26
AprAgents in AI
Introduction to Agent in AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed several industries and improved our daily lives, making it one of the most revolutionary technologies of our time. The idea of an agent, which refers to human beings that can observe their surroundings, make decisions, and perform actions to accomplish certain goals, is at the core of artificial intelligence (AI). We will go into the idea of agents in AI and learn artificial intelligence in this article, looking at their relevance in the field as well as their definition, traits, types, and uses.
What is an Agent in AI?
A hardware or software entity that uses sensors to observe its surroundings analyses the data using internal knowledge and representation in AI, then acts based on its internal intelligence to accomplish particular goals is referred to as an agent in AI. An agent is a hypothetical autonomous being that interacts with its environment, gains knowledge from its encounters, and modifies its behavior as necessary.
Definition and Characteristics of an Agent
Definition: An agent is a unique entity that is autonomous, located in a context, and motivated by aims or purposes. It can behave independently and make decisions without constant outside direction. The environment offers the required inputs and outputs for task performance, ranging from real areas to virtual domains. The agent uses its intellect to decide which course of action will help it attain its objectives.
- Characteristics: An AI agent can be characterized by a wide variety of various traits. The following characteristics rank among the most significant ones:
- Autonomy: An AI agent can decide for itself and operate without constant outside direction.
- Situatedness: The agent interacts with inputs as well as outputs to carry out tasks while operating inside a context, which could be physical or virtual.
- Goal-oriented: The agent is motivated by specified goals or objectives, and it uses intelligence to decide the best way to get there.
- Adaptability: Flexibility in decision-making is made possible by AI agents' capacity to adjust and react to changing conditions.
- Efficiency: AI agents use their autonomy & intelligence to complete tasks efficiently and effectively while maximizing the use of resources and obtaining desired results.
AI agents examples
AI agents examples can emerge in a variety of contexts and applications across numerous industries. Here are some ai agents examples:
- Siri
- Alexa
- Google Assistant
- Cortana
- Autonomous robots
- Autonomous drones
- Intelligent virtual characters in video games
- Recommender systems
- Autonomous vehicles
- Fraud detection systems in financial institutions
Types of Agents in AI & their Functions
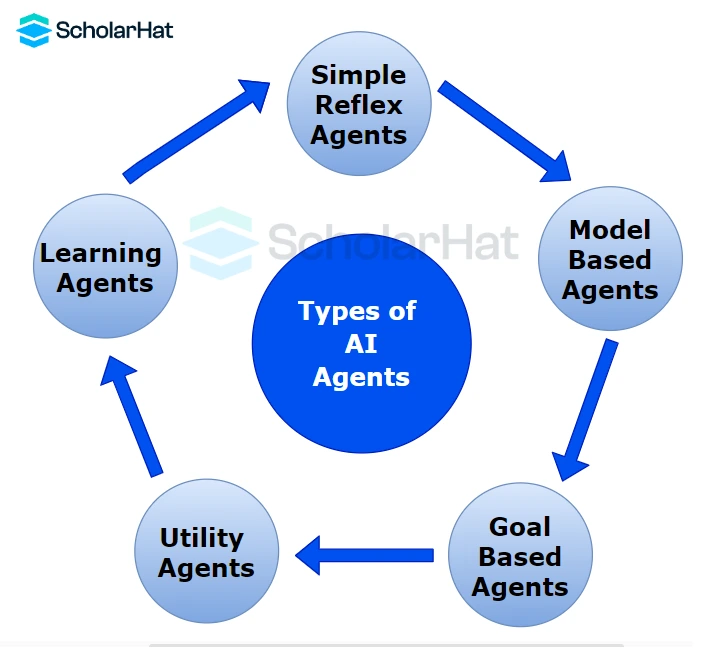
Following are a few types and their functions:
- Simple reflex agents: This is one of the most important types of agents in ai. These agents act purely in the present, without taking into account the past or the future. They work well in settings with quick and predictable results.
- Model-based reflex agents: Reflexive agents with a model-based internal state that is based on prior perceptions are those that make decisions under that internal state. They work better in dynamic circumstances with unpredictable results.
- Goal-Based Agents: Goal-based agents have a specific goal or objective they aim to achieve. They use their internal state and perceptions to create plans or strategies to reach their goals. These agents often employ search algorithms and heuristics to navigate through possible actions and outcomes.
- Utility-Based Agents: Utility-based agents make decisions by evaluating the desirability or utility of different outcomes. They consider the potential consequences of their actions and choose the one that maximizes their expected utility. These agents are often used in decision theory and economics.
- Learning Agents: Learning agents improve their performance over time by learning from their experiences. They adapt their behavior based on feedback and may adjust their strategies to achieve better results in the future. Reinforcement learning and supervised learning are common techniques used by learning agents.
