altered attribute is <BrowserRouter> in the History. |
| 3. | In this, the user switches between various pages according to each view. | The user perceives this as surfing between pages, but it's merely an illusion. |
57. Describe the concept of flux.
The unidirectional data flow is enforced by the architectural pattern known as flux. Utilizing a central store with authority over all data, it facilitates communication between various components and manages generated data. Any updates to the data across the application must happen exclusively here. Flux lowers run-time errors and gives the program stability.
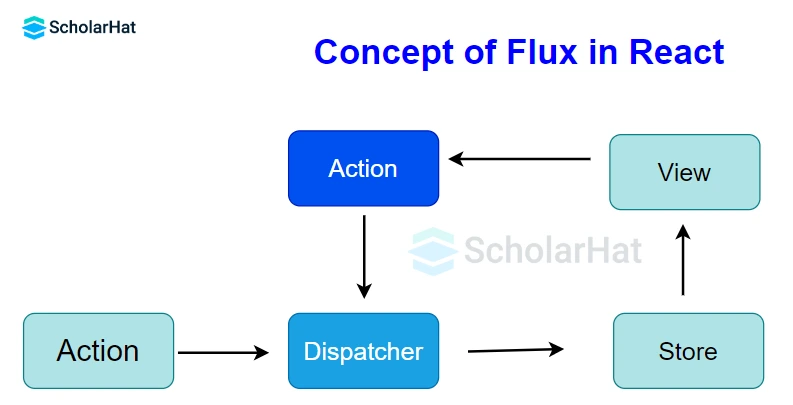
58. Explain Redux.
One of the most popular front-end development libraries available today is Redux. It is utilized for the overall state management of JavaScript applications and provides a predictable state container. Redux-developed applications are simple to test and exhibit consistent behavior across many settings.
Read Here: Most Asked Redux Related Interview Question and Answer
59. What three key principles does Redux adhere to?
- One and only source of truth: An object/state tree inside a single store contains the state of the entire application. It is simpler to debug or inspect the program and to keep track of changes over time using a single state tree.
- Read-only status: An action must be triggered in order to alter the state. A simple JS object that describes the change is called an action. The action is the minimal representation of a change to the data, the same as the state is the minimal representation of data.
- Modifications are made using pure functions: Pure functions are required to define the actions' transformation of the state tree. Functions classified as pure have a return value that is exclusively determined by the values of their inputs.
60. What is the difference between useEffect and componentDidMount?
61. How can you optimize performance in a React application?
React application performance can be optimized by the following factors:
- Using React's PureComponent or React.memo to avoid unnecessary re-renders.
- Implementing lazy loading with React.lazy and Suspense for code splitting.
- Using the useCallback and useMemo hooks to memoize functions and values.
- Avoiding inline functions and objects as props.
- Minimizing the use of the global state and keeping components as stateless as possible.
62. Explain the Context API in React.
- It provides a way to share values between components without passing props manually at every level.
- It is used to manage the global state in a React application.
- The createContext function creates a context, and Provider and Consumer components are used to pass and consume the context value, respectively.
63. What is React Suspense?
- React Suspense is a feature that allows components to wait for something like data fetching before rendering.
- It provides a way to declare a loading state while the component waits for asynchronous operations to complete.
- It works well with React.lazy for lazy loading components.
64. How does the useReducer hook work?
- The useReducer hook is used for managing complex state logic in React.
- It accepts a reducer function and an initial state and returns the current state and a dispatch function.
- It is similar to Redux but is built into React.
- The reducer function specifies how the state should change in response to actions dispatched by the component.
65. How do you handle forms in React?
- Forms in React can be handled using controlled or uncontrolled components.
- In controlled components, form data is handled by the component's state, typically using the useState hook.
- In uncontrolled components, data is handled by the DOM itself, usually with refs to access form values.
66. What are React Portals and how do you use them?
- React Portals provide a way to render children into a DOM node that exists outside the hierarchy of the parent component.
- They are used for rendering elements like modals, tooltips, or dropdowns that need to visually break out of the parent container.
- You can create a portal using ReactDOM.createPortal(child, containerNode).
67. How do you handle errors in React components?
- Errors in React components can be handled using error boundaries.
- An error boundary is a component that catches JavaScript errors in its child component tree, logs those errors, and displays a fallback UI.
- It is created using a class component with the componentDidCatch lifecycle method and a getDerivedStateFromError static method.
68. What is React.memo and when would you use it?
- React.memo is a higher-order component that prevents a functional component from re-rendering if its props haven't changed.
- It is used for performance optimization by memoizing the component and is useful when you have a component that renders the same output given the same props.
69. Explain the difference between useRef and createRef.
- useRef is a hook that returns a mutable ref object whose .current property is initialized to the passed argument.
- It persists between renders and can be used to store a reference to a DOM element or any mutable value. createRef is a method used in class components to create a ref.
