18
AprDifference between ASP.NET MVC and ASP.NET Web API
Difference between ASP.NET MVC and ASP.NET Web API: An Overview
While developing your web application using MVC, many developers get confused about when to use Web API, since the MVC framework can also return JSON data using JsonResult and handle simple AJAX requests. Understanding this distinction is essential, especially in ASP.NET Core training. In the previous article, I have explained the Difference between WCF and Web API and WCF REST and Web Service and when to use Web API over other services. In this Web API Tutorial, you will learn when to use Web API with MVC.
ASP.NET MVC
The Model View Controller (MVC) architecture separates an application into three parts: Model, View, and Controller. ASP.NET provides numerous choices for developing Web applications using ASP.NET Web forms. The MVC framework combines ASP.NET capabilities like master pages and membership-based authentication. MVC is included in the "System.Web.MVC" assembly.
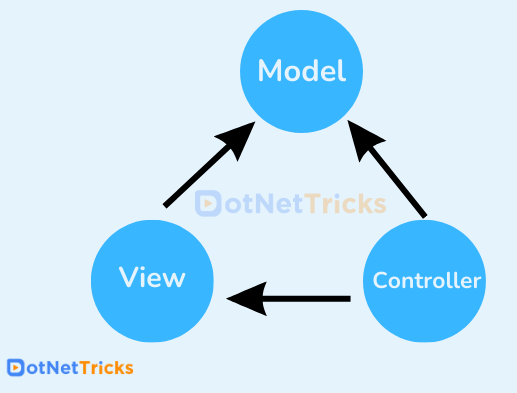
Components of MVC
The MVC includes the following components:
- Models: Models are the objects that are utilized to get and save model state in a database. Let's look at an example. An "item" object retrieves data from the database, conducts an operation, and then stores the changed data back in the database. If an application merely reads the dataset and sends it to the view, it lacks a corresponding class and physical layer model.
- View: View components display the User Interface (UI) of applications generated by the data model. For example, the Items table view displays a drop-down list and textboxes based on the current state of the "item" object.
- Controllers: Controllers are also known as components in MVC. These components handle user interaction and select a view to display the UI. The controller's primary function is to manage query string values and send them to the models.
| Read More: Rest API Interview Questions and Answers For Freshers |
ASP.NET Web API
The ASP.NET Web API supports displaying data in a variety of forms, including XML and JSON. It is a framework that makes it simple to respond to client requests by utilizing HTTP services. The response is determined by the client's requests. The web API creates HTTP services and manages requests via HTTP protocols. The Web API is open source and can be hosted within an application or on IIS. A GET, POST, DELETE, or PUT request can be made. We can define the Web API as:
- An HTTP service.
- Is intended to reach a wide spectrum of clients.
- The HTTP application is used.
Difference between MVC and Web API
There are numerous distinctions between MVC and Web API, including:
- We can use MVC to create a Web application that responds as both data and views, while the Web API is used to create HTTP services that only respond as data.
- The Web API request traces with the actions based on the HTTP services, but the MVC request traces with the action name.
- Based on the request's accepted header, the Web API returns data in various formats, such as JSON, XML, and others. However, the MVC uses JSONResult to return data in JSON format.
- The Web API allows for content negotiation and self-hosting. The MVC does not support any of these.
- The Web API supports MVC elements like as routing and model binding, although these are distinct and described in the "System.Web.Http" assembly. Furthermore, the MVC functionalities are defined in the "System.Web.Mvc" assembly.
- The Web API facilitates the development of RESTful services over the .Net Framework, which the MVC does not provide.
Combining MVC with Web API
- When we self-host an application, we integrate the MVC controller and the API into a single project. This facilitates the management of AJAX requests and allows for the return of responses in XML, JSON, and other formats.
- To enable application authorization, we integrated MVC and Web API. We create two filters in it: one for MVC and one for the Web API.
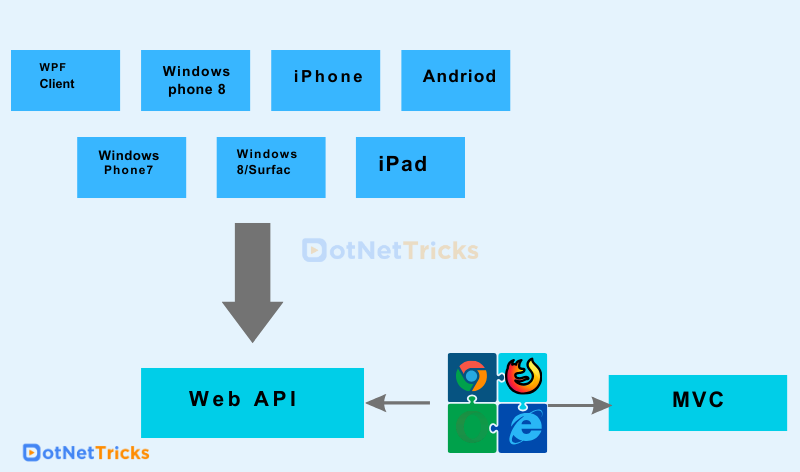
Summary
MVC and Web API, while similar, serve distinct functions. MVC creates online applications with data and views, whereas online API generates data-driven HTTP services. Key distinctions include data output (Web API is data-only), request tracing, format flexibility (Web API includes JSON, XML, and others), and features such as content negotiation and self-hosting (exclusive to Web API). They can be coupled to create self-hosted apps with AJAX and many data formats.