Uses of Agents in AI
Here are some specific Uses:
- In a variety of sectors, including healthcare, banking, transportation, and entertainment, agents are now more common and useful than ever.
- Agents assist in illness diagnosis, track patients' conditions, and provide individualized therapy suggestions in the healthcare industry.
- Agents in finance are capable of analyzing enormous volumes of market data, forecasting trends, and even carrying out deals on their own.
- Agents are very useful in the transportation industry because they can regulate traffic flow, optimize routes, and enhance overall vehicle safety.
- Entertainment industry agents provide a variety of functions, such as imitating virtual characters, offering interactive experiences, and customizing content recommendations to user preferences.
- The adaptability of agents enables them to find uses outside of the disciplines indicated, emphasizing their potential influence across multiple sectors.
- The application of agents in these fields shows how artificial intelligence technology is continuing to transform numerous industries, enhancing productivity, accuracy, and user experiences.
Agent Architecture in AI
Agent architecture in ai refers to the structure and design of an intelligent agent, which is a software system or other entity that can perceive its surroundings, make decisions, and take actions to accomplish particular goals. The agent architecture in ai describes how it analyses data, engages with its surroundings, and completes tasks.
Key elements of agent architecture in ai include the following:
- Perception: Through sensors and input channels, agents gather data about their surroundings. These sensors may be cameras, microphones, or other data-gathering devices.
- Knowledge representation: Agents use a suitable format to store and organize their knowledge about the outside environment. Depending on the particular application and requirements, this may involve databases, rules, terminologies, or statistical models.
- Reasoning and decision-making: To process their knowledge and come to decisions, agents use a variety of algorithms and reasoning methods. These can include methods for analyzing and interpreting data using machine learning, logical reasoning, and probabilistic reasoning.
- Planning and goal-setting: Agents can design plans or a series of actions to accomplish particular objectives. To create the most effective or adaptive plans, they take into account the present situation, the resources at hand, and the desired results.
- Execution of actions: Agents act in their surroundings to affect them. Depending on the agent's capabilities and domain, these activities may be virtual (such as sending a message) or physical (such as moving a robot).
- Learning and adaptation: By drawing on their past experiences, agents can enhance their performance over time. Based on information from the environment, they can update their knowledge, improve their decision-making techniques, or modify how they act.
- Interaction and communication: Agents can speak and work together with other agents or human users. To accomplish common objectives, this may entail exchanging data, coordinating efforts, or engaging in negotiations.
- Monitoring and evaluation: To make sure that their actions lead to the desired results, agents might evaluate their performance and keep an eye on their surroundings. They may regularly assess the success of their choices and revise their tactics as necessary.
Best Practices for Developing Agents
Establish clear goals and objectives: The agent's decision-making process will be guided by its goals and objectives, which must be established clearly.
- Design adaptability: Using machine learning techniques and algorithms, agents should be created with the potential to learn from their experiences and change over time.
- Foster collaboration: Encourage teamwork by creating agents that can interact and work together with humans or other agents to improve their capabilities and expand their range of use.
- Utilise machine learning methods: Use machine learning methods and algorithms to enable learning from data and enhance performance in the agent's architecture.
- Guarantee scalability: Create scalable agents to handle difficult tasks or big volumes of data efficiently.
- Think about ethics and privacy: To ensure ethical and responsible behavior, incorporate privacy protections into the design of the agent.
- Validate performance: Regularly evaluate and validate the agent's performance using appropriate metrics and evaluation methods.
- Emphasize interpretability: Strive to make the agent's decision-making process transparent and interpretable to address biases and gain user trust.
- Test in real-world scenarios: Test the Artificial intelligence agent in realistic environments to ensure its effectiveness and robustness in real-world applications.
- Continuously improve: Incorporate feedback loops and iterative improvements to enhance the agent's performance and address evolving requirements.
- Validate performance: Utilise relevant metrics and evaluation techniques to regularly assess and validate the agent's performance.
- Focus on interpretability: To address biases and win user trust, work to make the agent's decision-making process transparent and understandable.
- Real-world scenarios: It should be tested to ensure the agent's usefulness and robustness in practical applications.
- Enhance the performance: The performance of the agent and take into account changing requirements by including feedback loops & iterative enhancements.
Resources for further learning and practice
Online tutorials and courses: Explore Additional Learning and Practice Resources with us at https://www.scholarhat.com/training/artificial-intelligence-certification-training. There are numerous online tutorials and courses available that specifically focus on Artificial Intelligence.
Summary
Agents in AI play an essential part by facilitating intelligent behavior, autonomy, and decision-making. Agents can navigate challenging surroundings and accomplish specified objectives thanks to their capacity to perceive, process, and act upon information. We may anticipate seeing more agent integration in other domains as agent technology develops, revolutionizing industries and improving our daily lives. It's critical to carry on researching and creating agents ethically and responsibly, making sure they advance society.