- It returns a new ref object that can be attached to a DOM element via the ref attribute.
- useRef is typically used in functional components, while createRef is used in class components.
70. What are the custom Hooks in React?
Custom Hooks in React are functions that let you reuse logic across multiple components. They help make the code cleaner and avoid repeating the same logic in different parts of an application. Understanding custom hooks is important for React interview questions and writing efficient React apps.
71. What are the types of hooks in React?
React provides different types of hooks to manage state and side effects in functional components. These hooks are commonly asked in React interview questions and help developers write clean and efficient code.
Types of React Hooks:
- State Hook (useState) – Manages state inside functional components.
- Effect Hook (useEffect) – Handles side effects like API calls and DOM updates.
- Context Hook (useContext) – Accesses the global state without prop drilling.
- Reducer Hook (useReducer) – Manages complex state logic, often asked in ReactJS interview questions for experienced developers.
- Ref Hook (useRef) – Stores references to DOM elements or values that don’t trigger re-renders.
- Memoization Hooks (useMemo, useCallback) –These optimize performance by preventing unnecessary calculations or re-renders.
- Custom Hooks – User-defined hooks that reuse logic across multiple components, a key topic in React coding interview questions.
Learning these hooks will help you confidently answer React interview questions and answers in job interviews.
72. What is Strict Mode in React?
Strict Mode in React is a tool that helps developers find potential problems in their code. It does not change how the app works but gives warnings about issues like unsafe lifecycle methods or side effects.
It is commonly asked in React interview questions because it helps improve code quality. In ReactJS interview questions for experienced developers, you might be asked how to enable Strict Mode using <React.StrictMode> in the app’s root file.
Summary
In conclusion, preparing for a React interview requires a strong understanding of React interview questions and hands-on practice. By focusing on ReactJS interview questions, React coding interview questions, and advanced React interview questions, you can build confidence and improve your skills. Practicing React interview questions and answers will help you tackle real-world problems and perform well in interviews. With the right preparation, you can clear your ReactJS interview and secure a great job as a React developer.
Looking to dive deeper? Check out our ReactJS Certification Training to enhance your skills and boost your career. Plus, if you're just starting out, you can access our free ReactJS course or explore our free Angular course. It’s the perfect way to learn at your own pace!
| Download this PDF Now - React Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat |
Test your skills by following MCQs
Dear learners, attempt these mcq questions and know your abilities in tech
Q 1: What is React primarily used for?
FAQs
- Understand Fundamentals: Have a strong grasp of JavaScript, ES6+ features, and React basics like components, JSX, props, state, and lifecycle methods.
- Advanced Topics: Learn about hooks (useState, useEffect, useContext, etc.), context API, higher-order components, and performance optimization techniques like React.memo and useCallback.
- Practical Experience: Build and deploy several React projects to gain hands-on experience. This helps in understanding real-world scenarios and problem-solving.
- Read Documentation: Regularly read the official React documentation and stay updated with new features and best practices.
- Study Common Patterns: Familiarize yourself with common design patterns in React, such as Redux for state management, React Router for navigation, and React Context for passing data deeply.
- Practice Coding Problems: Solve coding problems on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank to sharpen your algorithmic thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Review Common Questions: Go through lists of common React interview questions and answers to understand what to expect and how to articulate your responses.
- Mock Interviews: Practice with mock interviews to get comfortable with the interview format and receive feedback on your performance.
- Official React Documentation: The official React docs are comprehensive and regularly updated. React Documentation
- Online Courses: Websites like Scholarhat, Udemy, Coursera, and Pluralsight offer in-depth React courses.
- YouTube Channels: Channels like Traversy Media, Academind, and The Net Ninja have excellent React tutorials.
- Blogs and Articles: Platforms like Medium, Dev.to, and freeCodeCamp regularly publish articles on React topics.
- Books: "The Road to React" by Robin Wieruch and "Learning React" by Alex Banks and Eve Porcello are highly recommended
- React Hooks: Deep dive into custom hooks, useReducer, useContext, and optimizing with useMemo and useCallback.
- Context API: Learn how to use Context for state management and to avoid prop drilling.
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Understand how to implement SSR with frameworks like Next.js for improved performance and SEO.
- State Management: Explore advanced state management solutions like Redux, MobX, and Zustand.
- Performance Optimization: Techniques such as code splitting, lazy loading, memoization, and avoiding unnecessary re-renders.
- TypeScript: Learn how to integrate TypeScript with React for better type safety and developer experience.
- Testing: Master testing React components using tools like Jest, Enzyme, and React Testing Library.
- React Suspense and Concurrent Mode: Explore how to handle asynchronous operations and improve app responsiveness.
- GraphQL: Understand how to fetch data with GraphQL and libraries like Apollo Client.
- Advanced Component Patterns: Higher-order components (HOCs), render props, and compound components for creating reusable, flexible components.
Take our React skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.








