18
AprUnderstanding Internet Information Service
IIS stands for Internet Information Service. IIS is a web server developed by Microsoft and used to host the Web application. It has its own ASP.NET Process Engine to handle the request. So, when a request comes from client to server, IIS takes that request and process it and send the response back to clients.
Web Server
Web Server is used for hosting the web application on a centralized location and can be accessed from many locations. It is responsible for handling all the requests that are coming from clients, it processes them and provides the responses.
IIS supports many system services that use the most common Internet protocols including HTTP, FTP, NTTP and SMTP.
Check IIS Installation
There are following two ways for finding IIS on your machine.
First Way to open IIS:
Go to run and type inetmgr command and press enter, it opens IIS configuration manager if it is installed to your machine.
Second way to open IIS:
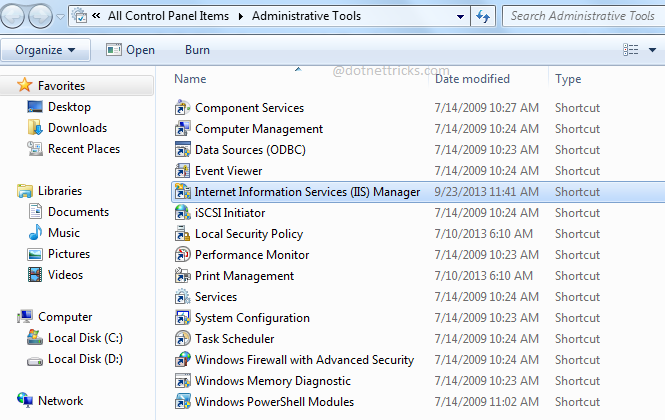
Go to control panel and then Administrative Tools; where you will find the shortcut for IIS as shown in below fig.
Brief History of IIS
Almost every version of IIS was released either alongside or with a version of Microsoft Windows:
IIS 1.0
IIS 1.0 was initially released as a free add-on for Windows NT 3.51.
IIS 2.0
IIS 2.0 was included with Windows NT 4.0.
IIS 3.0
IIS 3.0 was included with Service Pack 2 of Windows NT 4.0, introduced the Active Server Pages dynamic scripting environment.
IIS 4.0
IIS 4.0 was released as part of an "Option Pack" for Windows NT 4.0.
IIS 5.0
IIS 5.0 shipped with Windows 2000 and introduced additional authentication methods, management enhancements including a new MMC-based administration application, support for the WebDAV protocol, and enhancements to ASP. IIS 5.0 also dropped support for the Gopher protocol.
IIS 5.1
IIS 5.1 was shipped with Windows XP Professional, and was nearly identical to IIS 5.0 on Windows 2000.
IIS 6.0
IIS 6.0 was included with Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, added support for IPv6 and included a new worker process model that increased security as well as reliability.
IIS 7.0
IIS 7.0 was a complete redesign and rewrite of IIS, and was shipped with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. IIS 7.0 included a new modular design that allowed for a reduced attack surface and increased performance. It also introduced a hierarchical configuration system allowing for simpler site deploys, a new Windows Forms-based management application, new command-line management options and increased support for the .NET Framework. IIS 7.0 on Vista does not limit the number of allowed connections as IIS on XP did, but limits concurrent requests to 10 (Windows Vista Ultimate, Business, and Enterprise Editions) or 3 (Vista Home Premium). Additional requests are queued, which hampers performance, but they are not rejected as with XP.
IIS 7.5
IIS 7.5 was included in Windows 7 (but it must be turned on in the side panel of Programs and Features) and Windows Server 2008 R2. IIS 7.5 improved WebDAV and FTP modules as well as command-line administration in PowerShell. It also introduced the best practices analyzer tool and process isolation for application pools.
IIS 8.0
IIS 8.0 is only available in Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8. IIS 8.0 includes Application Initialization, centralized SSL certificate support, and multicore scaling on NUMA hardware, among other new features.
IIS 8.5
IIS 8.5 is included in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1. This version includes Idle worker-Process page-out, Dynamic Site Activation, Enhanced Logging, ETW logging, and Automatic Certificate Rebind.
IIS 10.0
IIS 10 is included in Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10. This version includes support for HTTP 2
Role of IIS:
IIS committed to all features as a Web Server. If you are a Microsoft web developer, then you know that Microsoft Visual Studio has inbuilt ASP.NET engine which capable to run ASP.NET web application from just click on Run button of Visual Studio. This scenario is well situated for local environment but not outside means no other person can access your developed web application. In this situation, IIS works for you.
IIS provides a well designed and tested WWW architecture that can help you achieve better performance, reliability, scalability, and security for our web sites.
What do you think?
I hope now you have a better understanding about IIS. Your valuable feedback, question, or comments about this article are always welcome.







