26
DecSQL Server Exceptions Working
SQL Server Exceptions Working: An Overview
SQL Server uses an exception model to manage exceptions and errors in T-SQL statements, similar to how exceptions are handled in other programming languages. To understand exception handling, you must first understand the various sorts of exceptions that SQL Server provides.
Entry-level data professionals with SQL Server skills earn up to $10,000 more annually. Kickstart your career with our Free SQL Server Courses Online now!
Read More - Top 50 SQL Interview Questions And Answers
Types of Exceptions
1. Statement-Level Exception
This type of exception aborts only the currently running statement within a batch of T-SQL statements. The rest of the T-SQL statements will execute successfully if they have no exceptions. Let us see the below example.
--Batch
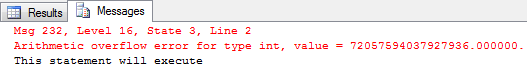
SELECT POWER(4, 28)
PRINT 'This statement will execute'
GO Using the POWER function, this SQL batch calculates 4 raised to the power of 28, and then prints the message 'This statement will execute'.
2. Batch-Level Exception
This type of exception aborts only the batch in which the exception occurs. The rest of the batches will execute successfully if they have no exceptions. The statement in which the exception occurs will be aborted and the remaining T-SQL statements within the batch will also stopped.
--First Batch
DECLARE @var DECIMAL;
set @var= CONVERT(DECIMAL, 'xyz')
PRINT @var
PRINT 'This statement will not execute'
GO
--Second Batch
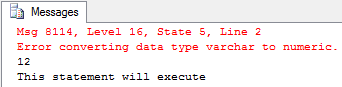
DECLARE @var DECIMAL;
set @var= CONVERT(DECIMAL, '12.35')
PRINT @var
PRINT 'This statement will execute'
GO The first batch attempts to convert the string 'xyz' to a decimal value, which results in an error and prevents the following print statements from being executed. The second batch correctly converts the string '12.35' to a decimal value, allowing both print instructions to be executed.
3. Parsing and Scope-Resolution Exception
This type of exception occurs during the parsing and the scope-resolution phase of compilation. This exception appears to behave just like batch-level exceptions. However, this has a little different behavior.
If the exception occurs in the same scope of the batch, it behaves just like a batch-level exception. If the exception occurs in a lower level of scope of the batch, it behaves just like a statement-level exception.
Parsing Exception
--Parsing Error
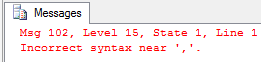
SELECTEmpID,Name FROM Employee
PRINT 'This statement will execute'
GO This SQL script contains a syntax issue owing to a missing space between "SELECT" and "EmpID", resulting in a parsing error that prevents the SELECT statement from executing, although the subsequent PRINT statement does.
--For Successfully execution we need to executed select statement as dynamic SQL using the EXEC function
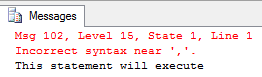
EXEC('SELECTEmpID,Name FROM Employee')
PRINT 'This statement will execute'
GO To run the SELECT statement successfully, it must be executed as dynamic SQL using the EXEC function. The following PRINT command will be executed regardless of the dynamic SQL execution result.
Scope Resolution Exception
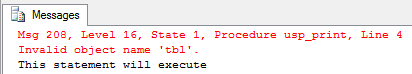
--First Create a procedure
CREATE PROCEDURE usp_print
AS
BEGIN
Select * from tbl
END
GO When this SQL script is executed, it generates a stored procedure named usp_print that selects all columns from the table tbl.
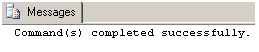
--Now execute above created procedure in batch
EXEC usp_print
PRINT 'This statement will execute'
GO
--Since the stored procedure creates a new scope. Hence rest statement will be executed This batch runs the stored method usp_print, which retrieves information from a table. The succeeding PRINT statement will run outside the scope of the stored procedure.
Read More
Summary
In this article, I try to explain how types of Exception in SQL Server with examples. I hope after reading this article you will be aware of exceptions in Sql Server.
By 2026, 70% of developer jobs will demand full-stack .NET skills. Stay ahead—enroll in our .NET full stack developer course and dominate the tech market!
FAQs
Take our Sqlserver skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











