21
DecWhat are the 5 Basic SQL Commands? (DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, DQL)
SQL Commands are the building blocks (meaning basic and essential parts that form the foundation of something) of every database operation, from creating tables to fetching and securing data. Without them, managing data in any application would be impossible.
SQL Commands are grouped into five main types that are DDL (structure), DML (data changes), DQL (data fetching), DCL (user control), and TCL (transaction safety). Each command plays a key role in making databases powerful and easy to manage.
So in this SQL Server Tutorial, We gonna explore basic SQL Commands, including what the 5 basic SQL commands are, their syntaxes, and examples too. By 2027, 75% of tech recruiters will prioritize SQL Server expertise. Enroll in our SQL free Certification Course today!
| SQL Commands Types | Purpose | Commands |
| DDL (Data Definition Language) | Defines the structure of the database |
|
| DML (Data Manipulation Language) | Works with the data inside the tables |
|
| DQL (Data Query Language) | Used to fetch/read data |
|
| DCL (Data Control Language) | Controls user access to the database |
|
| TCL (Transaction Control Language) | Manages changes in transactions |
|
Types of SQL Commands
We have different SQL commands for different purposes. We can group SQL commands into five major categories depending on their functionality. Types of SQL Commands are as follows:
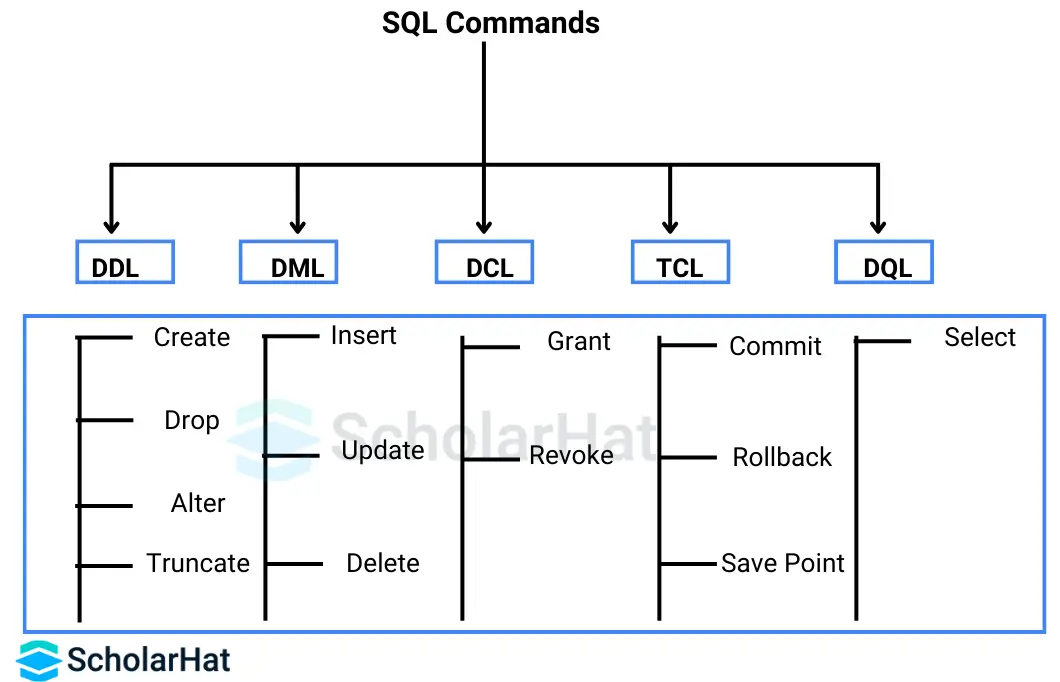
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
Data Definition Language (DDL) commands are used for creating a table, deleting a table, altering a table, and truncating the table. All the commands of DDL are auto-committed i.e. it permanently save all the changes in the database.
In this category, we have six commands:
| Command | Description | Example |
| CREATE | Used to create new database objects such as tables, databases, or indexes. | CREATE TABLE Students ( ID INT, Name VARCHAR(50), Age INT ); |
| ALTER | Modifies the structure of an existing table, such as adding, deleting, or modifying columns. | ALTER TABLE Students ADD Email VARCHAR(100); |
| DROP | Deletes an existing database object, such as a table or database. | DROP TABLE Students; |
| TRUNCATE | Removes all records from a table without logging individual row deletions, but keeps the table structure. | TRUNCATE TABLE Students; |
| RENAME | Renames a database object, such as a table or column. | RENAME TABLE Students TO Learners; |
| COMMENT | Adds comments or annotations to the database objects. | COMMENT ON TABLE Students IS 'Table for storing student information'; |
1. CREATE Commands
It is used to create a new table in the database. Here, you need to specify the name of the table and the name of each column in the table.
