06
FebInternet Information Service Architecture
IIS Architecture
IIS has two main layers - Kernel Mode and User Mode. The Kernel Mode contains the HTTP.SYS and User Mode contains WAS and W3 service. The subsection of both are shown in fig.
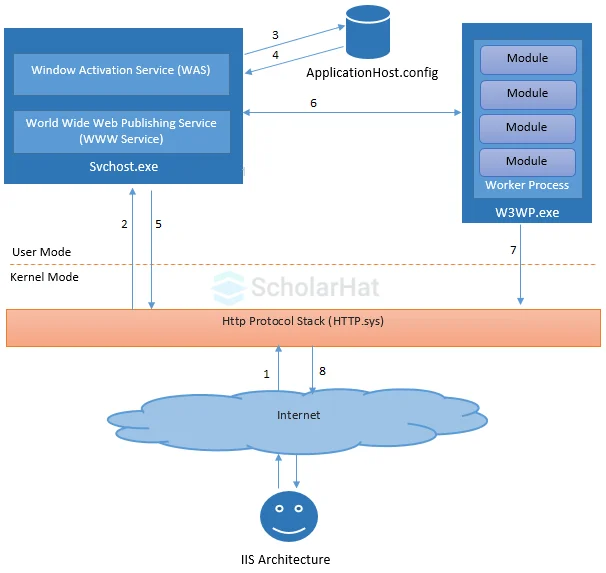
The above diagrams shows the flow of an HTTP request in process. The request-processing flow is described as:
An HTTP request first goes to HTTP.sys and now, HTTP.SYS is responsible for passing the request to a particular application pool.
HTTP.sys contacts to WAS and WAS requests configuration information from the xml file.
The configuration information is sent to WWW service receives.
The WWW service uses the configuration information to configure HTTP.sys.
Configured HTTP.sys contacts to WAS and now, WAS starts a worker process for the application pool to which the request was made.
The worker process processes the request and returns a response to HTTP.sys. The request is passed through an ordered series of module in the processing pipeline.
Role of HTTP.sys in IIS
HTTP.SYS is the part of kernel mode of IIS. Every client request is passes through the kernel mode, Http.sys then makes a queue for each and individual application pool based on the request. Whenever we create any application pool IIS automatically registers the pool with HTTP.sys to identify the particular during request processing. It provides the following services in IIS:
Routing HTTP requests to the correct request queue.
Caching of responses in kernel mode.
Performing all text-based logging for the WWW service.
Implementing quality of service functionality, which includes connection limits, connection timeouts, queue-length limits, and bandwidth throttling.
ISAPI Filter
ISAPI filters are DLL files that can be used to modify and enhance the functionality provided by IIS. ISAPI filters always run on an IIS server, filtering every request until they find one they need to process.
ISAPI filters can be registered with IIS to modify the behavior of a server. It can perform the following tasks:
Change request data (URLs or headers) sent by the client
Control which physical file gets mapped to the URL
Control the user name and password used with anonymous or basic authentication
Modify or analyze a request after authentication is complete
Modify a response going back to the client
Run processing when a request is complete
Run processing when a connection with the client is closed
Perform special logging or traffic analysis.
Handle encryption and compression.
Different Security Settings Available in IIS
IIS provides a variety of authentication schemes:
Anonymous (enabled by default)
Basic
Digest
Integrated Windows authentication (enabled by default)
Client Certificate Mapping
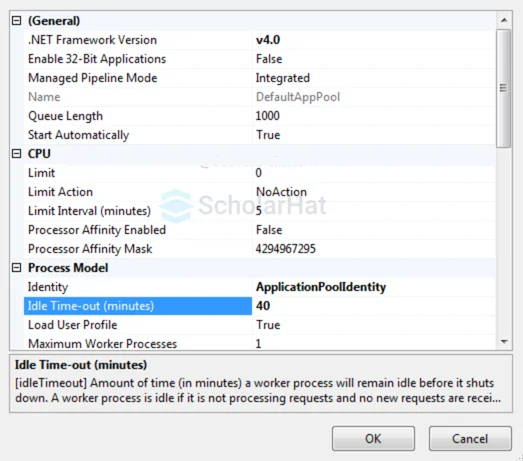
Set the Session Time Out in IIS
Follow the steps as shown in below diagram.
Step 1:

Step 2:
What do you think?
I hope now you have better understanding about IIS architecture. Your valuable feedback, question, or comments about this article are always welcome.