Syntax
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_1 datatype,
column_2 datatype,
column_3 datatype
); Example
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
EmployeeID int,
EmployeeName varchar(200),
PhoneNumber int,
Email varchar(255),
City varchar(255),
Country varchar(255)
);2. ALTER Commands
It changes the structure of a table by adding, deleting, or modifying columns in an existing table.
- To add a column in a database
ALTER TABLE TableName
ADD ColumnName Datatype;
- To delete a column in a database
ALTER TABLE TableName
DROP COLUMN ColumnName;
- To modify a column in a database
ALTER TABLE TableName
ALTER COLUMN ColumnName Datatype;
Example
--ADD Column DOB:
ALTER TABLE Employee
ADD DOB varchar(10);
--DROP Column DOB:
ALTER TABLE Employee
DROP COLUMN DOB;
--Add a column DOB and change the data type to Date.
ALTER TABLE Employee
ADD DOB year;
ALTER TABLE Employee
ALTER DOB date;
3. DROP
The DROP command is used to permanently delete a database object like a table, database, view, or index. Once dropped, all data and structure are removed, and cannot be recovered unless you have a backup.
Syntax
DROP TABLE TableName;
Example
DROP Table Employee;| Read More: Drop all tables, stored procedures, views, and triggers |
4. TRUNCATE Commands
This command deletes the information present in the table or all the rows from the table, but does not delete the table.
Syntax
TRUNCATE TABLE TableName;
Example
TRUNCATE Table Employee;Read More - Top DBMS Interview Questions and Answers
- Only with DDL commands do we need to write keywords (like table, procedure, view, index, function) with the syntax of the command.
- These commands are used to create/modify the structure of the database object.
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
These SQL commands modify the database. The commands of DML are not auto-committed i.e. it can't permanently save all the changes in the database. They can be rolled back. In this category, we have the following commands.
| Command | Description | Syntax Example |
| INSERT | Adds new rows of data into a table. | INSERT INTO table_name (column1,column2) VALUES (value1, value2); |
| UPDATE | Modifies existing data in a table. | UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1 WHERE condition; |
| DELETE | Removes existing data from a table based on a condition. | DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition; |
| SELECT | Retrieves data from one or more tables. | SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition; |
| MERGE | Combines INSERT and UPDATE operations based on a condition (supported in some SQL implementations). | MERGE INTO table_name USING source_table ON condition WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT; |
1. INSERT Commands
The INSERT command in SQL is used to add new rows of data into a table. It helps you store user input, records, or any new information in the database.
Syntax
INSERT INTO TableName (Column1, Column2, Column3, ...,ColumnN)
VALUES (value1, value2, value, ...);
or
INSERT INTO TableName
VALUES (Value1, Value2, Value3, ...);
Example
INSERT INTO Employee(EmployeeID, EmployeeName, PhoneNumber, Email, City, Country)
VALUES ('01', 'Sourav', '9921321789', 'House No 12', 'Jharkhand', 'India');
INSERT INTO Employee
VALUES ('01', 'Sourav', '9921321789', 'House No 12', 'Jharkhand', 'India');| Read More: How to insert values into the identity column in SQL Server |
2. UPDATE Command
The UPDATE command in SQL is used to change or modify existing data in a table. You can update one or more columns based on a specific condition.
Syntax
UPDATE TableName
SET Column1 = Value1, Column2 = Value2, ...
WHERE Condition;
Example
UPDATE Employee
SET EmployeeNamw = 'Surabhi', City= 'Mumbai'
WHERE EmployeeID = 7;3. DELETE Command
The DELETE command in SQL is used to remove specific rows from a table based on a condition. It deletes data but keeps the table structure unchanged.
Syntax
DELETE FROM TableName WHERE Condition;
Example
DELETE FROM Employee
WHERE EmployeeName='Devanshi';3. Data Query Language (DQL)
This SQL command is used to fetch/retrieve data from database tables.
| Command | Description | Example |
| SELECT | Used to query and retrieve data from one or more tables. | SELECT * FROM Students; |
| SELECT DISTINCT | Retrieves unique values from a column, avoiding duplicates. | SELECT DISTINCT Department FROM Employees; |
| WHERE | Filters rows based on specified conditions. | SELECT * FROM Students WHERE Age > 18; |
| ORDER BY | Sorts the result set based on one or more columns in ascending or descending order. | SELECT * FROM Employees ORDER BY Salary DESC |
| GROUP BY | Group rows share a property and perform aggregate functions on each group. | SELECT Department, COUNT(*) FROM Employees GROUP BY Department; |
| HAVING | Filters grouped data based on conditions, used with GROUP BY. | SELECT Department, AVG(Salary) FROM Employees GROUP BY Department HAVING AVG(Salary) > 50000; |
| LIMIT | Restricts the number of rows returned in the result. | SELECT * FROM Products LIMIT 10; |
| JOIN | Combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column. | SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.Name FROM Orders JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.ID |
1. SELECT
The SELECT command is used to retrieve data from a database. You can fetch all columns or specific columns from one or more tables.
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name;2. SELECT DISTINCT
Retrieves unique values from a column or a combination of columns, eliminating duplicate entries.
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name;3. WHERE
Used to filter rows based on specified conditions. Only rows that satisfy the condition(s) are included in the result.
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition;4. ORDER BY
Sorts the result set based on one or more columns in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order.
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name ORDER BY column1 [ASC|DESC];5. GROUP BY
Groups rows sharing the same values in specified columns and allows aggregate functions (e.g., SUM, AVG, COUNT) to be applied to each group.
SELECT column1, aggregate_function(column2) FROM table_name GROUP BY column1;6. HAVING
Filters grouped data based on specified conditions, often used with GROUP BY.
SELECT column1, aggregate_function(column2) FROM table_name GROUP BY column1 HAVING condition;7. LIMIT
Restricts the number of rows returned by a query.
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name LIMIT number_of_rows;8. JOIN
Combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column, enabling the retrieval of data across multiple tables.
SELECT table1.column1, table2.column2, ... FROM table1 JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;4. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
These SQL commands are used to handle changes affecting the data in the database. We use these commands within the transaction or to make a stable point during changes in the database, at which we can roll back the database state if required.
| Command | Description | Example |
| COMMIT | Saves all the transactions permanently to the database. | COMMIT; |
| ROLLBACK | Undoes transactions that are not yet saved to the database. | ROLLBACK; |
| SAVEPOINT | Sets a point within a transaction to which you can later roll back. | SAVEPOINT savepoint_name; |
| RELEASE SAVEPOINT | Deletes a savepoint, making it unavailable for future rollbacks. | RELEASE SAVEPOINT savepoint_name; |
| SET TRANSACTION | Defines a transaction's characteristics, such as isolation level or read/write. | SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL SERIALIZABLE; |
In this category, we have three main commands:
1. SAVEPOINT
This command is used to save a transaction temporarily. You can roll the transaction back to a certain point without rolling back the entire transaction.
Syntax
SAVEPOINT SAVEPOINTNAME;
Example
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(06, 'Pradnya');
SAVEPOINT S2;2. ROLLBACK
The ROLLBACK command in SQL is used to undo changes made during a transaction before they are saved. It helps you go back to the previous safe state if something goes wrong.
Syntax
ROLLBACK;
Example
ROLLBACK TO S2;
SELECT * FROM Employee;3. COMMIT
The COMMIT command in SQL is used to save all changes made during the current transaction permanently in the database. Once committed, the changes cannot be undone.
Syntax
COMMIT;
Example
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(05, 'Sakshi');
COMMIT;5. Data Control Language (DCL)
Data Control Language (DCL) commands are used to implement security on database objects like tables, views, stored procedures, etc. It consists of commands that deal with the user permissions and controls of the database system. In this category, we have two main commands:
1. GRANT
The GRANT command in SQL is used to give specific permissions to users, such as access to read, insert, or update data in a table. It helps manage and control who can do what in the database.
Syntax
GRANT PrivilegeName
ON ObjectName
TO {UserName |PUBLIC |RoleName}
[WITH GRANT OPTION];Example
GRANT SELECT ON Employee TO user1;
In the above syntax,
- PrivilegeName: It is the privilege/right/access granted to the user.
- ObjectName: Name of a database object like TABLE/VIEW/STORED PROC.
- Username: Name of the user who is given access/rights/privileges.
- PUBLIC: To grant access rights to all users.
- RoleName: The name of a set of privileges grouped.
- WITH GRANT OPTION: To give the user access to grant other users with rights.
2. REVOKE
The REVOKE command in SQL is used to take back permissions that were previously given to a user using the GRANT command. It helps in restricting access to secure the database.
Syntax
REVOKE PrivilegeName
ON ObjectName
FROM {UserName |PUBLIC |RoleName}
Example
REVOKE SELECT ON Employee_Info TO user1; Conclusion
In conclusion, SQL Commands are the basic tools we use to work with databases. They help us easily create tables, add data, update records, fetch information, and control user access. Learning these commands is very important if you want to manage or work with any kind of data.
80% of full-stack roles now require .NET expertise. Don’t miss out—join our full stack .NET developer course and future-proof your career!
FAQs
Take our Sqlserver skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











